Epiphyllum: characteristics, types, cultivation and reproduction

Epiphyllum is one of the most popular and beloved indoor plants. It belongs to the cactus family, but stands out from its counterparts with its large, beautiful and very fragrant flowers that form on leaf-shaped stems. For its bright appearance, it is also called "cactus-orchid" or "phyllocactus". From the article you will learn what types of this plant exist and how to care for it at home in order to make it not only bloom, but also bear fruit.


What it is?
The homeland of the epiphyllum is the tropical forests of South and Central America, partly Mexico, therefore it is also called the "forest cactus".
The plant was discovered by the English biologist Adrian Haworth in 1812. He gave him the unusual name "epiphyllum", which is translated from Greek as "at the top of the leaf" (epi - on top and phyllum - leaf). Apparently, the scientist mistook the wide, flat stems of the cactus for its leaves. The latter, in the form of small processes, are also present and are located in the hollows of the stems under the thorns.
Shoots are very long - in some species of phyllocactus, they reach 3 meters. Most often they are flat, with jagged edges and a few needles, although there are also triangular variants.


The flowers of the epiphyllum are conical and rather large: the size can vary from 10 to 30 cm in diameter, depending on the variety. Their color is also different: there are white, pink, red and yellow buds.
Epiphyllum blooms in spring and summer, while exuding an incredible fragrance.
Phyllocactus fruits are edible, sweetish in taste, resembling a plum in appearance, covered with sparse thorns. When ripe, they are most often red, but they can also correspond to the color of the flowers. However, the appearance of fruits must be preceded by cross-pollination, so at home it is very difficult, but possible, to ensure that the plant bears fruit.


After a brief description of the appearance and structure of a forest cactus, let's move on to its varieties.
Types and varieties
In the natural environment, you can find about 20 varieties of epiphyllum. The most common are listed below.
Oxypetalum (aka acute or sour-petal)
This variety has another name - "Queen (or queen) of the night." He received it for the royal luxurious huge white flowers, 20 cm in diameter and surprisingly fragrant. True, you can admire them only for one day. Oxypetalum is one of the largest types of epiphyllum: the bush grows up to 3 meters in height. Its stems are flat and wide - up to 10 cm - with wavy edges and a woody base.
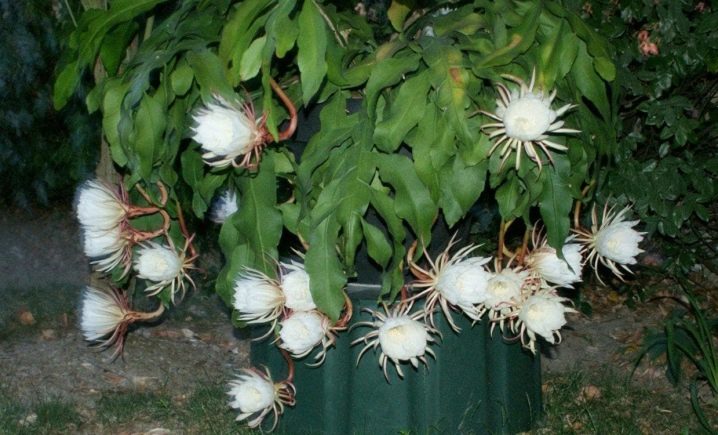

Guatemalan
In nature, there are 2 varieties of this variety, both with a very original wavy shape of the stems. In the first, the shoots look like oak leaves connected to each other. The second variety has wider and darker stems that twist and twist freely, changing the direction of movement and even their shape. The flowers of the Guatemalan epiphyllum are pink and medium in size.


Ackermann
It has hanging flat stems serrated along the edges. This species is popular for home breeding due to its beautiful bright red flowers and long flowering period.
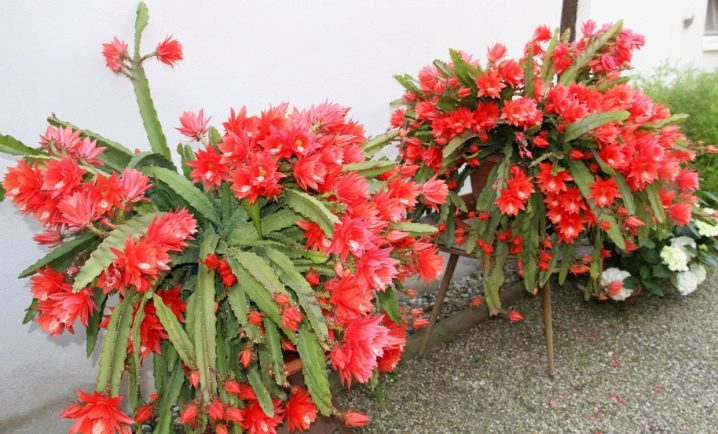

Angular (or Anguliger)
In nature, it grows only in Mexico. Branching shoots of a zigzag shape reach up to 1 meter in length. At the base, they are round or triangular and become stiff over time. Lateral shoots are flat, up to 8 cm wide.
Anguliger opens in late spring. The flowers are large, up to 15 cm in diameter, can have a variety of colors, but most often white or red buds are found.


Phyllanthus
The shoots have a rich bright green color. The primary stems can grow up to 1 meter, the secondary ones - only 50 cm. Flowers with pale pink petals and a yellow core are quite large, up to 25 centimeters in diameter.
Phyllanthus begins to bloom in June as single buds, and several areoles can bloom at once.


Dreamland
This type of epiphyllum has won the love of flower growers not so much because of its beautiful appearance, but because of its healing properties. So, it relieves the body of poisons and toxins accumulated, for example, as a result of alcoholic intoxication. It is also able to reduce the harmful effects of electromagnetic waves. But outwardly, the dreamland cactus is very spectacular. He is the owner of bright and very fragrant flowers, which can be of different colors: pink, red, white and yellow.


Hooker (or Hooker)
It has stems in the form of an arc with wavy edges and well-defined veins. The flowers of this cactus variety are white, with long, narrow and sharp petals. In its homeland - Cuba - it can reach impressive sizes.
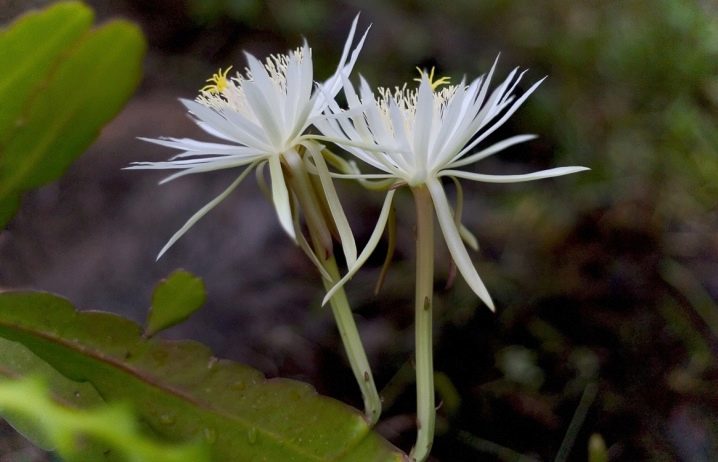

Lau
Fast-growing cactus with wide secondary stems (up to 7 cm) and long yellow-brown needles. True, it also fades quickly - the lifespan of each blossoming bud is no more than 2 days. Flowers open only in the evening.


Jagged
On the main stems of a round shape, secondary shoots of a greenish-blue hue are formed, which can reach a length of up to 1 meter. Delicate creamy buds bloom at night and delight the eye for up to 10 days. Flowering is accompanied by a pleasant aroma.
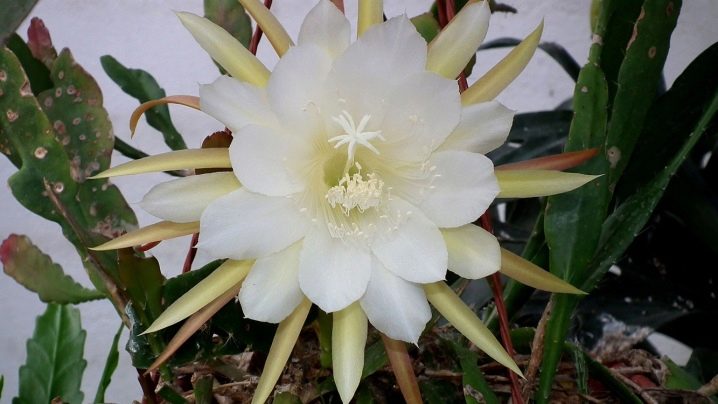

Based on the species that grow in nature, about 200 more varieties of epiphyllum were bred, also suitable for indoor breeding. The most famous hybrid representatives are Just Prue, Johnson's Epiphyllum, King Midas and others.


How to choose?
The purchase of epiphyllum should be approached very responsibly. From which you choose an instance, not only the period of its life depends, but also how efficiently the plant can bloom and bear fruit.
When buying phyllocactus, pay attention to its appearance.
Stems and leaves should be a uniform saturated green color without spots, cobwebs and dried out areas, as these signs may indicate the presence of pests or diseases, including viral ones. There should also be no damage on the stems - choose a plant with dense shoots, the integrity of which is not compromised.
Buy a cactus without flowers and buds, because during the transportation of the epiphyllum, they can crumble and these areoles will not bloom anymore.



Home care
Epiphyllum, like any cactus, is quite easy to maintain, especially during the dormant period. It requires increased attention only during the period of active growth and flowering, which lasts from mid-spring to mid-summer.


Lighting
The plant needs good lighting, however, direct sunlight is contraindicated. Therefore, it is better to place it on the west or east side. If you put the pot in the north, then it will lack light, and in the south, you risk burning the cactus. If it is not possible to provide an optimal location, then in strong sun, remove the pots from the windowsill or curtain the windows.


Temperature and humidity
The comfortable temperature during the flowering period is + 22-25 degrees. With the end of the vegetative period, it must be gradually lowered so that it reaches + 12-15 degrees in winter.
Air humidity should be medium, about 50%. In very hot weather and during the heating season, the epiphyllum must be sprayed with warm water or wiped with a sponge soaked in it. However, if the sun is too bright, this cannot be done, otherwise the plant will get burned.


Watering
The frequency of watering also depends on the time of year and the phase in which the plant is located. In the spring-summer period, with the beginning of the stage of active growth and formation of buds, the soil needs to be moistened more often - about 1 time per week. The water should not be cold and not from the tap, but separated and slightly heated. In winter and during the rainy period, it is enough to water the plant once every 2 weeks. We judge the need for moistening by the dry surface of the soil.



The soil
Ordinary land for planting epiphyllum is not suitable. Phyllocactus needs only fertile soil with a lot of nutrients and an acidity level of 5-6. However, it should not contain lime - it is contraindicated in the epiphyllum.
Of course, it is easier to buy ready-made soil in the store, but you can prepare it yourself, knowing the necessary components of the mixture.
Here are the most suitable and simple soil options:
- sheet earth (4 hours) + turf soil (1 hour) + sand (1 hour) + charcoal (1 hour) + humus (1 hour);
- sand from large grains of sand (4 hours) + leaf mixture (1 hour);
- peat mixture (4 hours) + sand (1 hour) - this option is best used for already mature plants.


Transfer
The transplant is primarily necessary for young epiphyllums. It should be carried out once a year in the spring, before the beginning of the flowering period. But for plants over 4 years old, it is shown only if the roots begin to grow strongly and break out through the drainage holes.
It is necessary to transplant an adult only after all the flowers have fallen off.
The transplant utensils should be low but wide. The weak roots of the epiphyllum are not able to penetrate the soil to great depths. They should be cramped - this will contribute to the rapid growth of new shoots and the active formation of buds.

At the bottom of the tank, a drainage layer must be placed, consisting of pebbles (or crushed bricks), foam and expanded clay. Drainage prevents stagnation of water in the pot. A suitable soil substrate is already poured onto it.
Before planting, the roots of the cactus must be dry and free of the old soil in which they were located. To do this, do not water the plant for 2 days before placing it in new soil.
Having planted a cactus, we place it in a shady part of the house, inaccessible to the sun's rays, and only slightly moisten the ground.


Fertilizer
During the active growing season, the epiphyllum needs micronutrient feeding. It is produced in spring and summer 2 times a month. Fertilizers can be purchased at a flower shop. The composition must necessarily include calcium, phosphorus and potassium.
When the buds begin to form in the plant, it is recommended to feed it with a mullein diluted in water - with it the cactus will receive the whole complex of nutrients.


Pruning
Trimming the epiphyllum is necessary for more than just maintaining aesthetics. The plant needs to get rid of shoots that are not capable of producing flowers.
These are old stems, on which buds were already forming. However, they can be removed only after 2-3 years from the moment of flowering, otherwise it will disrupt the functioning of the entire plant.
Shoots are subject to pruning, on which a flower can potentially never appear. These include triangular or cylindrical stems, there is little chance of blooming on thin and too weak stems, so it is also better to remove them. We rid the cactus of shoots with a stiff base, twisted and with cork formations - they not only will not give buds, but will also interfere with their healthy, full-fledged "brothers".
The stems are cut with a knife at the base, after which the cut site is treated with either a fungicide or activated carbon.


Bloom
The flowering period starts in April and lasts until the end of July.
Please note that buds will not appear on a young epiphyllum - the plant blooms only after 3 years. The lifespan of each bud is about 5-7 days.
During this period, the pot cannot be moved and transferred to another place, otherwise the fragile flowers will simply disappear.


Reproduction
There are 3 ways to reproduce phyllocactus at home.
Seeds
The seeds are planted in early spring. It is recommended to use wide and shallow plastic containers as a container for planting - they retain moisture better. Drainage is placed on the bottom of the dishes, then sand is poured. After watering, place the seeds there, sprinkle them with another layer of sand and cover them with glass or polyethylene to create a greenhouse effect. Containers with seeds are placed in a warm and sunny place at home, opening them daily for a few minutes for ventilation.
The sprouts appear first with needles, similar to ordinary cacti, then the thorns fall off, and the stem becomes flat and smooth.
However, flower growers are not very fond of the seed propagation method, since the buds on such cacti begin to appear only after 5 years.


Cuttings (basal processes)
This is the most common transplant method. A healthy flat shoot about 12 cm high is cut from a plant in the phase of active flowering or has just blossomed. The place of cut is a wide part of the stem, which is then narrowed, making the base of the cutting triangular.
Before planting, the shoots must be disinfected and dried to rid them of the plant sap flowing out of the cut area. To do this, place the cuttings in an upright position in an empty narrow bowl and leave there for two days.
We plant the dried shoots in plastic cups and bury them 1-2 cm in the prepared soil mixture, which should be crowned with a layer of river sand. Then we move the containers to the shady zone and refrain from watering the shoots during the day so that they take root better.


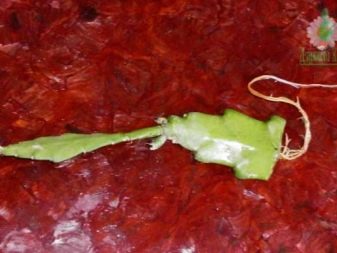

Sometimes the so-called aerial roots appear on the tops of the stems. This happens most often due to excess moisture. In this case, we tilt the appendix "head" to the ground and bury the upper part together with the roots. After the emergence of new shoots on the stem, carefully separate them from the mother plant and grow them separately.
By dividing the bush
During the transplantation of the epiphyllum, we divide the bush with rhizomes into several parts. We remove the plant from dried and not very healthy-looking areas and apply an antifungal agent, for example, a fungicide.
Then we plant the bushes in separate containers, put them in a dark place and do not water for 2 days.


Diseases and pests
Harm to the epiphyllum can be caused by the following insects.
- Aphid - sucks out plant sap, leaving green-brown spots on plant stems, is also a carrier of various viruses. You can get rid of aphids and remove stains by wiping the stem with alcohol, soapy water, or treating it with an insecticidal preparation.
- Spider mite - feeds on plant juices, which leads to yellowing of the stems and the appearance of a light white cobweb on them. As a rule, the insect appears when there is a lack of moisture, so by providing the flower with sufficient moisture, this problem can be avoided. The mite itself dies under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
- Shield - the name comes from the shield that covers the insect's body, protecting it from the effects of poisons. Dry and twisted plant stems indicate the presence of this pest. To destroy the scale insect, you must first wipe the cactus with alcohol, and then with an insecticide.
- Scratch - a powdery white insect that affects the stems of the plant, preventing its further growth.A white wax coating in the form of a cobweb appears on the cactus, which can be eliminated by treating the infected areas with alcohol or soap solution, and then with an insecticide.
- Slugs and caterpillars - can attack a cactus in the spring and summer, when the plant is outdoors, for example, on a balcony. Apply a toxic chemical compound to the epiphyllum in advance to prevent the appearance of these insects.



Diseases are usually caused by improper care, containment breaches, or viruses. We will consider the most common ones below.
- Rust - the appearance of small red and sometimes black spots on the stems. The reason for their appearance can be several factors: waterlogging of the soil, sunburn, or the accumulation of water droplets on the stems. Treatment: treatment of the plant with "Fundazol" and changing the conditions of care.
- Black rot - a disease in which the stem begins to turn black from the base. Treatment: after removing the damaged areas, spray the plant with Fundazol.



- Anthracnose - a fungal disease, which manifests itself in the appearance of pale brown spots on the surface of the stems, sometimes the border of the stem becomes brown. The method of treatment is to cut off all areas damaged by the fungus and treat the remaining healthy parts with a fungicide.
- Fusarium - in a diseased plant, the roots begin to rot, and the stems turn red. Fusarium occurs from excess moisture or hypothermia. Treatment: after removing damaged roots, the plant should be transplanted into new soil and watering should be reduced.
- Epiphyllum viral mosaic (or mosaic disease) is the most terrible disease for a plant, which most often leads to its death. It manifests itself in the form of light-colored spots and faded edges of the stems, and the buds of the cactus also begin to fall off. You can try to save the infected epiphyllum by removing all damaged areas, treating healthy ones with Fitosporin and quarantining the plant.
But if the treatment does not give results and the infection process continues, then it is better to destroy phyllocactus.



In order for the plant to delight you with its healthy and beautiful appearance for a long time, you must follow simple recommendations.
- Regular, moderate watering with warm, but not tap water - the chlorine contained in it can lead to yellow spots on the shoots. If the soil is waterlogged, the stems of the epiphyllum begin to change color, and the roots begin to rot. And due to lack of water, the shoots shrivel and become dry.
- The plant should receive fertilization, but in reasonable doses. Their excess will negatively affect the health of the flower - the shoots will crack and dry. And from the lack of trace elements - to frown. The exclusion of nitrogen from the composition of the top dressing will also have a beneficial effect on the health of the epiphyllum.
- Arrange the hardening of the cactus during the warm period: take it out for a while outside or on the balcony, just do not catch a cold.
- Conduct chemical treatments of phyllocactus to protect against pests and viruses.
- Organize an optimal thermal regime. Direct sunlight will cause burns and cause the shoots to wilt and turn yellow. Lack of sun does not allow the cactus to pick up buds and bloom.
- The soil must be suitable for growing epiphyllums and rich in nutrients. When transplanting a plant, try not to damage the roots - this will dry out and die off the shoots.
- Wood stems can be prevented with regular and correct pruning.
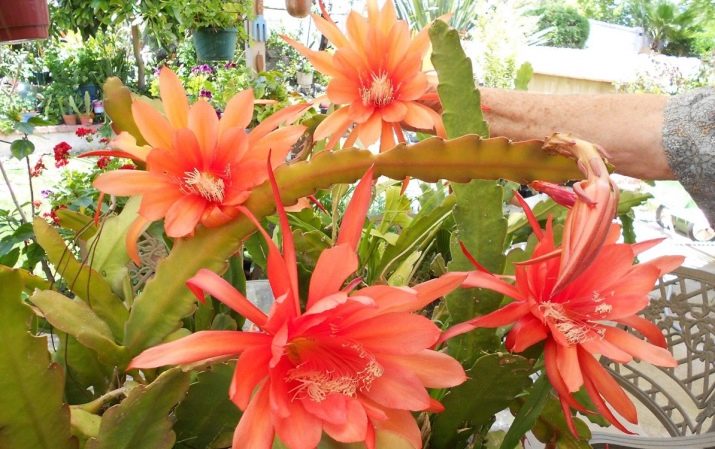






Epiphyllum combines a spectacular appearance, which manifests itself as much as possible during flowering, and the unpretentiousness of the cactus family. Thanks to this unique combination, it enjoys the well-deserved love of florists and takes pride of place on the windowsills of our apartments and houses.
For more information on caring for the epiphyllum, see the following video.















































The comment was sent successfully.