What is the difference between hardboard and fiberboard?
The question of what is the difference between hardboard and fiberboard can be heard quite often. Indeed, the differences between them lie only in some of the features of production, which impose their stamp on the characteristics of these products. But this does not prevent both hardboard and fiberboard from remaining popular materials for interior decoration, while going on sale under different names.
What it is?
Fiberboard (Fibreboard) is produced from industrial waste, softened and brought to a homogeneous state. This material has several varieties, differing in strength, hardness and type of external surface finish. All materials in this group are produced according to GOST 4598-86, pressed into sheets with a thickness of 2 to 15 mm (some types reach 40 mm for this indicator). Thin varieties show good flexibility, suitable for sheathing curved structures.



Raw materials for the production of fiberboard are obtained from wood processing waste. This includes wood chips, fire, sawdust, thoroughly washed and dried, and then crushed to fibers. The degree of grinding depends on the characteristics of the future slabs. In the future, the wood base is mixed with other components:
- resin binders;
- water repellents to increase moisture resistance;
- antiseptics to prevent rotting;
- fire retardants (for materials of fire-resistant class).
The process of forming plates from raw materials takes place under a pressure of 3-5 MPa with heating up to +300 degrees Celsius. Hardboard is a material that does not have a separate class, since it is included in the list of fiberboard subspecies. The difference is mainly in the hardness of the sheets and their characteristics, as well as in the method of production.
Another type of fiberboard is informally called masonite - it is obtained using the wet method, while hardboard is pressed dry.

Differences in production
And although these materials belong to the wood-fiber group, their production has certain differences that affect the final characteristics of the sheets. Wet pressing - the traditional way to obtain fiberboard - considered environmentally friendly. This is due to the fact that chemical binders based on formaldehyde are almost never used here, since they are often not added at all if the raw material is of coniferous origin. In this case, when heated, a natural analogue of resins, lignin, is released from the wood.
If it is not enough, add 3-7% of synthetic resins.


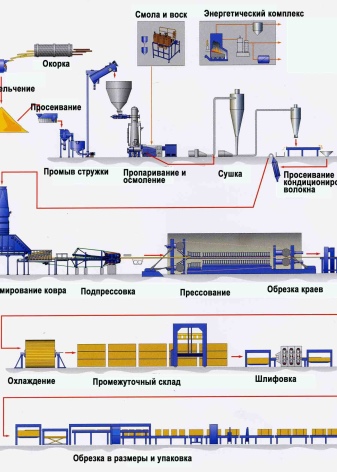
The wet method of fiberboard production (wet pressing) involves several successive stages.
- Chopped wood fibers are mixed with water in the required proportion, brought to a homogeneous state.
- The necessary additives are introduced.
- The mixture enters the dispenser.
- The future slab is squeezed out onto the tape in an even layer. Its surface has a characteristic mesh structure for accelerated removal of excess moisture. That is why the wet-pressed plate is easy to distinguish from other types - its back side is covered with a special pattern.
- Finished sheets go under the press, where they are subjected to thermal and squeezing effects. The average time required to create 1 plate is up to 15 minutes.
- The finished product is sent to special chambers with a certain temperature regime, where it is dried (“ripens”) for several hours. During this time, the mass is well sintered, acquiring all the characteristics declared in the standard.
- For the time of cooling, the sheets are transferred to another chamber, in which they acquire natural moisture. If this is not done, the material will actively swell on contact with air. Finished sheets are sent further - for coloring, lamination.


With such obvious advantages as environmental friendliness and wastelessness, wet pressing remains a more labor-intensive and expensive process than dry pressing. This affects the cost of production. In addition, the reduction in synthetic additives affects the strength and hardness of the finished material, significantly limiting the range of sheet thicknesses. Dry pressing is a method by which hardboard is produced. In fact, it is similar to that used in the manufacture of MDF, only the raw material has larger fractions. The boards are formed by combining the dry mass of fibers with a synthetic resin binder. By dry pressing, large-sized sheets with a thickness of up to 15-40 mm are created, which are in demand in furniture production, construction and other industries.
The hardboard production process is less laborious than fiberboard, it takes only about 5 minutes, during which the surface of the formed mass is exposed to a heated press. Fewer additives are required for such products, since they are not diluted with water. This significantly reduces the cost of production, but also affects the choice of additives to use (most often they are the most affordable synthetic resins containing formaldehyde). When choosing a material, it is important to focus on its emission class. The safest indicator is not higher than E1. It should be noted that hardboard with a higher volume of hazardous compounds is no longer produced in the EU countries.


Comparison of characteristics
The main difference between hardboard and other types of fiberboard lies in the characteristics of the finished material. Among the important differences are the following.
- Thickness... Hardboard sheets are produced up to 15 mm thick, less often - up to 40 mm. Fibreboard of soft types is most in demand in thin sheets of 2-8 mm.
- Strength... Typical values for fibreboard range from 100-500 kg / m3. For hardboard, this parameter is 550-1100 kg / m3. Twice the strength makes the material in sheets close in characteristics to solid wood.
- Thermal insulation properties. Wet pressing makes the material porous. There is even a special type of fiberboard with the "M" prefix, which is suitable for improving the soundproofing and heat-insulating characteristics of premises. Plates of increased density do not have such capabilities.


Having found out what is the difference between hardboard and masonite (fiberboard), produced by wet pressing, you can correctly determine the scope of the material. Hard slabs are not very flexible, but have higher load-bearing capacities. Moisture-resistant options are suitable for finishing the external walls of buildings, the usual ones are used for flooring, creating internal partitions, in the production of furniture and packaging.
A thin sheet of fiberboard bends well, so it can be used to create arches and other curved structures. In addition, the material is environmentally friendly and safe for health.



For information on how to lay fiberboard on a wooden floor, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.