How many boards are 4 meters long in 1 cube?

Any board, including unedged, - however, like any timber - provides for the calculation of the number of copies per cubic meter. It is cubic meters that is considered a forest of any type and type of processing.

Influencing factors
A cubic meter of timber is the number of boards occupied in the warehouse (and during transportation) by a given volume. If the client receives the requested number of boards per cubic meter, then for the selling company the costs (expenses) for the delivery of this or that wood material “to the client's gate” are also important. In addition to the number of unedged boards in each "cube", the effective (real) weight of one cubic meter is also taken into account.
The weight and delivery costs of unedged boards are influenced by:
- breed (species, subspecies) of the tree;
- the degree of wood drying;
- the number of boards per cubic meter.

The weight of a cubic meter depends on the second factor. It fluctuates significantly depending on humidity. Wood, the water content of which is up to 50% (by weight), belongs to wet (including logs floated down the river). Raw samples (which have been left lying for at least several days in dry weather) contain no more than 45% moisture.
Naturally dried wood - no more than 23%, thoroughly dried - no more than 17%. The average value is taken wood, dried to normal (natural, equilibrium) moisture content.
Absolutely dry boards do not exist, otherwise they would crumble under any perceptible impact from the outside.

Calculation features
To calculate the number of pieces of sawn and planed boards in a cubic meter, it is enough to recall only the formula for calculating the volume of a parallelepiped. It is precisely this that is a batch of boards from one to the required number of cubic meters.
The board is not sold per piece - it is sold in cubic meters: not every store or warehouse will meet the small retail buyer, selling him one or more copies. To calculate, do the following:
- multiply the length, width and thickness of the board by each other;
- divide the cubic meter by the obtained value.

All values are converted into a single denomination of calculus - linear, square, cubic meter.
The last value is likely to be fractional. For example, by ordering a board 40 * 100 * 4000 m and finding that their number is 24.8, the user, in the case of a large amount of finishing work (if the project allows), can write out 10 m3. Then the number of boards will be equal to the normal, whole - in this case, it is 248 copies.
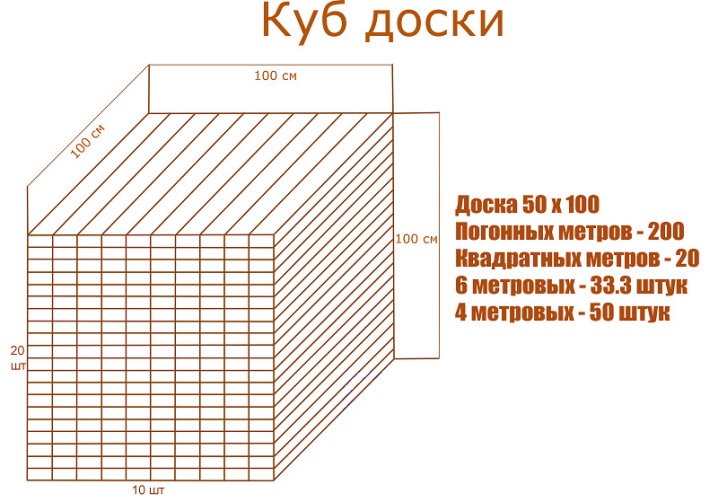
The volume of different boards
The number of 4-meter boards per cubic meter - for different widths and thicknesses - is shown in the table below.
|
Thickness and width, mm |
Number in 1 m3 |
Area covered by 1 "cube" |
|
20×100 |
125 |
50 |
|
20×120 |
104 |
49,9 |
|
20×150 |
83 |
49,8 |
|
20×180 |
69 |
49,7 |
|
20×200 |
62 |
49,6 |
|
20×250 |
50 |
50 |
|
25×100 |
100 |
40 |
|
25×120 |
83 |
39,8 |
|
25×150 |
66 |
39,6 |
|
25×180 |
55 |
39,6 |
|
25×200 |
50 |
40 |
|
25×250 |
40 |
40 |
|
30×100 |
83 |
33,2 |
|
30×120 |
69 |
33,1 |
|
30×150 |
55 |
33 |
|
30×180 |
46 |
33,1 |
|
30×200 |
41 |
32,8 |
|
30×250 |
33 |
33 |
|
32×100 |
78 |
31,2 |
|
32×120 |
65 |
31,2 |
|
32×150 |
52 |
31,2 |
|
32×180 |
43 |
31,2 |
|
32×200 |
39 |
31,2 |
|
32×250 |
31 |
31 |
|
40×100 |
62 |
24,8 |
|
40×120 |
52 |
25 |
|
40×150 |
41 |
24,6 |
|
40×180 |
34 |
24,5 |
|
40×200 |
31 |
24,8 |
|
40×250 |
25 |
25 |
|
50×100 |
50 |
20 |
|
50×120 |
41 |
19,7 |
|
50×150 |
33 |
19,8 |
|
50×180 |
27 |
19,4 |
|
50×200 |
25 |
20 |
|
50×250 |
20 |
20 |
The consumer often gets rid of a detailed calculation or simplifies it - just use the above values. However, the sequence of calculations is valid for all lumber and solid wood of the same type. The degree of drying and the type of wood do not affect either the board size or the conversion scheme. The values from this sample allow you to approximately orient yourself in the mass of the cube of such a board.

Small adjustments for non-planed wood are also made by the quality and tightness of the boards in the stack.
If an inspection is carried out on site - in a warehouse, upon receipt directly at the facility - a small amount (up to several percent of the total volume, weight and number of copies) will be rejected, for example, due to cracks, an abundance of knots falling out of the board, not quite high-quality processing of surface layers of wood. Edged boards are often ordered in quantities that are one-tenth more than the value specified in the project. For unedged boards, this "overkill" will be up to 20%. If this rule is not observed, the delivery of the completed object will be slowed down, and the contractor will incur additional costs for the delivery of timber.

Conclusion
Knowing the cubic capacity - and the area of the covered surface - in each specific case, the executing company will spend several times less time on recalculation than if it had not used the selection table. This will ensure the timely delivery of the object.













The comment was sent successfully.