All about the pine sawfly
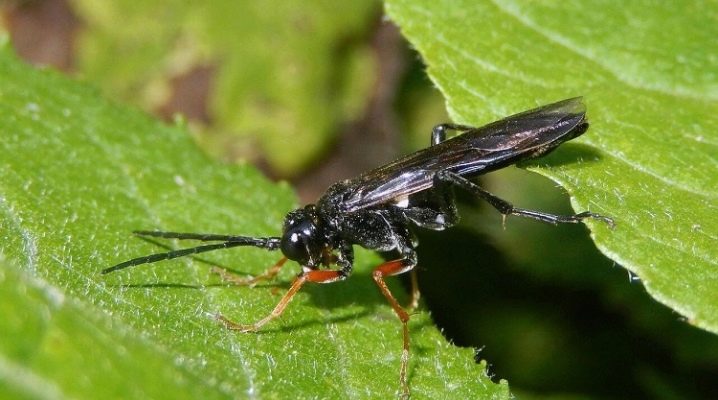

Knowing everything about the pine sawfly, as well as about other pests of conifers, is necessary not only for foresters in the Far East, where 2 species are often found - red and ordinary. This is also necessary for those who use decorative conifers in landscape design.
The insidious insect can give two generations a year, making a complete transformation. The danger to the tree is represented by the larvae eating young needles, which then dries up. It is estimated that it is enough to ignore the presence of Hymenoptera on a tree for 3-4 years for the pine to die.
Insect description
The pine sawfly is a representative of the large army of pests that attack conifers. Among them there are cone-eaters, trunk-eaters, root-eaters, sucking and pine-gnawing, beetles and butterflies. There are other species that do not infect conifers themselves, but lay eggs or larvae, from which destroyers of any woody texture appear - from buds and needles to the root system.
The order of Hymenoptera, to which the sawfly is ranked, is one of the most developed. It includes social insects. Sitting bellies are sawflies and horn-tails, but this is a common etymology. Many of them are pests of cultivated crops - forests, rapeseed and bread.
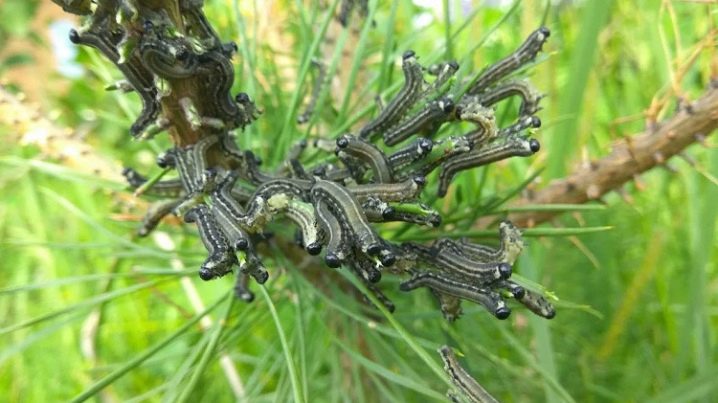

The common sawfly is pine and spruce, but this does not mean that they are limited only to their species, they can also infect other plants with needles. According to their preferences, they belong to the needles:
- redhead lives in groups of 2-3 dozen pieces, eats needles from last year's harvest;
- the common one feeds on young shoots, but makes spring clutches in older needles;
- the red-headed (sawfly weaver) lives on an ordinary pine tree, but does not disdain the Weymouth pine either.
On the pine, you can see insects that vaguely resemble bees, they also have a belt between the chest and abdomen. The ovipositor is the reason they got their name. It looks like a saw without a handle, although not everyone has it, but some species. Females are larger than males, brownish-yellowish, with variable patterns on the scutellum and abdomen. Males are smaller in size, with comb-like antennae, orange paws and smooth black integuments. Representatives of the population successively go through all 4 stages of full development - from the egg laid by the female from the dentate ovipositor to the larva, pupa, and imago.
The female can lay a different number of eggs, from 3 to 12 dozen. The second generation hibernates in cold areas and calmly tolerates the cold. Green oval eggs are laid in the needles. The light gray larva of the red sawfly with a white stripe grows up to 2.5 cm. The larvae of the common pest are greenish or yellowish, with a shiny brown head. Pupae are located in a yellow cocoon, beetles are small in size, not even a centimeter long.
It is vital to fight them, otherwise the coniferous forest or decorative plantings die.


Signs of infection
You can focus on the presence of any life form, each of them is a real or potential danger. Sometimes their number is so significant that you can hear the rustle of the falling excrement of caterpillars, devouring the needles, and a thin layer of secretions, already dried and fresh, forms under the trees. It is not worth bringing the state of the landings to this. An infection can be detected by different signs:
- years of adults in April or May (depending on climatic conditions, individuals do not feed, but lay clutches);
- eggs laid in needles are covered with green foam, which the female emits, creating a protective shell;
- new adults can be seen at the end of the second summer month or early August;
- the larvae of the red sawfly are visible on the tree in May, there can be hundreds of them on the branches in case of mass infection;
- potential offspring can be found in the bark in the form of eggs or larvae in a cocoon, which are hidden in the soil, when digging a site for the winter.
The two species that are found in Russia have differences in color, number of generations and food preferences (last year's or young needles). However, the presence of the sawfly can be unmistakably diagnosed by damaged needles with laid eggs, flying imago, gnawing larvae. In the pre-winter time - along cocoons with larvae in the soil or eggs under the bark of trees. The larva eats several dozen needles, the damaged needles turn yellow and dry. You may not see a single representative due to winter diapause, but dried branches are an unmistakable sign. False caterpillars eat the edges, adult larvae eat the needles to the ground.
An outbreak of infection can last up to 3.5 years, followed by other pests, for example, bark beetles. And then the tree dies.


Mechanical control measures
You can get rid of a pest using several methods, and often only their complex application can save you. Forestry measures involve in the process of planting forests, planting not ordinary, but Crimean pine, which is less susceptible to infection, enrich the soil with nitrogen by planting green manure, or create mixed forests. There are biological methods and chemicals. The use of mechanical methods is the simplest and oldest solution that does not require either toxic compounds or special costs.
In special sources, only one of these methods usually appears, which can be used in a summer cottage, private or suburban land ownership:
- collecting larvae by hand (like the Colorado potato beetle from potatoes, but only with the use of protective gloves and an insecticide solution into which they are thrown off);
- knocking down the pest with a stream of water from a hose from the upper, hard-to-reach branches and collecting them on the surface of the soil;
- digging up the soil immediately after harvesting and for the winter so that the cocoons with the larvae do not overwinter.


This is an unproductive and time-consuming method, instead of which summer residents prefer to use the so-called folk remedies. These include spraying with a garlic or mustard solution, infusion of tobacco or makhorka. There are biological methods being developed by scientists. Insects are infected with viral infections, they breed natural enemies - ants, tahinas and wasp wasps, attract insectivorous birds. In a small area, relatively safe biological insecticides or pheromone traps (if found commercially available) can be used.
The most interesting mechanical device is the trapping belt. There are two types: some are covered with a non-drying sticky compound, others are saturated with poison that is deadly for larvae heading into the soil to pupate.
Both means are good only if comprehensive pest control is being carried out, because while the second generation goes to winter, it, together with the first, can destroy a huge number of needles. This does not affect the eggs laid by the adults; a new generation of devouring larvae will successfully hatch from them.


Chemical methods of pest treatment
Mass infestation means the need to treat not only dying trees, but also healthy ones located nearby. For this purpose, forestry uses airplanes spraying systemic insecticides, although internal contact also turned out to be effective if they are used in tandem with systemic agents.A double action is obtained from the infected needles, which the sawfly larva eats, and the contact ones help to destroy other life forms (adults do not feed at all, they are needed only to obtain a new generation).
Insecticides for personal use can be purchased in the form of a concentrated emulsion or granules, soluble in water, powder, and even in a ready-made spray bottle. "Pinocid", "Decis Profi" or "Prestige KS" - well-proven means, but if it is difficult to acquire them, use "Karbofos" or "Chlorophos", you can add "Cyromazin" or "Buprofezin" - inhibitors of chitin synthesis in pests.














The comment was sent successfully.