Expanded polystyrene 50 mm thick: characteristics and scope
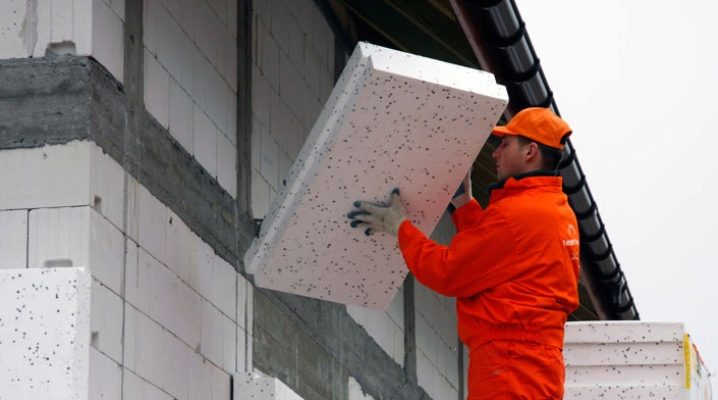

For many years, the leader among heat insulators has been 50 mm expanded polystyrene - a versatile and affordable material.
Polystyrene foam 50 mm: characteristics and application of the popular heat insulator
The material itself is a tightly compressed polystyrene cell filled with air.
Due to the peculiarities of its composition and structure, PPS has the following characteristics:
- a light weight;
- good moisture resistance;
- low thermal conductivity.
All this allows the material to reliably protect structures from freezing and dampness.
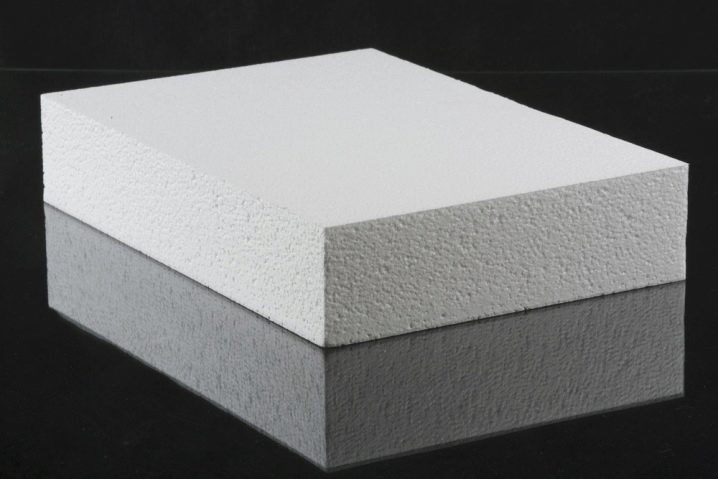

The thickness of the insulation can be different, but 50 mm is considered optimal - this layer is quite enough to keep the heat inside the room. For comparison, to achieve this effect, you need 95 mm of mineral wool.
Polyfoam is sold in plates, size 1x1 or 1x2 m, 8 pieces per package.


Advantages and disadvantages of the material
Polystyrene insulation has the following advantages:
- does not create additional load on the foundation of the building and supporting structures;
- durability - the service life of the material is at least 40 years, while it does not lose its characteristics;
- ease of transportation and installation;
- good adhesion and interaction with adhesives;
- resistance to temperature extremes and the effects of most aggressive environments.
Also, most modern types of polystyrene foam insulation are processed with special compounds that protect the material from rodents and pests.


At the same time, polystyrene foam has disadvantages.
- Low vapor permeability... In order to avoid the accumulation of steam inside the room when using foam as insulation, it is necessary to equip good supply and exhaust ventilation.
- Not resistant to UV radiation. For this reason, the foam must be hidden from exposure to sunlight.
- Loss of performance when interacting with solvents, which does not allow to apply paints and varnishes to PPS.
- Low resistance to external mechanical stress... Polyfoam is a rather fragile material, therefore, when working with it, care must be taken so that it does not break or crack.
The presence of the latter can significantly affect the quality of EPS, increasing thermal conductivity and the risk of moisture penetration.

It is not the material itself that is toxic, but the vapors of the styrene, which decrease over time and do not exceed the maximum permissible and safe for humans. Therefore, experts advise to use PPP, which has been “spent” for a long time in the warehouse. The combustibility of expanded polystyrene depends on the production technology. For example, polymer granules filled with carbon dioxide are self-extinguishing.


Brands, their characteristics and application
Modern manufacturers offer sheet 50 mm expanded polystyrene of various brands, differing in material density.
- PSB-S15 (density 11-15 kg / m3). Such material conducts less than 0.037-0.04 W / m ° C and is able to withstand compression of no more than 40 kPa.

- PSB-S25 (16-25 kg / m3) with a thermal conductivity of 0.038 W / m ° C and strength up to 100 kPa.

- PSB-S35 (from 25 kg / m3). This brand of expanded polystyrene has a thermal conductivity of 0.035-0.039 W / m ° C and is capable of withstanding loads up to 140 kPa.
- PSB-S50 (40-45 kg / m3).The thermal conductivity of this type of PPS is 0.04-0.043 W / m ° C, the strength is up to 60 kPa.


The letter "C" in the marking indicates that fire retardants were used in the production - substances that increase the fire safety of the material.
Each grade of PPS has its own application. For example, PSB-S15 is used in small structures for internal thermal insulation of private houses. PSB-S25 is used for external thermal insulation works at larger facilities, PSB-S35 is suitable for insulating facades and floor.
As for the densest sheets of expanded polystyrene with a thickness of 50 mm, they are most often used in the formation of a road surface. In private construction, this type of PPP is not in demand due to the rather high cost.



You will learn more about what expanded polystyrene is and how it is produced below.













The comment was sent successfully.