All about Stephanandra

The desire of many gardeners to learn everything about the peculiarities of growing and breeding Stephanandra is primarily due to the decorative properties of this plant. This shrub came to our region from the land of the rising sun and Korea. It is now widely used in landscape design. The main advantages of the popular garden culture are the chic crown and unique flowering.
Shrub description
According to the classification, Stefanandra belongs to the Rosaceae order of the Rosaceae family. One of the important features of their representatives is the presence in the embryo of two cotyledons located opposite each other. The genus includes several species, and the natural habitat of the described plants is in the regions of East Asia. But they are most often found in Japan and Korea.


All varieties are shrubs with a fairly branched crown formed by well-developed branches. An adult culture can be up to 2.5 m in height, but for this it will need up to 30 years or more. It turns out that Stefanandra cannot boast of a significant annual increase. The decorative properties are provided by graceful branches. It should be noted that the diameter of the crown of the bushes reaches impressive dimensions, and it is measured in the range from 2 to 2.5 m.
Stefanandra's branches most often have arcuate contours, as they bend towards the ground under their own weight. Young shoots are usually reddish brown. But as the shrub grows, brown or grayish and light brown fragments appear on the bark. The stems themselves are distinguished by a glossy (bare) surface.

Leaf plates with carved contours are attached to the shoots with small petioles in length and are arranged alternately. The leaves themselves are ovoid with a pointed tip. The almost smooth edge of the plates is decorated with small rare teeth. In some species, the foliage is distinguished by pronounced dissections or the presence of small blades.
The beginning of the abundant flowering of Stefanandra falls at the end of May. - the beginning of the first summer month, and this beauty parade continues until autumn... Inflorescences with panicle outlines are formed on the tops of the shoots. They consist of small bisexual flowers and differ from each other in density.
After the completion of pollination, that is, from September to October, the fruits ripen in the form of elongated, small-sized brown leaflets.


Types and varieties
Today, a rather modest list of Stefanandra varieties is cultivated. Moreover, most often on the sites you can find two varieties of shrubs.
- Stephanandra incisa - split-leaved (incised-leaved) variety, which has a bush-like shape and a crown height of 1.5-2 m with its width within 2-2.5 m. Shoot growth in this species is slow, and the bushes reach their peak only by 25-30 years.
- Crispa. In this case, we are talking about a dwarf representative of the Stefanandra family. It is the most compact (height and width - within 0.5 and 2.5 m, respectively), dense, bumpy, deciduous shrub. The list of its main distinguishing features includes deeply incised leaf plates that have a bright green color. In autumn, the crown of the plant turns yellow or orange. Curved shoots can reach the ground and take root.


Another species was named Tanakae. Such a stefanandra reaches 2.5 m in height with a crown width of about 2 m. An important distinguishing feature is the relatively large leaf plates. In the first year of life, the shoots of the bushes have a brown-burgundy bark, which over time becomes noticeably lighter or takes on a grayish tint.
In addition to all of the above, there is also a hybrid of the Crispa variety called Oro Verde. Experts bred it as a result of a successful cross with Stephanandra Tanaka. It is important to note that these shrubs grow no more than one meter above the ground, which makes them quite compact and attractive to use in the formation of a unique landscape. The flower petals have a creamy color, which makes them look good against the background of rather large leaves.


Growing
With proper care and timely implementation of all agricultural techniques, Stephanander, regardless of the type, will decorate any site from early spring to late autumn. Experienced gardeners recommend paying special attention to young bushes. In principle, the cultivation and reproduction of this plant does not provide for any special manipulations.
Location
First of all, it is necessary to choose a place well-lit by the sun's rays for the "man's wreath". But, as practice shows, a location in partial shade is also quite suitable.
At the same time, it has been proven that Stefanandra will develop more actively and grow faster in flower beds with full lighting.


The soil
The soil for planting or transplanting the described shrub must necessarily meet the following requirements:
- freshness;
- ease;
- nutritional value.
The best option would be a substrate, which should contain leafy soil, river sand and peat compost in a ratio of 2: 1: 1. It is recommended that the acidity values are medium and equal to 6.5-7 pH.



Planting and transplanting
All such agrotechnical activities are carried out in the spring. It is important that there is an interval of at least 1.5-2 m between the holes for seedlings. If a site for planting with heavy soil is chosen, then drainage with a thickness of about 15 cm should become a mandatory element. Sand with a coarse fraction, crushed stone, broken brick and expanded clay are used as material for filling the bottom of the pits.
The planting material in the prepared holes is positioned so that the root collar is at the level of the soil surface. When planting young animals, superphosphate is introduced at the rate of 40 to 60 g in each well. The use of complex dressings is allowed.


Watering
Stefanandra bushes care includes regular irrigation. In the hot and dry summer months, it is necessary to water the crop 2-3 times a week. In this case, the water consumption for each planting unit is 2 buckets. It is important to monitor the condition of the soil, which should have time to dry out between waterings. If the season is with precipitation, then the intervals between humidifications increase.

Top dressing
Fertilizers are applied to the soil annually. Ammonium nitrate, urea and mullein are used already in the first year after the landing of Stefanandra in an open area. For 10 liters of water add 15 g, 10 g and 1 kg of these ingredients, respectively. It is important that they are applied in early spring and before the leaf blades are deployed. It is also worth noting that each adult (from 10 years old) requires 10 to 12 liters of such a solution.



Pruning
Overgrown bushes are best treated in early spring. At the same time, correct pruning involves the removal of all dried, frozen, damaged and old branches. Experienced gardeners recommend getting rid of shoots that have begun to grow deeper into the crown. This prevents thickening and a lack of light for the full development of the shrub, from which leaves can eventually begin to fly around.
All cuts should be immediately processed with garden varnish.


Reproduction
Now gardeners get Stefanandra's young in several ways. And in this case we are talking about both seed and vegetative methods. The second option involves the following methods of reproduction of an ornamental shrub.
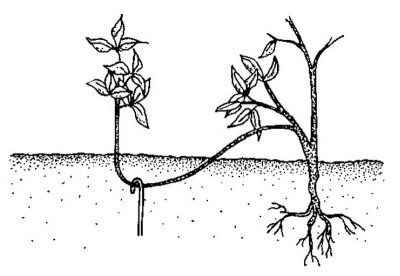
- Layers. This technique has established itself as the simplest and most effective. Here, the key role is played by the ability of branches to root themselves in contact with the soil, as in their natural habitat. Gardeners in the spring choose the strongest plant and bend its branches to the ground. After the creeping shoots are fixed on the ground.
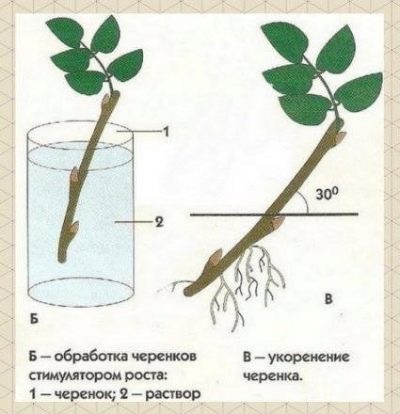
- Cuttings. It is important to note that both green and semi-lignified shoots are suitable for reproduction. The cuttings have a minimum length of 10 cm and are cut in summer. By the way, on the blanks, the places of the cuts can not be processed - immediately place the planting material in the ground. After that, the seedlings are immediately watered and create a shading shelter for the first time. It should be noted that in practice almost 100% of cuttings are successfully rooted.
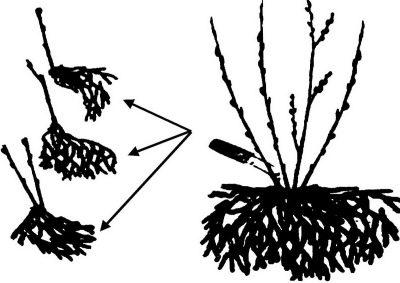
- By dividing the bush. In this case, it is worth recalling that the described plant grows rapidly, and also has the property of effectively rooting when the shoots reach the ground. Well-developed and matured specimens can be easily dug up and, separated from the mother bush, transplanted to another place. Such operations are carried out in the spring months.
Those who decide to make a choice in favor of multiplying the culture by seeds are advised to take into account that this method is relatively time-consuming. In addition, it is characterized by good performance. One of the main points is that the seeds are necessarily stratified. It is also worth considering the need to thin out the seedlings, if initially small gaps were left between them. This is due to the fact that the described flora representatives tend to grow actively. When sowing, the planting material is slightly deepened, after which watering is carried out.
In addition to all these options, you should pay attention to growing seedlings. This method is quite successfully used by some modern gardeners. Here it should be taken into account that young growth moves into open ground only after reaching six months of age.
This approach is due to the fact that the root system takes enough time to develop and get stronger.


Diseases and pests
One of the clear advantages of the described shrub is its increased resistance to diseases and attacks of harmful insects. At the same time, the greatest danger is posed by regular violations of the rules for caring for Stephanandra. Pest control is carried out using standard methods using modern drugs.
In the context of diseases, gardeners most often have to deal with the following troubles.
- Powdery mildew, also called ashes. The manifestation of the disease is, first of all, the appearance on the plates of white stains, which quite actively spread over the entire surface. Due to a dry lime-like and very dense coating, photosynthesis eventually stops, after which the leaves will die off.
- Rust is a disease with fungal etymology. It is quite easy to identify it by growths in the form of small pads on the foliage. These formations, crumbling, sprinkle everything around them with a characteristic reddish color. By the way, thanks to her, the very term "rust" appeared. Another clear sign is the loss of the natural color of the foliage. The plates turn yellow prematurely and fall off very quickly, without waiting for autumn.
- Gray mold caused by fungal spores. Symptoms are softening of the stems, the appearance on the leaf plates of a characteristic bloom in the form of a gray cannon, after which the leaves quickly turn yellow and fall off. Buds are less frequent and misshapen.



The sources of the listed troubles, as a rule, become:
- excessively dense soil that does not have time to dry out;
- violation of the rules and frequency of watering;
- frequent and heavy rainfall in tandem with high air temperatures.
Treatment of these diseases is reduced to getting rid of all affected areas, followed by treatment of the shrub with fungicides. The list of the most effective and popular drugs includes Bordeaux liquid, Topsin and Fundazol. But it is important to remember that along with an excess of moisture, its deficiency will also be destructive, which, first of all, leads to damage to the root system of plants. As a result, the roots begin to rot, the foliage turns yellow, and the bush itself may die.
In advanced cases, the affected plant is dug up and burned, the ground at this place is processed.


What is combined in landscape design?
One of the main features of the described plant is that the bushes retain their aesthetics throughout the season. At the same time, Stefanandra looks most bright in autumn due to the play of yellow, pink and red foliage colors. As a result, the shrub looks good and advantageous against the background of its coniferous neighbors. The list of the latter includes, for example, euonymus, hebe and boxwood.





































































The comment was sent successfully.