Planting grapes

Planting grapes is a process that requires special attention from the gardener. In order for the vine to give a signal harvest after 3 years, it is necessary to take into account many factors - from the type of soil on the site to the nearby plants. Tips for beginners will help you understand the optimal layouts of seedlings and cuttings, as well as other intricacies of this process.


When is the best time to plant - in autumn, spring or summer?
You can determine when to plant grapes correctly based on the appearance of the shoots. The best time for most varieties is autumn and spring; it is undesirable to plant in summer.
In cold regions, preparations for planting in the fall begin in August. The seedlings are transferred to the ground at the end of September or in the 1st decade of October.
Only plants are suitable for autumn planting:
- with a ripe vine;
- with a developed root system;
- with 8-10 eyes.
When transferred in autumn to open ground, weak plants simply do not survive. If they have an undeveloped root system, green vines, it is worth waiting until spring.
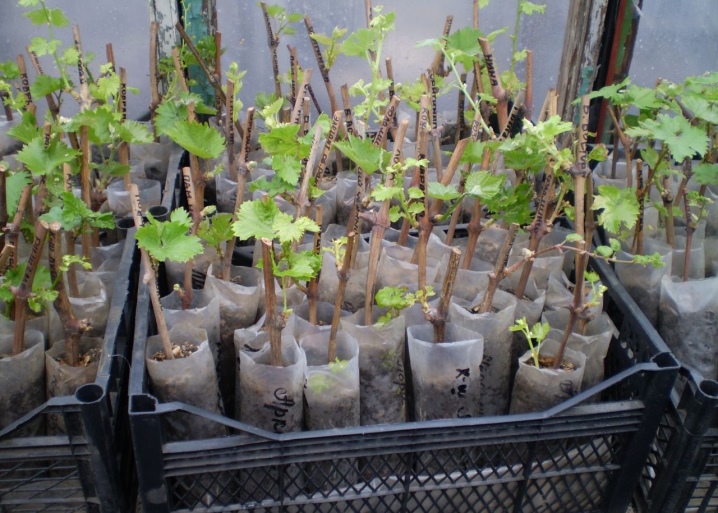

The shoots prepared for autumn planting are placed in the soil pre-watered with warm water - this is how it becomes compacted. The procedure is repeated after sprinkling the roots with earth. Such measures during autumn planting increase the survival rate of grapes, reduce the risks of infection with infectious diseases.
Saplings for the winter must be covered. Previously, it is worth wrapping the shoot with lutrasil or any other fibrous agromaterial on a polypropylene basis. This will increase the chances of a successful wintering, even for an incompletely ripe vine.


The spring planting time begins from the moment the soil warms up to + 10-12 degrees. On average, this norm corresponds to the 3rd decade of April. It is important that atmospheric temperatures at the time of landing do not fall below +14 degrees. For vegetative shoots, these dates are shifted to the end of May, since they are more vulnerable to the influence of external factors.
Early spring agrotechnical measures are recommended to be carried out before the start of sap flow in the grapes, that is, until the plant has budded. In this case, the pit will have to be prepared in the fall, and in the spring, about 3 weeks before transferring the plant to the ground, cover it with a black film to warm the earth.
Summer is not the best time to plant grapes. But if it is necessary, the plant must be taken along with an earthen clod in order to reduce root injury.


Choosing a place
Planting plants in a permanent place is an important point that requires special attention. When growing grapes in open ground and in a greenhouse on the site, it is necessary to take into account the orientation to the cardinal points. Optimal for this light-loving and heat-loving plant are considered to be the southwestern, southern or western location. It is good if the seedlings are placed next to houses or other buildings - this will allow the shoots to receive additional heat at night. This technique works well when adapting varieties with medium ripening times in the northern regions - the berries ripen faster, they turn out to be sweeter.


The southern, south-western and western parts of the exposure are also the best options for planting on slopes.
At the same time, it is important to avoid lowlands, where the vine is exposed to the increased effects of frost. It is recommended not to place grapes next to large trees. It is better to retreat from them by 3-6 meters so that the root system of the larger "neighbor" does not affect the growth of seedlings.

We take into account the type of soil
Different types of soil require some attention to planting. The grapes are grown on sandy, black earth and clay soils. For each of the soil composition options, the preparation process will be markedly different.
Chernozem and clay
Lignified shoots require pit preparation before planting in such soils. It has a square section with dimensions of 80x80 cm and a depth of 80 cm. In the bottom part, a special nutrient layer is prepared up to 250 mm high:
- 7-10 buckets of humus;
- fertile soil for bedding up to the level;
- mineral fertilizers (300 g of superphosphate and potash);
- 3 liters of wood ash.


All this is placed at a depth of about 10 cm, compacted. It is covered with a loose layer of fertile soil by 5-10 cm. A space of about 50 cm remains on top of the pillow - it is used for planting, having previously formed a mound in the center of the pit. It is important that the "heel" of the lignified plant is 0.5 m deep, at the top of the embankment. The roots should be straightened in a cone.
Saplings from shortened cuttings are placed vertically, with a length of more than 25 cm - obliquely, so that the base of the growth is 25 cm below the edge of the pit. It is not poured up to the top with soil, it is compacted, 20-30 liters of water are poured under the root.
After the top layer of the soil has dried, loosening is performed, watering twice with an interval of 14 days. Then the soil is loosened, mulched, and the procedures are repeated after heavy rains or artificial moisture application.


Sands
Landing on the sand has its own differences. Such soil is much more susceptible to temperature fluctuations. In summer, it warms up intensively, in winter it freezes quickly and deeply. The same applies to the ability to preserve nutrients and moisture. Due to its composition, sandy soils are initially poorer than chernozem and clay.
This drawback is eliminated when planting grapes by increasing the depth of the pit to 1.05 m while maintaining its size. At the bottom, a "hydraulic lock" is laid out of dense clay 20 cm thick, similar to a saucer.
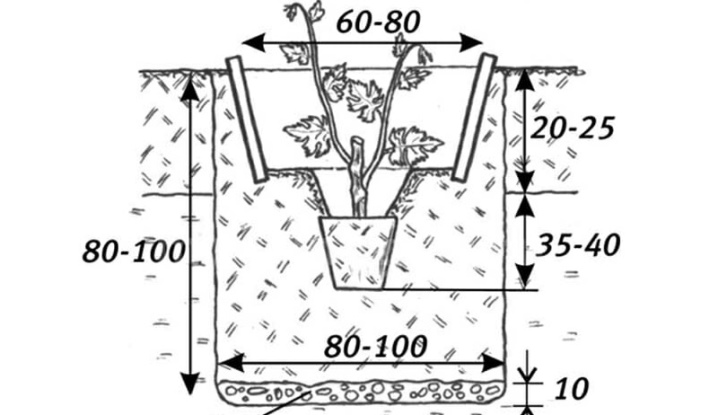
On top of it is placed a nutrient cushion of humus, fertile soil and fertilizers up to 250 mm in height.
When choosing potash dressings to place in the hole before planting, it is important to give preference to those that also contain magnesium. The seedlings are deepened by 60 cm, to the base of the growth from the edge of the pit, at least 30 cm should remain. Watering with an interval of 7-10 days is carried out three times. Its intensity is increased. For 1 plant, add 30-40 liters of water.


Should you plant different varieties side by side?
When forming a vineyard from different varieties, it is worth placing their plots taking into account a number of factors. For example, the grouping of plants is widespread according to:
- appointment;
- ripening time;
- frost resistance;
- the height of the bush.
You should not be afraid of cross-pollination in amateur viticulture. But it is still better to choose crops with bisexual flowers, which practically do not depend on the activity of insects during the transfer of pollen. They are less dependent on external factors. Bushes that form flowers of only the female type require a mandatory location next to self-pollinated varieties.


Fertilizers when planting
The main dressing necessary for grapes when planting is organic fertilizers in the form of humus, compost. They are brought in abundantly, up to 70-100 liters per pit. Such feeding forms a nutrient medium for plants. Complex fertilizers are added dry directly to the soil - usually superphosphate, as well as potassium or potassium-magnesium mixtures in the amount of 300-500 g.
Wood ash and ash help to deoxidize highly calcified soil, 3 liters per 1 m2 is enough.


Planting vegetative seedlings
The basic rules here are the same for lignified and vegetative seedlings.
The hole is made 250 mm deep in clay soil or chernozem, 300 mm - in sand. The planting scheme on the site is determined individually, based on the plant variety. Preparation of a pit for grapes is done in advance, using the necessary fertilizers, taking into account the type of soil. Then it is compacted, 2-3 times with an interval of 7 to 10 days, 20-40 liters of water is spilled - this will allow the soil to shrink.
Greenhouse seedlings are called vegetative. They have a closed root system with a green growth of at least 15 cm. If there are 2 shoots, each should be about 70 mm long.
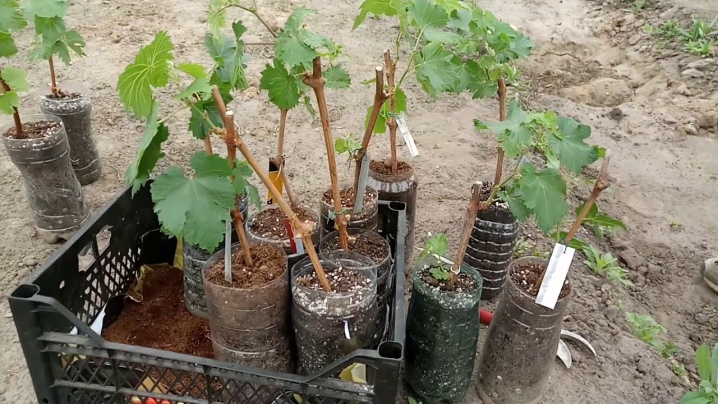

Seedlings in containers can be planted in the usual way, without the shell. In order for the earthen lump to be easily removed, the plants stop watering 5-6 days before they are transferred to the ground.
If the second planting method is selected, only the bottom of the container is first cut off. Then it is placed on a prepared site in the hole, covered with soil, not reaching 25 mm to the green shoot. In autumn or spring (when planting in September-October), the hole is dug from one side. The plastic container is cut and removed.
This allows less trauma to the delicate roots of a vegetative seedling, stimulates the development of heel processes when dew is inhibited, which, with the usual method of planting, have to be cut over time.


Preparation
The process of preparing seedlings for transfer into the ground begins with inspection and selection of material. Healthy young plants are always strong, without blisters, spots, blackheads, plaque. The normal thickness for them is from 3 mm. Leaves should be green without gray or brownish bloom, uniform color. When choosing a ready-made planting material, it is better to give preference to one that is placed in a transparent container with a clearly visible root system.
Annual shoots select well-ripened ones. Their cut will turn out to be bright green. For planting, choose plants with 3 or more buds. The annual growth is ripe, it has a straw color. It is important to inspect the plants for spots, defects.
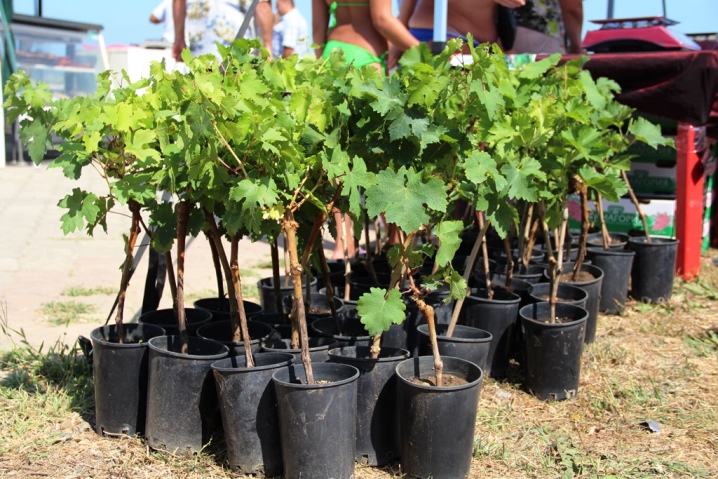

Falling off the eyes after light pressure can be considered an alarming sign.
The prepared seedlings should not be allowed to dry out, dehydrate. In preparation for planting, soaking is carried out in clean, settled water for 12-24 hours. Then the one-year shoot is cut off, only 3-4 eyes remain.
The upper nodes are freed from the roots, the lower ones only refresh. The exception is planting material obtained from shortened cuttings. In this case, all roots are only pruned without completely removing. It is recommended to superficially treat the growth with the antifungal drug "Dnok" in a solution of 5 g / 1 l of water.


Hardening
Vegetable seedlings must be hardened to prevent them from burning out under the influence of sunlight. It is produced like this.
- Plants are kept for 4-6 days under a canopy or in the shade of trees during daylight hours. For vegetative seedlings grown in low light and high temperatures, the hardening time is increased by 1.5 times. They can be recognized by their thin elongated shoots and very light leaves.
- The next 8-10 days they are placed in an open place. The seedlings need to be in direct contact with the sun. This completes the hardening.
It is worth noting that seedlings that did not undergo this procedure, with early spring planting (in the 3rd decade of April), in the absence of micro-greenhouses as an additional shelter, can perceive the transfer to open ground as the onset of autumn. In this case, they will demonstrate a cessation of growth, lignification and ripening of shoots. This is how they prepare for wintering. This should not be feared - by the end of June or earlier they will recover in growth.


Planting stages in spring
From the 2nd decade of April to mid-May, lignified one-year-old seedlings are planted in the ground.Green vegetative shoots are transferred to the soil not earlier than the end of May and until July. The pit is prepared in advance, about 1 month in advance.
7 days after the last portion of moisture is added, a hole is formed in the prepared area for the container: 55 cm deep on black earth or clay soils, 65 cm deep on sand. A seedling carefully removed from the container, which has previously been hardened, is placed in it.
It is important not to destroy the clod of earth in which the plant is located.
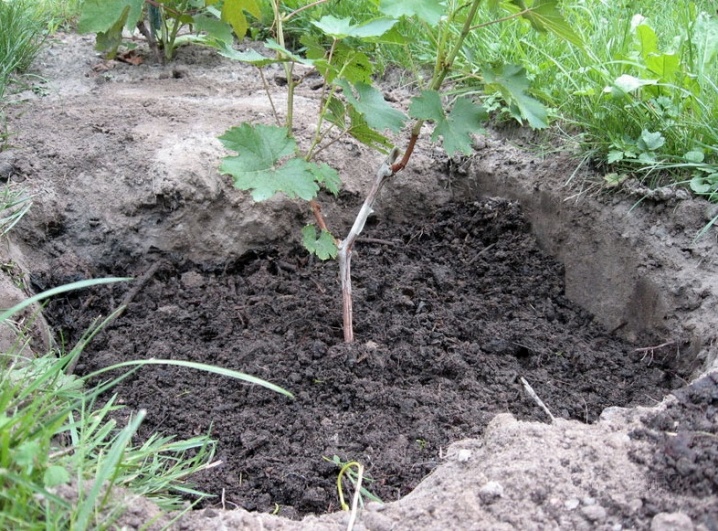

After that, the hole is filled with fertile soil, compacted and thoroughly watered. A peg is placed next to the seedling. The plant is being tied up. Non-acclimatized seedlings will need a shading screen on the south side for the first 10 days. It is built from tree branches or a plywood board, a sheet of tin.
During the first year of life, a vegetative seedling needs attention. On the bush, all side shoots are removed, except for the central one. The garter must be preserved.
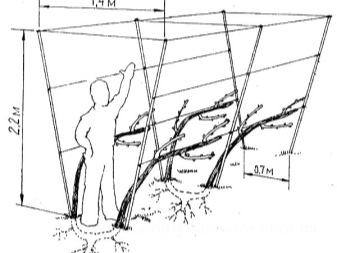
If the bushes are not placed individually, it is possible to form a vineyard on supports, after driving in the pillars 2 m high to a depth of 60 cm into the ground. The distance between them is made about 2.5-3.5 m, then the wire is pulled above the ground at a height of 40, 70 and 100 cm, support rails are placed according to the number of seedlings. The grapes are planted in rows, as it grows, it will braid the supports, making it easier to care for and harvest.

Planting stages in autumn
The time for planting grapes in the autumn comes in October, lasts until the frost. It is important here to pay attention to the protection of the tender young shoot. For this, an artificial shelter is formed from a plastic bottle with 3 holes for air circulation.
The landing order will be as follows:
- choice of location;
- formation and preparation of a pit 80x80 cm in size;
- placing a seedling on a constructed mound;
- falling asleep with soil without fertilizers to the place of growth;
- installation of a shelter from a plastic bottle cut from the neck;
- watering with 3-4 buckets of water.
Before frost, all that remains is to take care of shelter for young grape bushes.


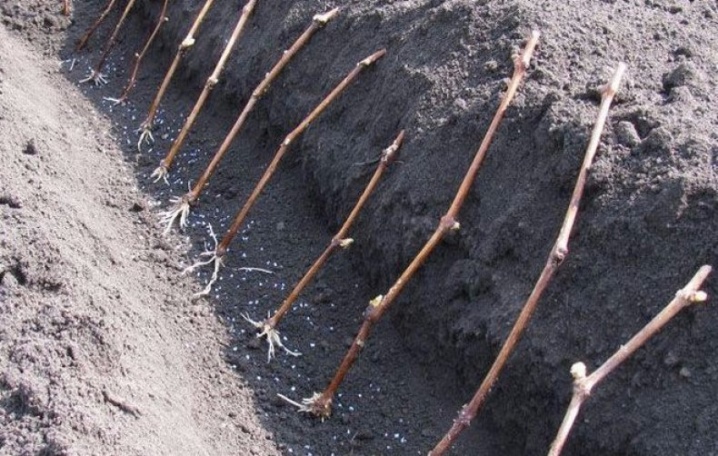
Planting cuttings
Cuttings - shoots without their own root system - are always rooted in the fall. After the foliage has fallen off, a healthy fruiting vine is cut off, separating the central sections of the two-year-old shoots. Several future shoots from 20 cm long with 2-4 living buds on each are formed from it. Then they are placed in moist soil at a distance of about 15 cm from each other, poured with warm water, covered with a film from the cold.
Overwintered cuttings will sprout in spring. When the frost stops, the mini-greenhouse is ventilated. It is fully opened only when stable warm days are established.

What crops can be placed nearby?
Among garden and horticultural crops, there are many plants, the neighborhood with which can be considered favorable for grapes. They can be roughly divided into several groups.
- Siderata. They enrich the soil with nitrogen. This category includes legumes and cereals - rye, mustard, lupine, clover. It is important that the plants have enough moisture. In arid regions, such a neighborhood would become more dangerous than beneficial for grapes.
- Cucumbers. When grown on a trellis, they get along well with grapes.
- Strawberry. Conditions in the shade of a vine work well for its bushes. And the difference in the depth of development of the root system does not create competition for moisture and nutrients.
- Onions and garlic. They are the natural enemies of most insects.
- Roses. They are planted as an indicator of mildew, which is dangerous for grapes. It appears earlier on roses.
- Early varieties of white cabbage. They have a good effect on the growth and development of grapes.
- Greens. Spinach, sorrel, dill do not harm grapes. They can be placed in the aisles.



Fruit trees, such as plum, cherry, apple and pear, are considered to have a neutral effect on grapes. It is only important to place them at a sufficient distance so as not to shade the bushes.Contraindicated grapes "neighbors" in the form of raspberries, tomatoes, other solanaceous plants, corn.
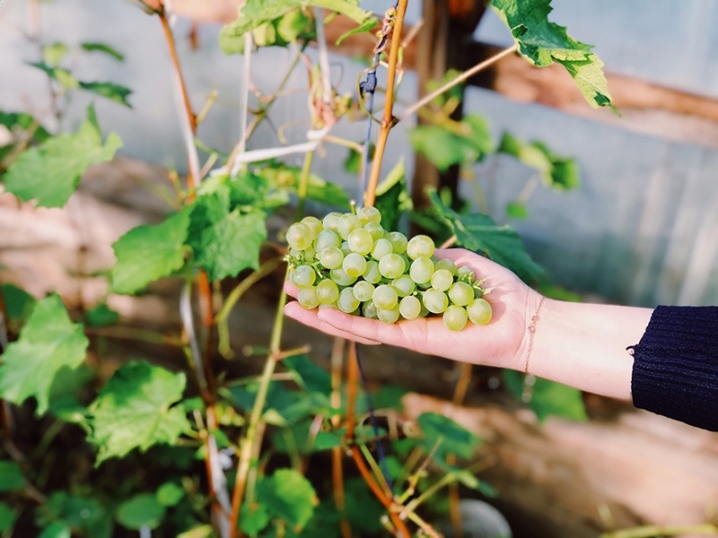
What year after planting should fruiting be expected?
Having planted grapes on the site, gardeners are happy to wait for the harvest. But there is no need to rush. The first vines on plantings from cuttings will come out only after 4 years. In vegetative or annual seedlings, this process is faster. You can collect the first bunches for 2-3 years.

Tips for Beginners
New wine growers have to deal with many things that they are not ready for. Among the important tips that will definitely help you figure it out, the following points can be noted.
- Do not place grape seedlings too close to buildings. The minimum distance between them should be 0.7 m.
- On sandy soils, it is better to use the trench method of planting grapes.
- In the northern regions, seedlings are often left in a school (in a shelter) to the very signal brushes. At the same time, the plants are not transplanted into the ground, but are left in buckets, only sprinkling them with earth. For the winter, the seedlings are transferred to the basement.
- If the planting is not spot-on, the location of the different varieties must be carefully planned. With their spontaneous placement, it is difficult to comply with the norms of the distance between plants. For juice-wine varieties, they are 0.8 m, for dining rooms - at least 1.5 m.
- When planting, the grafted seedlings are placed not vertically, but horizontally, at an angle. Otherwise, plants from southern or European climates will show poor vine maturation.


Find out more information about planting grapes in the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.