Campsis: description, types and varieties, planting and care rules
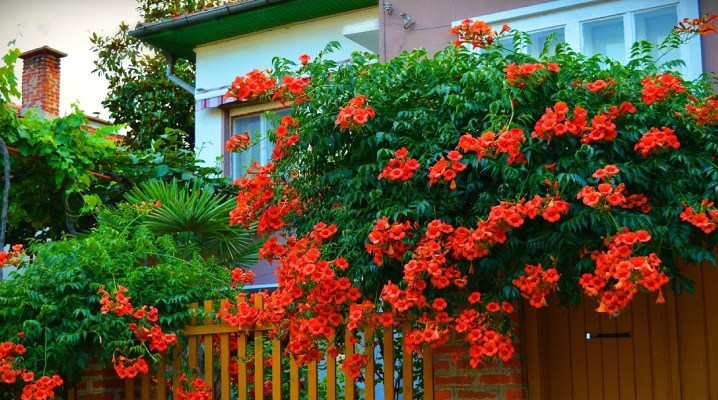

Kampsis is the name of a garden plant that can be grown in the middle zone or in the south of Russia. Thanks to modern breeding, this perennial deciduous vine has many varieties and varieties. Kampsis is used in landscape design, it decorates the adjoining territory and can act as a hedge. The beauty and aroma of blooming kampsis gives pleasure not only to a person, but also serves as an object of attention to insects and bees - for this reason, it is undesirable to plant it near the windows of residential buildings.


Description
A fast-growing vine called kampsis is a member of the bignonium family. In nature, Kampsis has two species: one is large-flowered, it has Chinese roots of origin, and the second is rooting, which has an American range. Back in the 17th century, the North American species began to spread actively in European countries, decorating parks and squares. An adult plant is a liana, which, under favorable conditions, quickly grows up to 10-15 meters and turns into a tree-like bush.
Therefore, it is also called a tree liana, although some varieties may outwardly look like a shrub or even a small tree.


Campsis is grown because of its attractive and aromatic inflorescences. The flower of this plant is an excellent honey plant; outwardly, it resembles a large bell with a tubular base. The color of the flower can be crimson-red, bright orange, yellow-pink. In inflorescences, up to 12-15 such flowers are usually collected, and outwardly they resemble a panicle. The flowering of the plant begins in the second decade of June and continues until the end of summer. After the flower withers, in the fall, the creeper forms a fruit with seeds, called a pod. When the pod ripens, it bursts spontaneously, and the seeds fall into the soil - thus the plant multiplies by self-sowing.
Liana leaf plates are large, reach up to 15-20 cm, consist of 9 or 11 small leaves, which are combined on the central vein and are located on it alternately. Each such leaf has serrated edges and does not exceed 5-6 cm in diameter. Despite the fact that the liana is thermophilic, in winter it is able to show frost resistance and survive frosts down to minus 20-25 ° С. In regions of central Russia with more severe climatic conditions for the winter, Kampsis is sheltered.


Types and varieties
Campsis has, in addition to its natural species, also hybrid varieties. This plant has always attracted the attention of not only gardeners, but also breeders. Today, the perennial plant has many varieties that have become known throughout the world.


Rooting
Campsis radicans (campsis radicans) is a rooting species of deciduous liana, which differs from its other counterpart in that it has the ability to form long aerial roots, thanks to which it quickly captures the space around it. In addition, it was noticed that the rooting liana has a higher frost resistance and vitality to adverse factors when compared with other varieties.
Based on this species, several hybrid varieties of Kampsis were bred.
- "Judy" - garden liana, which grows up to 4 meters and blooms throughout the summer period until mid-October with bright yellow flowers, the core of which is orange. This variety feels equally well both in the southern regions and in the Moscow region. The frost resistance of "Judy" is quite high for a vine - it can winter at a temperature of -20 ° С.
For wintering, the lianas are removed from the supports, bent to the ground and covered with spruce branches.
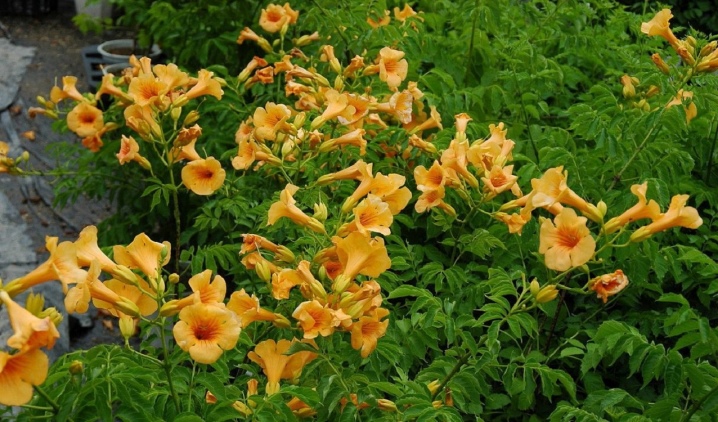

- Trumpet Vine Is a very powerful liana, which quickly grows to 9-10 meters per year, overcoming any obstacles on its way: it can lift boards with its roots, break asphalt, pass through sewer pipes and destroy weak supports. If desired, it can be formed like a tree, if you deal with its crown from the moment of disembarkation. This variety blooms profusely, the color of the flowers is yellowish-red or yellow-pink. The variety is very popular in European countries. Loves the sunny side, but in the shade it can stop blooming.
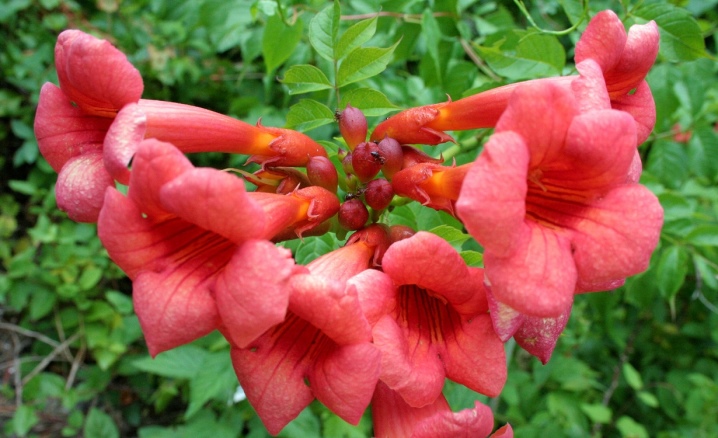

- "Flamenco" - the plant has increased growth and reaches more than 10 meters. Flowering begins in mid-July and lasts until mid-October. The flowers are deep red in color and reach up to 7-8 cm in diameter. Watering is needed moderate, this vine does not tolerate excess moisture. In winter, the plant will be able to withstand cold temperatures down to –17 ° С.


- "Flava" - this liana grows up to 15 meters in height, the flowers are large, reaching 4-5 cm in diameter and up to 9 cm in length, their color is lemon yellow. Flowering is very abundant, it begins in early June and lasts until mid-autumn. The deciduous liana tolerates frosts well and does not die even at –20 ° С, but for wintering it needs to make a shelter.
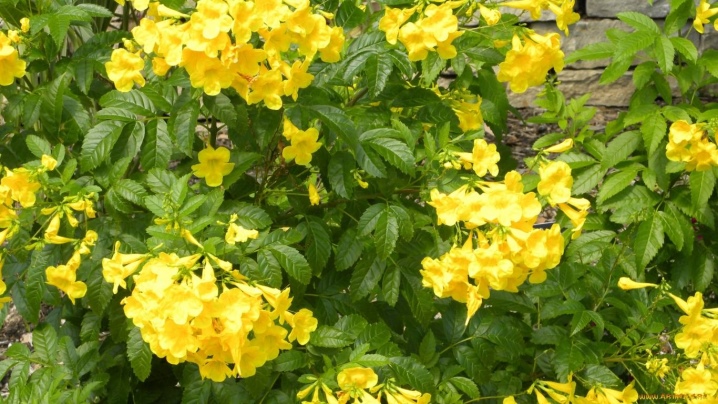

Bignonia - this is also called Kampsis because of its belonging to the family of the same name, it sheds leaves for the winter, which grow back very quickly with the arrival of spring heat.
Large-flowered
Campsis grandiflora (campsis grandiflora) is a large-flowered perennial species that has larger flowers in comparison with rooting, for which it got its name. This species does not have aerial roots, but clings to the support with the tops of its shoots. In comparison with its counterpart, it does not tolerate winter frosts well and can die already at a temperature of -18 ° С. For this reason, it is not grown in the regions of central Russia.
The large-flowered species is based on a hybrid variety called Kampsis Thunberg. In this vine, the flowers are orange-yellow in color, and the tube at the base of the flower is shortened.


Hybrid
Campsis hybrida (Kampsis hybrid) is a hybrid combination of large-flowered and rooting species of Campsis, artificially bred. Thanks to selection, the hybrid plant received all the positive properties taken from both natural species, and began to have good resistance to low winter temperatures and, during flowering, delight us with large flowers.
The color of the flowers can be red, orange, pinkish-yellow, white-pink.


Landing features
To grow campis outdoors, choose the southern or southeastern side of the garden. The plant does not like drafts and, when it grows, looks for support for itself, so you should not plant other plantings next to it. Liana is quite powerful, it can even destroy the foundation of buildings, therefore, when choosing a place where to plant it, one should take into account its peculiar aggressiveness. The perennial is undemanding to the composition of the soil, but it grows best on loose and fairly moist fertile substrates.
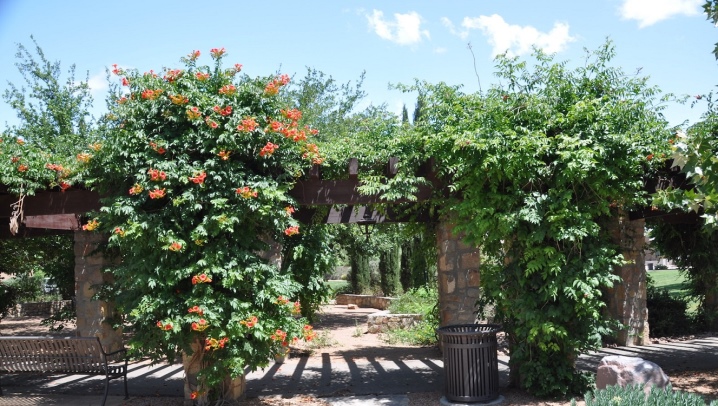

Campsis must be planted in the spring, for which a 30x30 cm landing hole is preliminarily prepared. If the soil is clay, a drainage layer of broken brick or expanded clay is laid on the bottom of the hole. Next, a soil mixture is prepared, consisting of earth, humus and sand, taken in equal quantities. A portion of the mineral fertilizer is added to the finished substrate.The hole is half-filled with the prepared soil mixture, the cutting is planted, the roots are straightened and covered with the remaining soil. The soil around the creeper is tamped and watered abundantly. Immediately after planting the plant, a support is also installed next to it, along which the vine will climb up as it grows.


Subtleties of care
Once the seedling is placed in a permanent growth site, it will need to be cared for continuously. And although Kampsis is an unpretentious and very viable plant, it will still require some attention to itself.
Watering
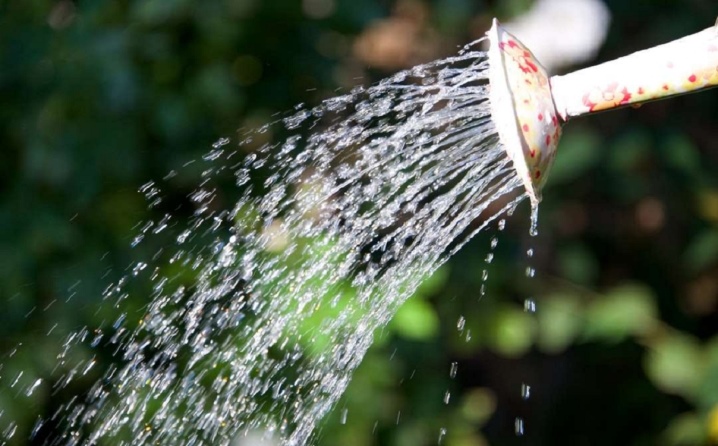
A perennial needs regular watering, and this should be done in such a way, in order to prevent prolonged drying of the soil, but at the same time it is impossible and unnecessarily waterlogged... So that the moisture does not evaporate quickly, weeds are removed around the kampsis and the soil is mulched. In the summer, when in the southern regions there is a rather high above zero temperature, the vines are watered abundantly in the morning and evening every day.

Loosening
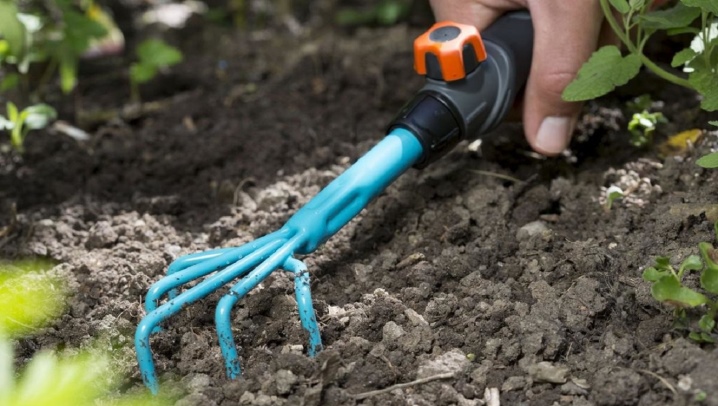
For better growth and development, after watering, the soil around this perennial plant must be periodically loosened. It is especially important to perform this procedure when the composition of the soil is heavy and dense.
Regular loosening will contribute to the enrichment of the roots with oxygen and will increase the absorption of moisture by the plant and nutritious mineral dressings.

Top dressing
If you grow a liana in fertile chernozem soils, then the first couple of years it will not need additional feeding. In other cases, when the composition of the soil is poor, the plant needs to regularly introduce nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer complexes. They are brought in together with watering, and this must be done at least once a month from April to September.


Pruning
Due to the rapid and rapid growth, the vine needs to be cut periodically in order to form a beautiful crown for it. The formation of a bush should be dealt with immediately after planting it.... To do this, the plant is cut off, leaving its aboveground part of 15-20 cm in size. Further, when the shoots grow, you will need to choose the strongest and save them, and the rest must be removed. Growing shoots should be constantly directed towards the support so that they are fixed on it, and if necessary, they can be tied to this support. After 2-3 years, the length of the main shoots will be about 4 meters - this will mean that the perennial has formed.
Each year, the side shoots of the main shoots should be pruned so that they branch out more densely. This is done in early spring until the buds begin to awaken. In addition, broken shoots or those damaged by frost are removed from creepers. In order for the plant to bloom profusely and for a long time, gardeners recommend removing fading inflorescences and cutting the branches on which they were formed with them.

Preparing for winter
No matter how hardy and viable the Kampsis is, this plant loves warmth, therefore, wintering for creepers requires preparation, which is carried out in the fall. Before building a shelter, wilted leaves and flowers are removed from the vines. They are raked away from the plant so that in the spring they do not cause the development of fungal infections and mold. A shelter created from branches of spruce branches or a special covering material will help a heat-loving plant overwinter. They cover it on top polyethylene.
If the shoots of the plant cannot be removed and attached to the ground, then such forms are covered vertically, fixing the insulation with wire, ropes, staples.


Reproduction methods
A mature plant will constantly supply you with planting material. After flowering, the matured pods contain a variety of seeds that can be germinated. In addition, when pruning, you will have a huge number of viable cuttings, and this plant can also reproduce very well with branches.
Seeds
Propagation by seeds, which are contained in ripe pods, has its own characteristics. It is noticed that hybrid vines grown from their own seeds almost do not inherit the characteristics of the original parent variety. That is, you may not succeed in a hybrid variety, but either a large-flowered or a rooting species of a wild plant will grow. In addition, a plant sprouting from seeds at home blooms several years later than its hybrid counterparts. However, this is the simplest method of breeding Kampsis, and it is quite possible to apply it.
Before planting in the ground seeds of deciduous liana do not require prior stratification, they are well stored at room temperature and do not lose their germination at the same time. Sowing seedlings is carried out in the spring, using a loose and well-absorbing soil substrate for this purpose. The seeds are laid out on the surface of the soil and lightly sprinkled with them, and then they put the greenhouse in a warm place, covered with glass or polyethylene. After 1 month, the first shoots will appear, and when they have 3-4 pairs of true leaves, the seedlings can be dived and planted in open ground.



Undergrowth and branches
Liana can be propagated by root shoots, which are always formed in large quantities in perennials. To do this, you need to dig out such a basal process, separating it from the main root, after which it must be transplanted to a permanent place and care for it until the seedling takes root properly. This procedure is carried out either in early spring or in autumn, when the plant finishes its flowering.
If you want to increase the number of plants with the help of branches, then you need to find one of the stems that grows closest to the soil surface, and bend it, fixing it with brackets in this position and lightly sprinkling it with earth. At this time, you need to ensure that the soil near the branch is always loose and moist. Next year, in the spring, roots will appear at the bend. It can now be detached from the mother plant and transplanted into a permanent location.
It has been noticed that such seedlings root best of all and start growing quickly, retaining all their hybrid properties.

Cuttings
Cuttings can be used to propagate Kampsis. This method can only be used in the summer, since cuttings are carried out in June-July, so that the plant has time to take root before the arrival of winter. You can get planting material by cutting a stem with green leaves from a plant. For rooting, you need to take only the middle part of the shoot. The leaves are removed from it, but 2-3 top leaves are left and shortened by about half. In a previously prepared mini-bed, which is located in a shaded place from the bright sun, these cuttings are planted, placing them at an angle of 40-45 degrees. Then the planted seedlings are regularly watered, and the soil is well mulched. Rooting occurs quickly, after which the seedlings will have to be transplanted to a permanent place.
In spring, cuttings obtained from crown pruning can also be rooted, but shoots at least 1 year old are suitable for this purpose. They are planted on a prepared bed, while they take root perfectly.



Diseases and pests
Perennial vine kampsis is a plant with good immunity, but sometimes, with inappropriate care, he can develop certain diseases.
- Bacterial rot - the reasons for its appearance are excess moisture during watering or infection with pathogenic bacteria. Rot is manifested by the fact that the shoots and petioles of the leaf plates turn black, and the leaves themselves become soft, watery and translucent. If you look at the root of the plant, the affected areas will be softened. Treatment consists in removing all affected parts, and then treating the plant with a fungicide solution.
- Fungal infection - manifested by the formation of brown and dark gray spots on the leaves. This problem arises if it is humid and cool near the plant.To prevent the development of the fungus, it is necessary to remove all organic matter from the foot of the plant in a timely manner, especially if it grows in the shade. It is important not to forget to do this on the site in the fall, when Kampsis has dropped the foliage. Treatment is carried out with Bordeaux liquid, sprayed with a solution of colloidal sulfur, or other fungicidal preparations are used.
- Viral contamination - manifests itself in that the diseased plant does not bloom, pods do not form, and the leaves are covered with yellow spots that are rough to the touch, sometimes resembling a mosaic. The affected areas of the plant are removed, and if it is completely damaged, then it is dug up and destroyed.
For the treatment of healthy parts of the vine, it is sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate.



In addition to various diseases, viable campsis can be exposed to an invasion of insect pests. Most often, this vine suffers from aphids, which can occur during the hot and dry summer months, or if you overfeed your plant with excessive nitrogen fertilization. Cope with aphids will help treatment of Kampsis with an insecticide solution.


Use in landscape design
In the garden or on the territory of the courtyard, with the help of kampsis, they make the design of a hedge that separates the economic zones on the site. The climbing plant can be planted along the fence, which will support the long stems of the campsis. Liana can be used to decorate a recreation area by directing the growth of a perennial to a gazebo, veranda or outbuilding. This powerful vine is not placed next to other plants, as it will quickly drown out their growth, leaving no chance of survival.


When choosing a place to place a kampsis, it should be remembered that liana tends to grow aggressively. It will be very difficult to get rid of the root growth of this perennial and viable plant later. The strong root system is able to resume its growth within 7-10 years after you completely remove this plant from the ground. Experienced gardeners joke that lovers of kampsis are divided into two groups: those who dream of planting it on the site, and those who want to get rid of it.
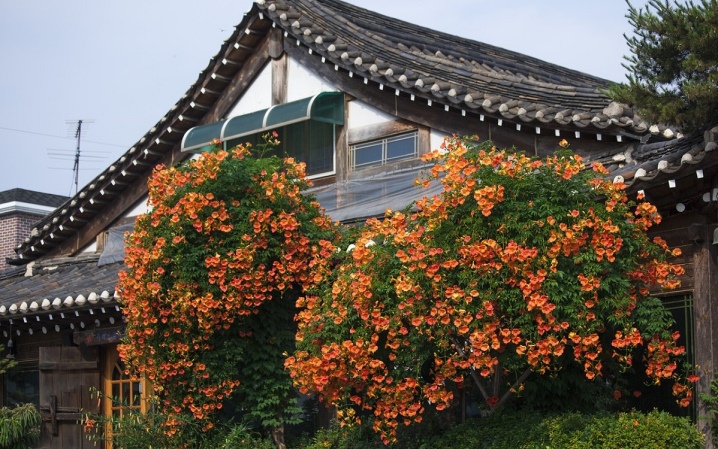

In order to control the rapid growth of perennial vines on the site, it should be pruned abundantly every spring. If you skip such a procedure for at least 1 year, then aggressive kampsis will quickly form thickets, which will be difficult to disassemble. Landscape designers advise flower growers to start permanent work with Kampsis to form its crown immediately after planting cuttings. In European gardens and parks, a liana, using the skillful direction of growth of its shoots, is turned into a compact bush or tree with a spreading crown and braided shoots that imitate the trunk. In Russia, kampsis is most often allowed to grow freely along the fence, directing the growth of shoots towards the street.
At the same time, the flowering plant really decorates the territory and the entrance group near the gate or wicket.


For more information on Kampsis, see the next video.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.