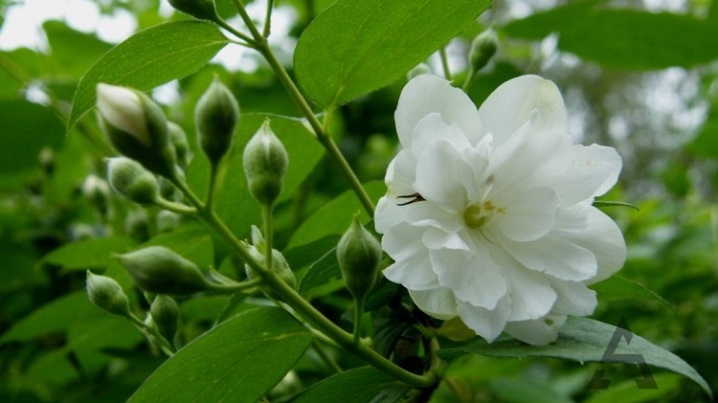
All about chubushnik (garden jasmine)
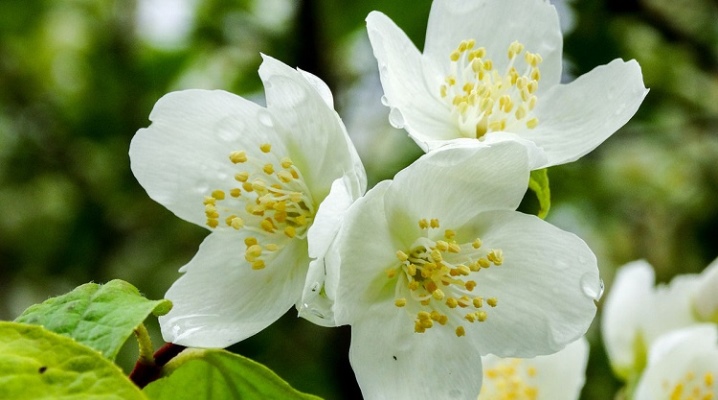

Chubushnik, popularly known more under the name "garden jasmine", is a charming plant that is not very demanding to care for and amazes with its magnificence and aroma during the flowering period. Many gardeners plant this crop on their site, but at the same time they often ask the question: "Why does the shrub bloom poorly?" Let us consider in more detail the description of garden jasmine and its varieties, the peculiarities of planting and care for central Russia, Siberia and other places.






What it is?
Chubushnik (Latin Philadelphus) is a perennial shrub belonging to the Hydrangeaceae family. Under natural conditions, the shrub is found in southern Europe, east Asia and North America. The Latin name is formed by merging the words: "phileo" - love and "adelphos" - brother, which emphasizes the close coupling of opposite shoots. The name "chubushnik" is associated with the fact that in ancient times the branches of the plant served as an excellent material in the manufacture of chubuk (hollow wooden rods) necessary for filling pipes for smoking.
Popularly, the shrub is better known as "garden jasmine" because of the similar structure of inflorescences with real tropical jasmine, although in reality these plants belong to different families.
To date, more than 70 species of mock-orange are known, they differ in height, leaf shape, flowering time and flavor characteristics.


Common features in a botanical description of a culture are:
- strong fibrous root system;
- straight trunks and branches;
- thin bark of gray or brown color;
- white or light cream flowers, collected in a brush;
- small fruit boxes with seeds.



The height of the plant, depending on the variety, varies from 1 to 2.5 m, rare specimens grow up to 4 m. The leaves are green matte, 2 to 6 cm long, have an oblong or ovoid shape. The flowering period is about 2.5 months, but you can admire such splendor when planting several different species and varieties on the site: one bush blooms for about 3 weeks under favorable conditions.
After the petals fall off, fruit boxes with numerous seeds are formed. In general, the shrub is unpretentious, grows quickly in the sun and in partial shade and pleases with abundant flowering.


Overview of species and best varieties
First of all, the mock-orange attracts with its snow-white flowering and pleasant aroma. It may seem to inexperienced gardeners that there is not much difference between the varieties. But if you look closely, you can notice differences not only in the growth and shape of the leaves, but also in the structure of the inflorescences - they are simple, semi-double and double. It all depends on the type and varietal characteristics. The following types of chubushnik are considered the most common.
- Coronary. Differs in good winter hardiness. It has a large number of varieties with beautiful foliage. Dissolves buds in early June and blooms for 2.5-3 weeks. The scent spreads over several meters and has honey notes. Some varieties can grow tall (over 3 m).


- Large-flowered. The name of the species speaks for itself - it is distinguished by the large size of the flowers (more than 5 cm in diameter), but the aroma is weakly expressed.


- Virginia. Photophilous and thermophilic species, but when covered with soil it can withstand moderate winters (down to –23 ° C).When the shoots freeze, sanitary pruning is needed in the spring, and then the bush is able to restore the crown and bloom in the second half of summer. The species is characterized by a rounded shape of dark green leaves and double flowers. The height of the bush is from 1 to 2.5 m.
It does not tolerate waterlogging of the soil, but it perfectly adapts to transplanting to a new place at any age.


- Thin-leaved. Popularly known as "wild jasmine", as its thickets can be found in the natural environment of a mixed forest. Unpretentious plant. The size and density of the leaves depends on the lighting. When planted in sunny areas, they are large and dense, in the shade they are thin and translucent, in the light they are quite dense. Blooms in June for 2 weeks. The flowers are white and large. Withstands frosts down to –30 ° C, which makes the species suitable for planting in northern regions.


- Small-leaved. A low-growing shrub with small leaves. Its inflorescences are interesting, they resemble cherry flowers in shape, and strawberries in smell. Low winter hardiness. The bushes feel good when planted in the southern regions, they can adapt with good shelter in the middle zone of our country, but it is undesirable to plant in Siberia and the Urals.


- Odorless. A tall species, the bushes reach a height of up to 4 m. The leaves are long, on non-flowering shoots - 10-12 cm, on flowering ones - 6-7 cm. White flowers about 5 cm in size have absolutely no smell.


- Lemoine. The name of the species is directly related to the family of the famous French breeder Victor Lemoine. Chubushniki became the last cultures to which he turned his attention. Their cultivation also interested the florist's wife and son, and they took an active part in the selection. A family contract has bred about 40 varieties. Common features are a wide-spread crown and brown shoots. The leaves are lanceolate, about 4 cm long, the size of the flowers is 3-4 cm. The plant growth ranges from 1 to 2.5 m. It has a large number of aromatic varieties with an increased level of decorativeness.


Crown varieties
- "Aureus" (Aureus). Yellow-leaved variety. Decorativeness is given not only by flowers, but also by leaves, which change their color during the season. In the spring, they have a juicy yellow tint, in the summer they are bright green, and by autumn they become yellowish-green. The inflorescences are simple white, in the middle there is a yellow stamen. The aroma is intense. It blooms well in a sunny area, in partial shade it forms much fewer inflorescences. At the end of the flowering period, it needs sanitary pruning.

- "White Lady". A slow-growing variety, in an adult state, the bush reaches a height of about 1.5 m. The crown is spherical, it grows 1 m wide. The leaves are oval, dark green in color. Flowering begins in early June. White semi-double flowers fill the garden with a pleasant aroma.
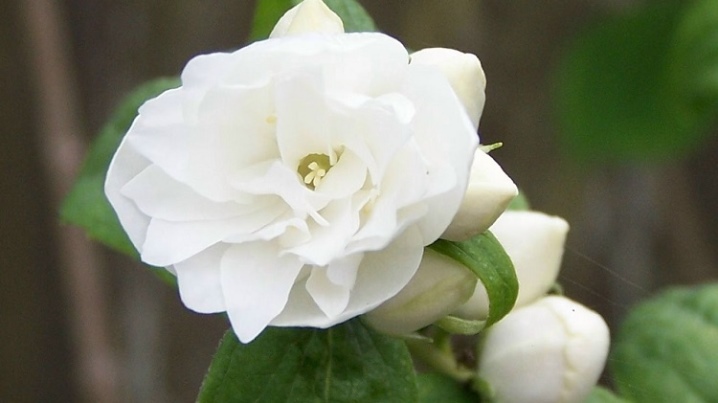

- "Variegatus" (Variegatus). A low shrub, when planted in central Russia, the height does not exceed 1.3 m. The buds bloom in the 20th of June. Flowering is not very long, flowers are simple cream shade with yellow stamens. The leaves are large, 7-8 cm long, with a white edging along the edge.

- "Snow avalanche". The bush is notable for its flowing branches with small oval toothed leaves along the edge. In early June, white semi-double flowers appear in large numbers, which exude a pleasant aroma, reminiscent of the smell of wild strawberries. Flowering lasts about 20 days.
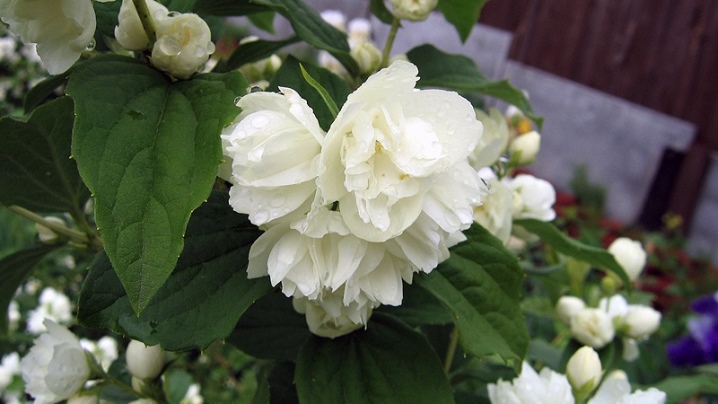

Virgin varieties
- Justynka. A low shrub 1.2-1.5 m tall, grows well and develops in partial shade. The foliage is large, oval, deep green in color. The length of the leaves is about 6-7 cm. Pure white double flowers are collected in inflorescences of 6 pieces, reaching 4-5 cm in diameter.
Flowering occurs in July; in mid-September, repeated, but less abundant and short flowering is possible.
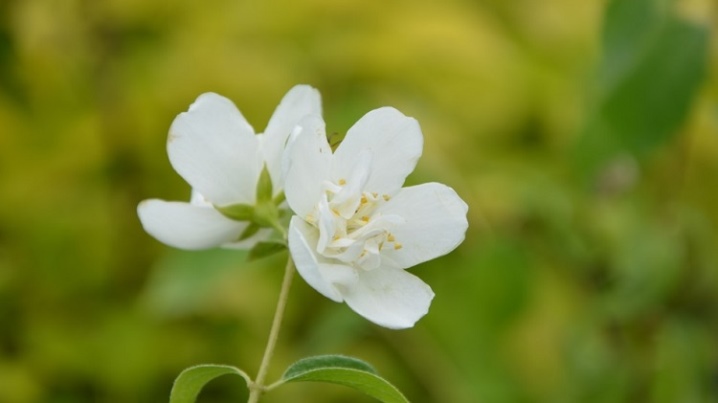

- Minnesota Snowflake. An undemanding variety, it is resistant to cold and can grow successfully in any region. Terry flowers of a snow-white shade form lush inflorescences of 5-7 pieces. The abundant flowering of the variety lasts for 2.5 weeks - from late May to mid-June. The flowers have a sweet aroma. The bush can grow up to 2 m in height.

- Snowbelle. Spreading branches give a special decorative effect to the variety. The growth of the bush does not exceed 1.5 m, and the crown grows 1 m wide. Toothed leaves with slight pubescence on the inner side. White flowers bloom at the end of June.
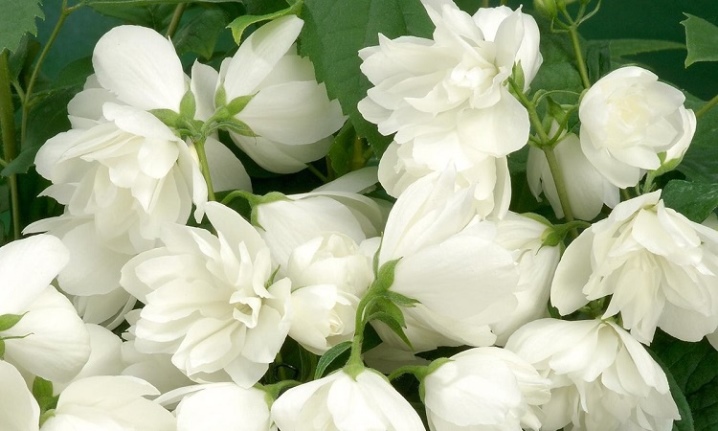

Large-flowered varieties
- "Komsomolets". The variety was bred in 1951 by Professor N.K. Vekhov. Differs in beauty and winter hardiness, well adapted to the changeable Russian climate. Suitable for breeding in Siberia. An adult bush grows within 1.7-2 m. The leaves are dark green with a glossy sheen. Flowers are large, double, 5 cm in diameter, located along the entire length of the shoot. Blooms for 3 years after planting.
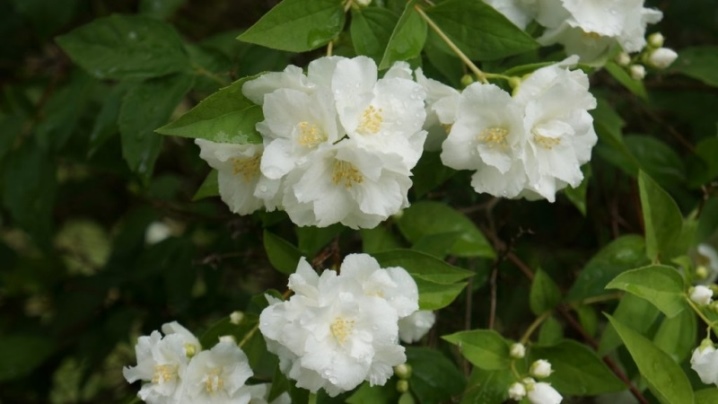

- "Glacier". Low shrub about 1.5 m tall. It takes root well and grows quickly in width. In comparison with other varieties, it has huge inflorescences up to 7 cm in diameter. It surprises with its unusual flowering. In structure, the snow-white double flowers resemble roses, densely covering the shoots. A thermophilic variety that needs additional shelter for the winter.
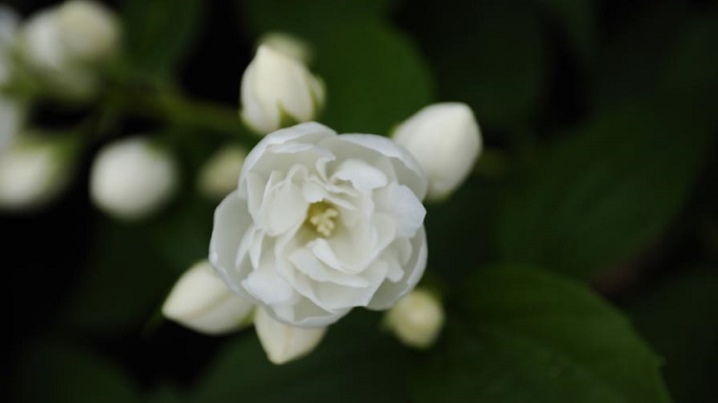

- "Pearl". A low-growing bush with a neat crown of bright green leaves. At the end of June, beautiful white double flowers appear with a pearl-pearl overflow and fragrant fragrance. The inflorescences are large - about 6 cm in circumference, they fade in 3 weeks. It is frost-resistant, tolerates low temperatures down to –27 ° С.
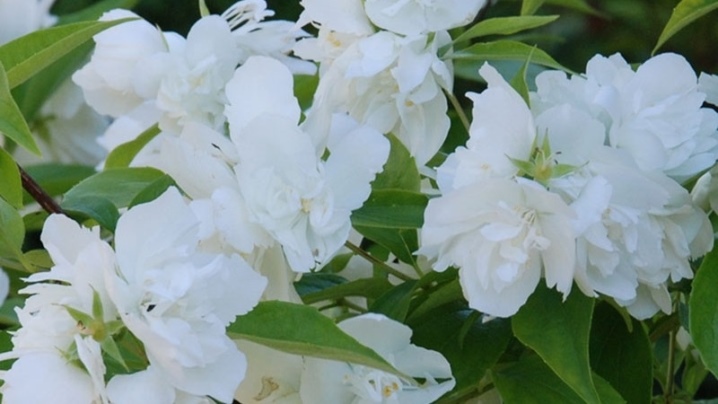

Thin-leaved varieties
- Multiflora. Decorative variety with an abundance of large inflorescences, consisting of 10-12 flowers. It dissolves in mid-June.
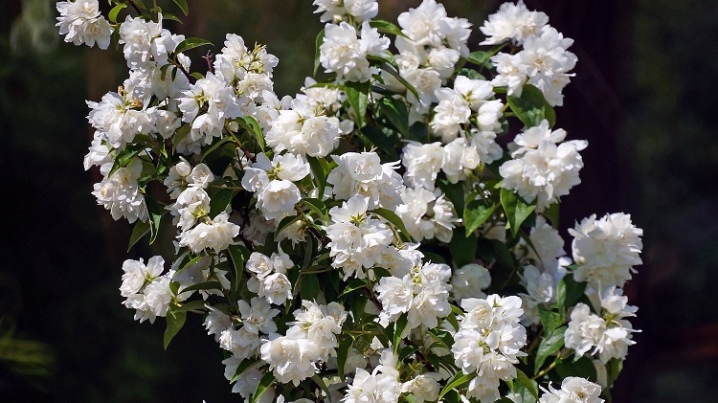

- "Subintegra" (Subintegra). Shrub with a spherical crown, leaves - large, even. Inflorescences are white, collected in a brush of 5-7 flowers, about 3 cm in diameter, odorless.
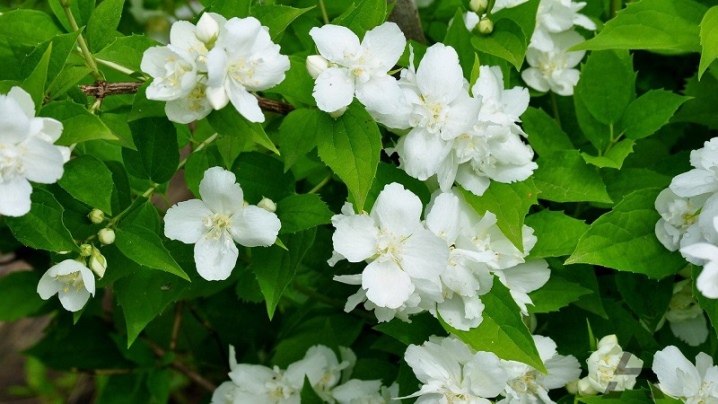

- "Dentata" (Dentata). Differs in unpretentiousness in terms of soil selection. The shape of the leaves is noteworthy - oblong with a strongly pronounced jagged edge.
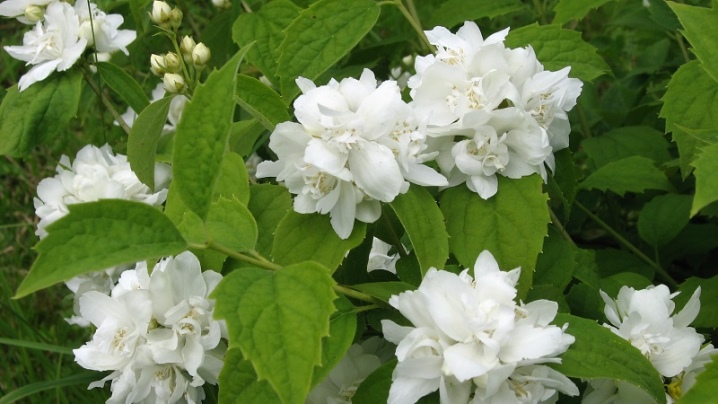

Small-leaved varieties
- Mont Blanc. Dwarf variety, grows up to 1.2 m. Shoots are brown in color with slight pubescence. The leaves are small, 3-4 cm long, even or with small denticles along the edge. Long and abundant flowering begins in the second half of June and ends in about a month.
During this period, the bush looks snow-white, from a large number of inflorescences, shoots tend to sag from their severity.
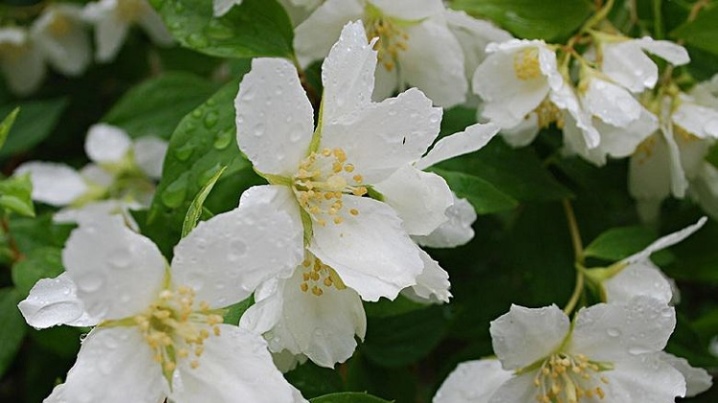

- "Avalanche". Shrub 1-1.5 m high, with an abundance of thin trunks and curved shoots. Leaves are small, oblong_ pointed at the end, light green in color. The inflorescences are simple white or with a light cream shade, resembling small bells with a long yellow stamen in the center. The aroma of flowers is strawberry.
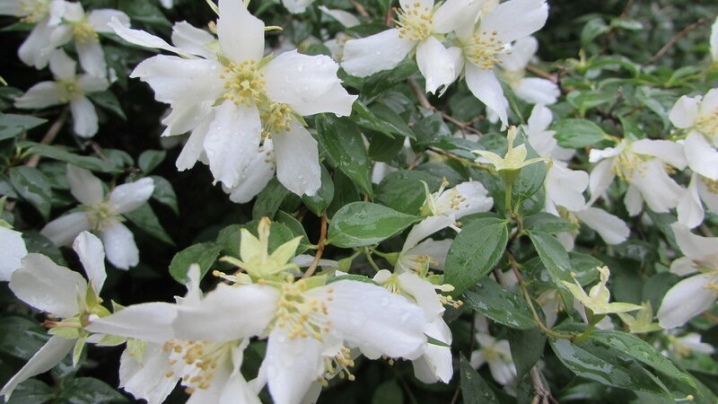

- "Moonlight". It grows within 1.3-1.5 m. It has a dense crown with small dark green leaves. Double cream or white flowers with a faint shade of green fill the garden with a strawberry aroma. Blooms from the second half of June for 20-25 days.

Odorless varieties
- "Grandiflorus" (Grandiflorus). A tall, spreading bush, reaches 4 m in height, the width of the bush in a circle is about 3 m. The bark is brownish in color. Blooms later, begins to bloom in early July and blooms throughout the month. During this period, the bush is unusually beautiful. Snow-white flowers are absolutely devoid of aroma, but they attract admiring eyes. They are rather large in size - 6 cm in diameter, with wide petals and an abundance of stamens. The variety is unpretentious and feels good in partial shade.
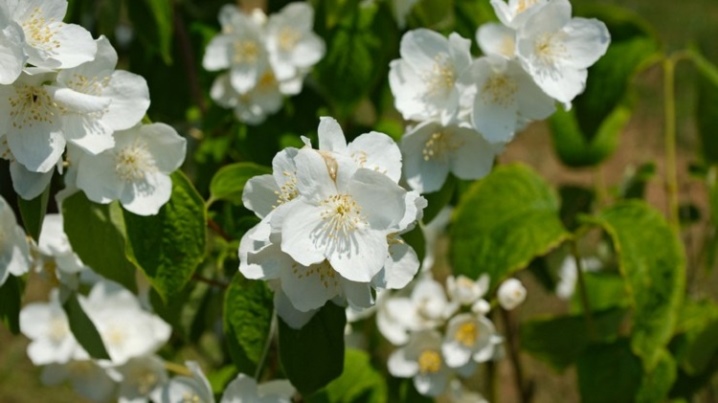

- Elbrus. It got its name from its vertical crown and flowering characteristics. Large snow-white double flowers, collected in inflorescences of 15-20 pieces, are formed only on the tops of the shoots and resemble a mountain with a snowy peak. Flowering is lush and long lasting from the end of June, the flowers have no smell.
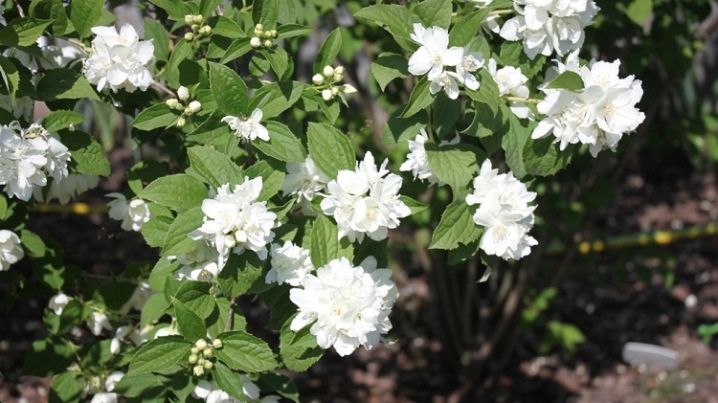

Lemoine varieties
- Albatre. Bush, consists of straight, strong shoots 1.5-2 m high. The leaves are lanceolate, pale green, medium-sized, 3-4 cm long. The flowers are white, simple and semi-double, 2-4 cm in diameter with a pleasant smell reminiscent of a pineapple.
One of the few Lemoine varieties, characterized by increased winter hardiness.
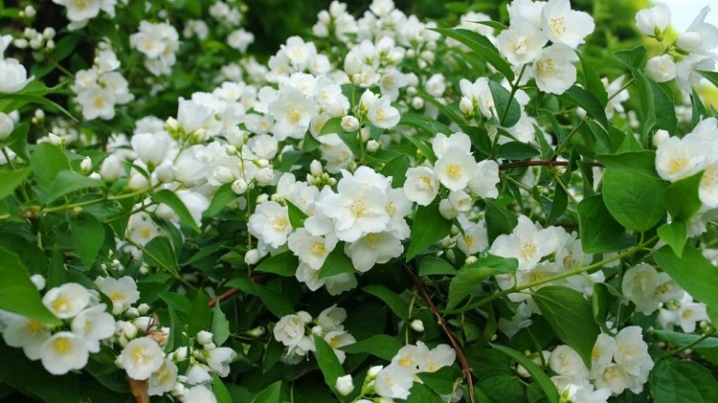

- "Manteau d'Hermine" (Manteau d'Hermine). Has a spreading, but very compact crown. It grows about 1.5 m in height. Leaves are small, pointed at the end, light green in color. It blooms for a long time for almost 2 months. White semi-double flowers, 3 cm in diameter, collected in inflorescences of 5 pieces. The aroma is delicate, not very pronounced. The variety is more demanding on the soil.
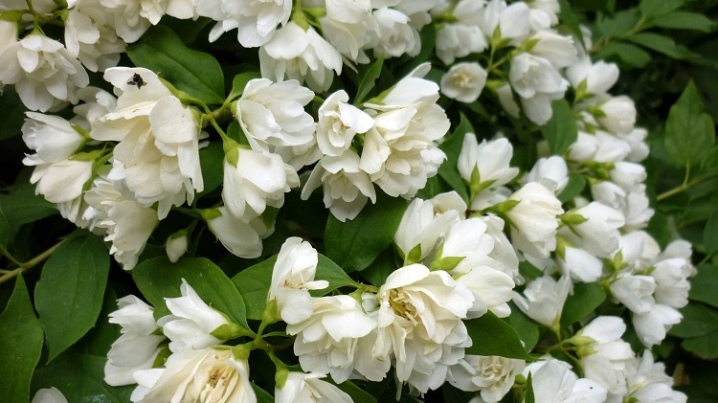

- Virginal - a flowering shrub with dense foliage and a spreading crown, reaches a height of 2-3 m. The variety is obtained by crossing the virgin and small-leaved species. The buds bloom in early July. During the period of active flowering, large white terry fragrant ones completely cover the branches. Unpretentious, fast growing, resistant to weather changes. With bright sunny days, it is capable of re-blooming in autumn.

Boarding and transfer rules
For long-lasting and abundant flowering, it is recommended to plant a mock-orange in well-lit open sunny areas. In shaded areas, shoots tend to be excessively stretched, and the inflorescences will be small in size.
The best time for planting is autumn, from the second half of September to mid-October. Spring planting is also permissible, but depending on the weather conditions of the region, you need to have time to plant the plant before the buds open, so that it adapts faster.


Planting stages.
- Pit preparation. It should correspond to the strength of the root system. The optimal size is 60 X 60 cm. If you plan to plant several bushes, the distance between the pits should be from 0.5 m to 1.5 m, depending on the variety and type of crown. Between dwarf varieties, a distance of 0.7-0.8 m is permissible, for tall species and Lemoine varieties characterized by spreading crowns, it is recommended to leave more than 1.1 m.When planting bushes as a hedge, a distance of 0.5-0.7 m is permissible ...
- Drainage of soil. Place a 15 cm layer of drainage at the bottom of each planting pit. For this, you can use broken brick or crushed stone. Drainage is necessary to subsequently prevent stagnant water. Sprinkle on top with garden soil, you can also mix it with a small amount of humus and sand.
- Landing. After the soil has settled, the root must be lowered into the hole, placing the root collar on a level with the surface of the site and sprinkle with earth, slightly compacting it with your hands.
- Watering the plant. Immediately after planting, the chubushnik seedlings need abundant watering - 2 buckets of water per 1 bush. When the moisture is absorbed and the soil settles in the hole, add a layer of dry earth on top.
- Mulching. A day after planting, it is advisable to mulch the near-trunk circle with sawdust or peat with a layer of 3-5 cm.



If for some reason a plant needs to be transplanted to another place, then the age should be taken into account - the older the bush, the worse it tolerates changes and the harder it is to recover.
It is better to completely transplant the bush before it reaches the age of 7 years. The transplant is carried out at the same time as the initial landing. A young chubushnik tolerates the procedure easily, but in the first year in a new place it may not bloom.
A planting hole for an overgrown bush should be prepared in advance, in about 1.5-2 weeks, so that the soil has time to settle thoroughly. The day before transplanting, the plant must be watered abundantly, and the day before it is advisable to remove dried branches and shorten old shoots. On the scheduled day, the bush is carefully dug up and planted in a new place with careful watering.


Care features
The main care of an ornamental bush is reduced to watering and pruning branches to form a beautiful crown.
Watering
In the first weeks after planting, watering is carried out 1 time in 2 days, but in small volumes so that there is no stagnation of moisture.After 2 weeks, its frequency decreases - it is enough to water each bush with two buckets of water weekly. After moistening, loosen the soil around the trunks and remove weeds.
From top dressing, the chubushnik perceives slurry well, which should be diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 10. A bucket of fertilizer is applied every spring only 1 time. From 3-4 years of age, you can add superphosphate (20-30 g) urea (15 g) and potassium sulfate (20 g) to spring feeding by dissolving them in 10 liters of water.
In summer, garden jasmine should be fed after the end of the flowering period with wood ash, scattering it around the trunks before watering.


Pruning
To obtain lush flowering, the plant must be pruned every year. It is worth considering the fact that only strong shoots of the last year bloom profusely, and a small number of inflorescences bloom on old weakened branches and the bush looks unattractive. That's why it is necessary to do pruning after flowering - carefully cut off the faded branches to new growths that have appeared this season, which are concentrated in the lower part of the shrub. The next season, these young shoots will get stronger and become strong, which will contribute to the formation of lush inflorescences in a year.
Sanitary pruning is best done in the fall, it provides for the elimination of dry and painful branches, as well as drowning the crown of the shoots. In order to rejuvenate the bush, pruning is done in early spring, before bud break. Several main trunks are shortened to 40-50 cm, and the rest are cut to ground level. Places of cuts should be treated with garden varnish or a 7% carbamide solution, and the soil should be mulched with a layer of peat. By the fall, strong young shoots will grow, which by the next summer cottage will refresh the appearance of the bush.
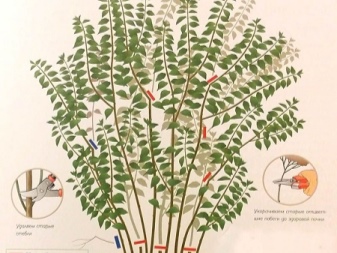

Shelter for the winter
When choosing a variety of chubushnik, it is worth considering its varietal characteristics and winter hardiness. Not all garden jasmines are capable of withstanding our unpredictable winters. Care must be taken when planting classic French varieties. In severe frosts, which are characteristic of the Urals and Siberia, even unpretentious and frost-resistant varieties may freeze.
The following varieties are considered resistant to cold weather: "Snow Avalanche", "Arctic", "Elbrus", "Zhemchug", "Yunnat", "Romashka" and some other varieties from the selection of Vekhov, which do not need additional shelter, except for mulching the trunk circle. Regardless of varietal characteristics, it is recommended to cover seedlings of the first year of planting and shrubs up to 4 years of age for the winter, since the root system of young plants is susceptible to temperature extremes.
When planting spreading varieties of Lemoine in central Russia, it is better to be careful and cover the bushes thoroughly.


Shelter of the chubushnik is carried out in stages.
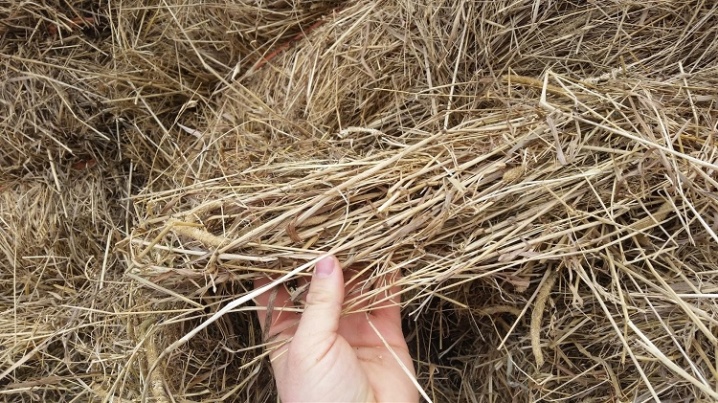
- Mulching. First, the soil around the trunks is mulched with peat, fallen dry leaves, hay or sawdust in a layer of 10-20 cm. A higher layer is contraindicated so that the root collar does not rot. If the height of the shelter is less than the recommended size, then at the onset of low temperatures, the root processes will freeze.

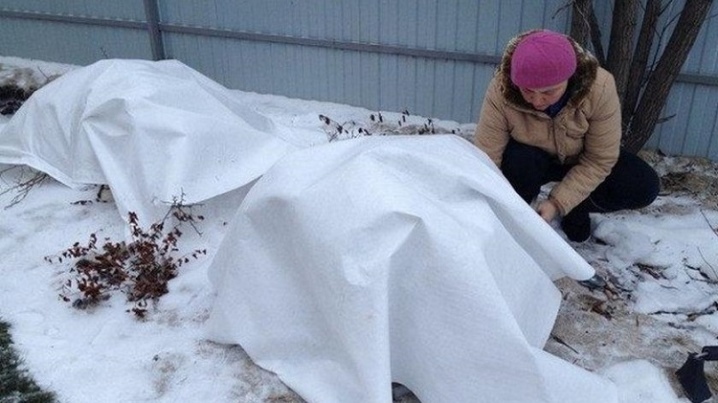
- Shelter of the crown. The branches remaining after pruning are collected in a bunch and carefully, avoiding fractures, pulled together with a rope. On top of the chubushnik bush is covered with non-woven material that allows air to pass through (agrofibre, lutrasil, burlap or light polypropylene bags for household needs are suitable). It is unacceptable to use polyethylene film, since it does not have air permeability, then fungi and mold may appear on the roots and shoots of the plant. In Siberia and the Urals, decorative varieties can be additionally insulated with spruce branches.
With the onset of spring, the growing processes of the chubushnik gradually begin. At first, old branches may seem unviable, but you should not rush to remove them.Sap flow begins with young shoots, the opening of buds and the appearance of leaves on adult branches occurs a little later.

Breeding options
All garden methods are acceptable for propagation of garden jasmine.
- Seminal. Closer to autumn, seed pods are formed on the faded shoots, which can be collected and used for subsequent sowing. It can be done in two ways: before winter in the garden in the open field, followed by shelter, or in spring by seedling methods, placing the seeds in separate small containers. In the first method, the seeds are sown in prepared grooves and covered with sand. At the onset of sub-zero temperatures, the crops are covered with a layer of dry foliage or spruce branches, which are harvested with the onset of spring. In the second case, sowing is carried out in March and the seedlings are grown until June, after which they are transplanted into an open space.
But it should be taken into account that the seeds of hybrid forms do not retain the varietal characteristics of the parent individuals, therefore this method is unsuitable for them.


- Cuttings. Chubushnik can be easily propagated by cuttings of young green shoots. In June, having chosen suitable shoots, they cut the shoots into pieces 5 cm long, but so that they have 2 leaves on them. Prepare the soil by mixing it with a little sand and watered. Then they make small indentations of 0.5-1 cm in it and lower the cuttings, leveling and tamping the soil. At the end of the process, the cuttings are covered with a cut plastic bottle. During the season, shelters are periodically removed for ventilation and watering. The established cuttings are ready for transplanting into open ground in the fall.


- Layers. Reproduction is carried out in late April - early May. To do this, choose one of the strong lower shoots and bend over to the soil. A place for removing the bark is determined on it and removed 1 cm wide. Then the shoot is pinned to the ground with a piece of wire or a metal bracket. The place where the bark is cut is sprinkled with earth, carefully tamped with hands and watered. It is necessary throughout the summer cottage to monitor the condition of the layer, periodically watering and adding soil. By the end of summer, the rooted shoot can be separated from the bush and planted in the chosen place. Also, the transplant can be postponed until next spring.


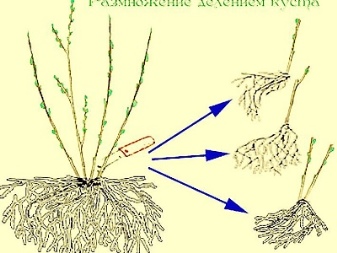
- By dividing the bush. This method is preferable to use for strongly overgrown bushes that grow for a long time in one place. The procedure is carried out in the spring before the leaves appear or in the fall. The bush is watered abundantly, dug up and divided into 2-4 parts, so that each has several roots.
Planting holes are prepared for the plots and transplanted on the same day in order to prevent the roots from drying out.

Diseases and pests
Compliance with the rules of planting and care will contribute to favorable growth and lush flowering of the bushes. Chubushnik is generally resistant to diseases; the causes of problems such as drying out and falling leaves are most often due to insufficient watering or strong exposure to direct sunlight. In this case, the plant needs to be watered more frequently and shade slightly.
Rapid wilting and darkening of flowers indicates too dry air. and the need to spray the leaves and inflorescences with plain water. Tying buds, but the absence of their opening or the appearance of small flowers that do not correspond to the characteristics of the variety, is a signal of a lack of light. If for 4 years after planting the chubushnik still does not bloom, then this is also due to a lack of sunlight, it needs to be transplanted to a more open and lighted place.


In rare cases, garden jasmine can be affected by these diseases.
- Gray rot. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus of the genus Botrytis. It tends to multiply with frequent and prolonged rains or sudden changes in temperature. Gray rot is capable of infecting the entire plant in a short time.Initially, brown spots appear on the leaves and lower shoots. The fight against the disease is reduced to the removal of damaged leaves and shoots, as well as the obligatory spraying of the bush with Bordeaux mixture. When several bushes are located nearby, in order to avoid the spread of gray rot to neighboring plants, it is necessary to spray healthy bushes as a preventive measure.


- Septoria. The causative agent is the Septoria mushroom. The presence of the first signs of the disease is evidenced by the appearance on the upper side of the leaves of small dark brown round spots with a diameter of 2-5 mm. In the future, the fungus completely infects all the leaves, and they begin to dry out and fall off. The spread of the fungus to the shoots leads to the fact that the plant forms fewer inflorescences and fades quickly. Septoria should be dealt with in the same way as with gray rot: remove damaged leaves and treat the bushes with Bordeaux liquid.
You can also spray the plants with Baktofit or Fongilan solutions.


Pests can pose a threat to the chubushnik.
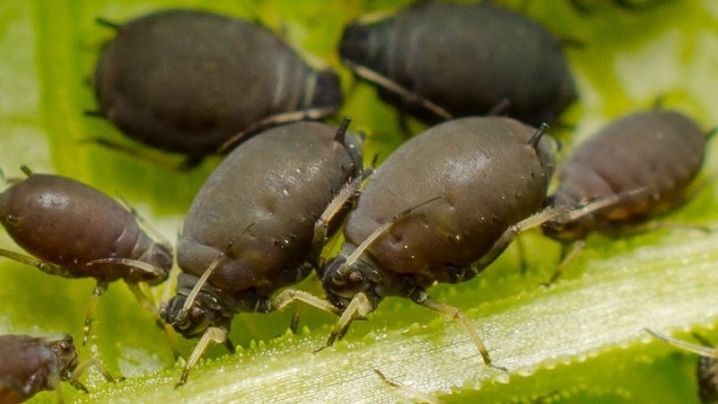
- Bean aphid. These harmful insects can choose plant sap as food. As a result, the leaves suffer - they curl, deform and remain underdeveloped. Spraying with means: "Akarin", "Decis", "Bison", "Iskra" will help to overcome aphids. Also, folk remedies will help in the fight against it: spraying with an infusion of garlic, onions or wormwood.

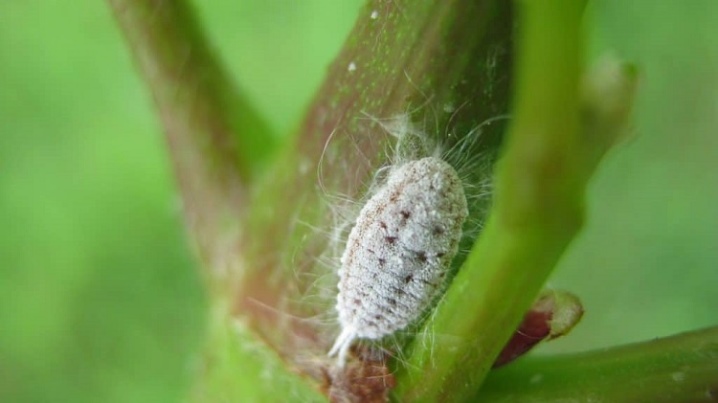
- Mealybug. The presence of these pests can be recognized by the appearance of a white powdery bloom on the foliage. Worms slow down the growth of the shrub by sucking the juices from all parts of the plant. In case of damage, the bushes should be sprayed as soon as possible with any of the drugs: "Aktara", "Calypso" or "Confidor". It is better to carry out the processing in 2 stages, with an interval of 10-14 days.

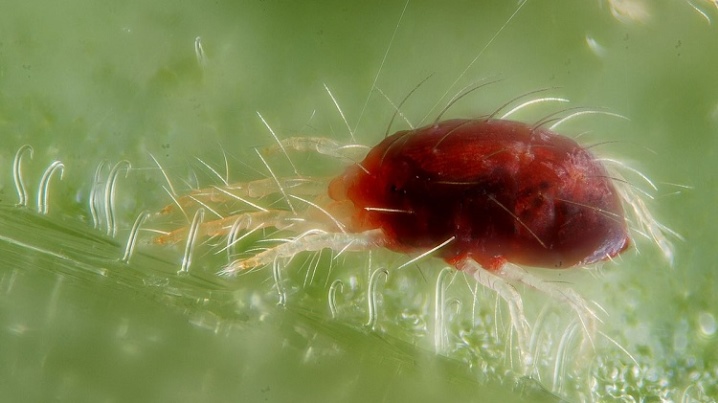
- Spider mite. Insects get to the mock-orange in different ways and attach to the lower part of the leaves, so that they may not be immediately noticed. They harm the plant by feeding on its sap, which causes yellowing and drying of the leaves. With the timely detection of pests, it is enough to spray the bushes with a weak soapy solution, and if there are a large number of them, you need to treat the bushes with 0.3% Keltana emulsion or with Vertimek and Lightning preparations. Spraying is best done 2 times, keeping 7-10 days between them.

- Whiteflies. If the mock-orange is planted near a greenhouse where vegetable crops grow, then there is a risk that it can be attacked by whiteflies, which often feed on vegetable juices, but do not bypass garden crops on their way. They, like spider mites, hide on the underside of the leaves. On the upper side of the leaves, a characteristic shiny plaque appears from their excrement, which leads to the development of sooty fungi, which subsequently lead to the death of the shoots. You can notice the disease on the surface of the leaves - the places of plaque become white, and then the affected leaves turn completely black. To get rid of the whitefly, you can use the method of spraying with soapy water or preparations "Aktara", "Vertimek" or "Confidor".

Use in landscape design
Chubushnik is valued for its high decorativeness, so it can often be found in landscape design. It looks great both in single landings and group compositions. Often, its plantings are used as a hedge or zoning in garden plots and adjacent territories. The spreading crown will serve as good protection from wind and prying eyes. The height of the hedge can be adjusted from 1 to 3 m by trimming the crown as needed. At the dacha, the chubushnik is often planted near recreation areas: near gazebos, benches and ponds.
Dwarf varieties look spectacular when framing flower beds and garden paths. They are also beautiful in flower arrangements. They harmonize well with peonies and hydrangeas. From climbing plants with a mock orange, clematis and climbing roses look advantageous.It goes well with most plants.
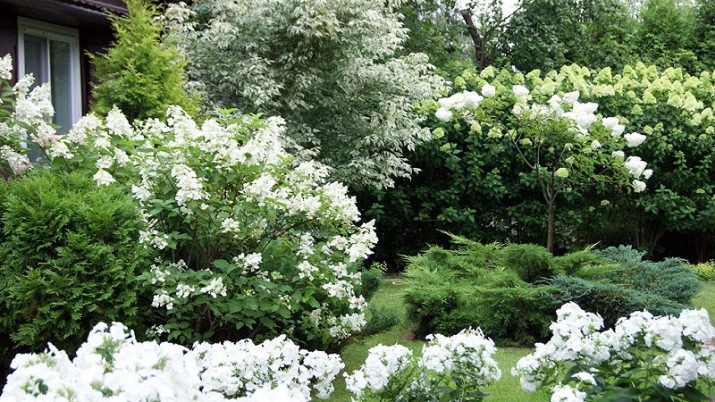






During the flowering period, his snow-white outfit will go well with weigela, thuja, juniper, spirea. It will look great against the background of conifers, which will emphasize its excellent flowering. The bushes get along well next to many deciduous trees, it can be planted next to maple, spruce, rowan and birch.
The herbaceous lawns of the garden can be revitalized with single-planted mock-orange bushes. Medium and tall representatives with a spreading crown or shoots hanging downward look exquisite.
Chubushnik is a plant loved by many, it will certainly decorate any place in the garden area and will delight with its charming flowering and pleasant aroma.






In the next video, you will find all the necessary information about the chubushnik.



































































The comment was sent successfully.