Planting garlic before winter
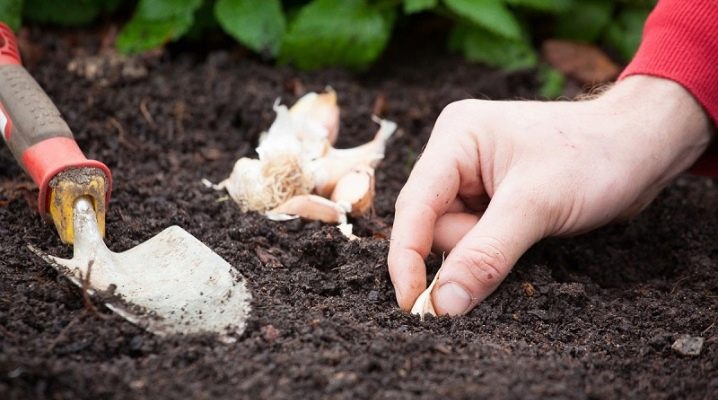

It is better to think about growing garlic in the fall. And planting it before winter is a good idea, promising a considerable harvest of a bulbous plant. But planting is a multi-stage process: you need to choose the right timing, prepare the land, take into account the scheme, and not make a mistake with subsequent care.


Optimal terms for different regions
Garlic is considered a cold-resistant plant, but it is still better to plant it 3-4 weeks before the first real cold weather. The cloves must grow roots, adapt, but not yet have time to germinate - this is how you need to guess with planting. In this form, the bulbous will survive the winter calmly, and in the spring they will grow.
We will find out when to plant by region.
- In the middle lane, the optimal period for planting comes in the 20th of September and lasts until mid-October. And it is better to choose those days when the heat is no longer predicted, but there may be night frosts. But not every year such days coincide on the calendar, therefore, the date of planting of garlic can change from year to year.
- In the Moscow region, the landing dates practically coincide with the dates that are typical for the middle lane.
- In the Urals, garlic is planted predictably earlier, in Siberia they also think about it at the beginning of the first autumn month.
- In the southern regions, you can safely plant garlic in open ground in November - in the south this month the winter is not yet so severe that the cloves die in the freezing soil.
The optimum soil temperature for planting garlic is + 10-12 degrees (even if it is slightly lower). But garlic is definitely not planted in the frozen ground.
Best predecessors
Garden crops should alternate in time and space. This is a special, unshakable condition for obtaining a high-quality harvest of any plant on the site. The best plants of the previous season for winter garlic would be legumes, cucumbers, squash and melons. That is, you can definitely plant garlic after pumpkin, peas, beans and squash. A garden bed where white cabbage previously grew, as well as beets and peppers, are also suitable. But unsuccessful predecessors can be called radishes, carrots, potatoes, onions, herbs and, finally, garlic itself. If the latter once grew on the site of the intended landing, then the difference between the landings should be at least 3 years, and preferably 4 or more.
It is also important to say about the neighborhood: if the crops are correct, they will only contribute to a better harvest of garlic, while bad ones will inhibit the growth of the latter. And garlic itself is considered a very beneficial neighbor for many plants: thanks to its fungicidal and bactericidal properties, it will protect other crops from pests. It is good if horseradish or calendula grows next to the garlic, as well as tomatoes or chicory. Garlic will prevent the appearance of pests on strawberries, carrots, beets, cucumbers, tomatoes.
Important! Garlic itself is an excellent natural repeller for carrot flies, bears, as well as aphids, spider mites, Colorado potato beetles, whiteflies. It also makes the causative agents of late blight and rust more harmless.



Preparation
You need to prepare both the culture itself for planting, and the place.
Seed material
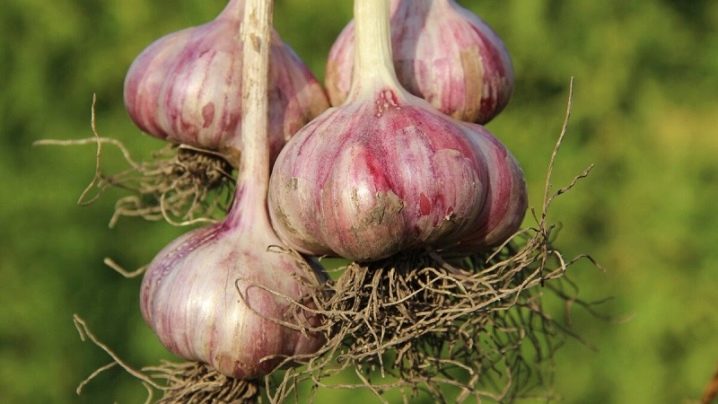
Garlic of exclusively winter varieties is suitable for planting. He (unlike, for example, spring garlic) will have large homogeneous cloves, located in one row around the arrow. It is an arrowhead garlic that produces a bright green tube with buds.And on it small bulbs are already ripening, they can also be planted in the garden in the fall. The variety of garlic must be suitable for the climate. The varieties bred in Ukraine, for example, are considered very successful: "Ukrainian White", "Lyubasha", "Spas", "Violet Kharkivsky". But Skif, Yubileiny 07, Nadezhny, Gribovsky, Messidor (Russia and the Netherlands) will also be good. The taste of the presented varieties is expressive, resistance to diseases is high, keeping quality is good.
And it is not difficult to prepare the selected variety of garlic: sort out, reject sick, very small, low-quality cloves with superficial injuries. Each clove must be separated from the others, just do it delicately so that the outer shell and bottom are injured. The latter can be cleaned to help the material take root - just be careful not to damage the scales. And now selected healthy specimens need to be soaked in compositions for a couple of hours, and in several at once.
What are these solutions:
- ash (0.4 kg of ash per 2 liters of hot water, half an hour soaking is enough);
- manganese (it should be dark pink);
- saline (3 tablespoons per 5 liters of warm water);
- copper sulfate (1 teaspoon in 1 bucket of water);
- Fitosporina-M.
All this is done so that the selected material is not only viable, but also decontaminated, highly resistant, ready for wintering. Then it must be thoroughly dried.


A place
This crop prefers sunlight, so it should only be planted in an open area that is well lit throughout the day. In a shaded area, you cannot get a proper harvest. From the north, the place should be sheltered from winds and drafts. It is great if it is a small hill, for example, a warm bed, or maybe a gentle hill. But if you plant garlic in a lowland, then heavy rainfall and spring snow melting will lead to the fact that water will collect there, and this is fraught with rotting of the culture.
Wetlands for planting should also be avoided, as well as waterlogged areas of the garden. With high groundwater levels, the harvest of garlic will also not be optimal. Attention! If manure was introduced into the ground this season, you cannot plant garlic there. A plant in such a soil will actively begin to grow tops, which makes the heads of garlic too loose and small, and also completely unstable against fungi.
What should be the ideal soil for garlic:
- loose;
- with neutral acidity (pH 6.5–7);
- fertile;
- breathable;
- permeable.
Garlic will grow best on light loam. Where the soil is heavy and clayey, it will not develop well. Acidic and alkaline soils will not work for garlic either. It is necessary to prepare the ground for planting at least a month before the event itself. This time is enough for the soil to settle naturally. It is better if the bed is located from north to south.


Here is a preparation plan.
- Remove the site - all rubbish, stones, weeds directly from the roots must be removed from the area.
- Apply fertilizer - spread the fertilizer evenly over the entire surface. It is better if it is organic together with mineral compositions, that is, tandem. You can fertilize the ground with humus at the rate of 1 bucket per square. You can add 200 g of wood ash per square. Or 20 g of superphosphate per the same square meter. You can sprinkle potassium sulfate, also 20 g. And this potash fertilizer is almost the best: it contains sulfur, and if it is deficient, garlic will not grow normally. Phosphorus and potassium compounds are, in principle, very important for garlic: they increase its cold resistance, and the heads of the plant are saturated with sugars.
- Optimize the soil - for example, if it is heavy and clayey, you will have to add sand and low peat to it, bucket per square. If both are impossible, sand is a priority. If the soil is light and sandy, add humus or compost and low-lying peat. If it is acidic, wood ash is introduced into the soil, you can replace it with dolomite flour (200 g per square).If the soil is alkaline, high sour peat will do, 1 bucket per square.
- Dig it up - about a shovel bayonet, 30 centimeters.
- Loosen with a rake - after fertilization, this must be done.
- To form a bed is better if it is high: 25 cm high and 1 m wide. If the garden is in a lowland, a high bed is required.
- Water - moisten the earth from a watering can. If while the earth is settling down, it does not rain enough, it is better to organize independent watering.
- Protecting the soil will be akin to preventing fungal diseases. The soil is watered with a fungicide or a solution of copper sulfate, 1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water.
Well, the material for sowing is ready, the garden bed too, you can start.


Is it possible to plant spring garlic?
You should not do this, since spring varieties are intended specifically for spring planting. They tolerate frost much worse. There are options when such an experiment will be successful, but they are quite troublesome. At the very least, you will have to use a straw shelter, other organic matter.
How to distinguish spring garlic from winter garlic: its head does not have a stem, but consists of two and a half dozen small cloves, which are arranged in several rows. The taste of such garlic is much milder; in winter it is more pungent and pungent. But keeping quality is perhaps better - it is safely stored all winter until spring (sometimes even longer).

Landing rules and scheme
This is always a clear algorithm, step by step and rather specific - any discrepancies are already fraught with negative features of the development and growth of the plant. We will learn how to properly plant garlic before winter.
- Make landing pits, grooves. You can use a small spatula if that's more convenient. The distance between the pits should be 10 cm, and the row spacing should be at least 20 cm. But the rows should be strictly parallel. If you are not sure that everything will work out smoothly, it is better to pull the rope for correct orientation. The optimum depth of the planting fossa is 8-9 cm. If you do not want to make fossa, let there be grooves.
- Plant the teeth into the formed pits or grooves. Landing should be exclusively bottom down. It is not necessary to press the cloves into the ground, because then the earth under them will be compacted, and their rooting will already be problematic. A distance of 10 cm must be maintained between the teeth. The holes must be made with the same gap.
- Cover the cloves with earth. You can give a lift to fertile soil specially for this.
- Water the soil. It can be ordinary water, or in addition to it, "Fitosporin-M", which will be an excellent prevention of fungal diseases.
- Mulch the garden bed. Peat, fallen leaves, and humus are suitable for this. The mulch layer is quite high - 10 cm.
There is nothing complicated, obviously, in the landing. And instead of cloves, by the way, you can use the bulbs already mentioned above, which are formed on the arrows of the culture. Strong and large cloves will grow from them in the next season, which will also become a good planting material. In addition, there is no hassle with bulbs in terms of correcting the timing, everything is exactly the same as with a traditional planting.
But you don't need to make holes in the garden - you will need grooves. And the bulbs are planted to a depth of 2 cm.


Do I need to water after planting?
Yes, this is a mandatory item for the entire operation. And if there is no rainfall within a week and a half after planting the garlic, then you will have to organize watering on your own a couple of times. This will help the garlic take root faster. But the main features of garlic care are not watering, but frost protection. It is for this that the soil is mulched, a warm natural pillow is created. But if it happens in the southern region, such a measure can be safely abandoned.
And when the first frosts come, in addition to mulch, you can cover the garden with straw or spruce branches. In the spring, as soon as the temperature becomes positive, the covering material must be removed immediately so that last year's (it turns out like this) garlic does not squeeze. In principle, this is where all the pre-spring care is over. Everything else awaits garlic in the spring. After the earth dries up, it will be watered, loosened, weeds will be weeded out. And then everything follows the traditional scheme of spring garden work.















The comment was sent successfully.