Features of attic floor insulation

The roof protects various buildings and structures from precipitation and wind. An attic under the roof serves as the boundary between the warm air from the house and the cold environment. To reduce the outflow of heat from the heated room to the outside, thermal insulation of the attic space is used.
Why insulate?
For comfortable living conditions in winter, houses are heated, consuming a huge amount of heat carriers. The cost of heating only increases every year. In order to save costs and reduce heat loss, energy-saving double-glazed windows are installed and the walls, floor and ceiling are insulated with heat-insulating materials.
More than a third of the heat from the house comes out through the roofas the warm air rises upward. Through the non-insulated ceiling, warm streams leave the living quarters and rush into the attic, where, in contact with the roof covering, they form condensation on the floor beams and the rafter system. High humidity leads to deterioration of the material and the growth of fungi, reducing the durability of the roof structure.

If the attic space is actively used or serves as an attic, then the roof itself is insulated. When the attic is not in use, the attic floor is insulated. Installation is carried out on the beams of a cold attic.
In this case, you can achieve the multifunctionality of the insulation:
- protection from hot hot air in the attic during the summer period allows the living space to remain cool;
- sound absorption function: noise from howling wind and precipitation is reduced;
- retention of warm air indoors during the heating season is achieved through the creation of an insulating barrier.


The use of various types of insulation will reduce the level of heat loss by 20%, which will extend the life of the roof without repairing and replacing wooden elements.
Types of attic floors
Depending on the location, the floors are divided into interfloor, attic, basement or basement. To create the ceiling and floor in buildings, load-bearing elements are constructed, consisting of beams and slabs. Reinforced concrete slabs, steel and wooden beams are used as attic floors. When erecting brick and panel high-rise buildings, reinforced concrete floors are used. Beam flooring is used in low-rise construction. On wooden beams there is a beam, logs and boards of a large section, stacked on load-bearing walls.



Each type of floor, wood or concrete, has its own advantages and disadvantages. Reinforced concrete slabs are durable and fire-resistant, but difficult to install and require increased wall strength during construction. Wooden floors have a lower load on load-bearing walls, are suitable for construction with any kind of building materials, they are mounted without the involvement of construction equipment. The disadvantage of wood is its fire hazard, therefore, wooden structures need additional processing with flame retardant impregnations.
Whatever material the attic floor is made of, it is necessary to carry out thermal insulation work, since the thermal conductivity of concrete and wood is high. The insulation scheme consists of a vapor barrier, the insulation material itself and waterproofing, forming a layered cake that helps to perform a protective function for the roof and heated rooms.



Attic floors, which serve for a multi-level division of premises, must meet certain characteristics:
- Strength. Overlappings must withstand heavy loads.
- Fire resistance. The fire resistance limit is regulated by technical requirements. It is different for all materials: concrete withstands 1 hour, and untreated wood - 5 minutes.
Variety of materials
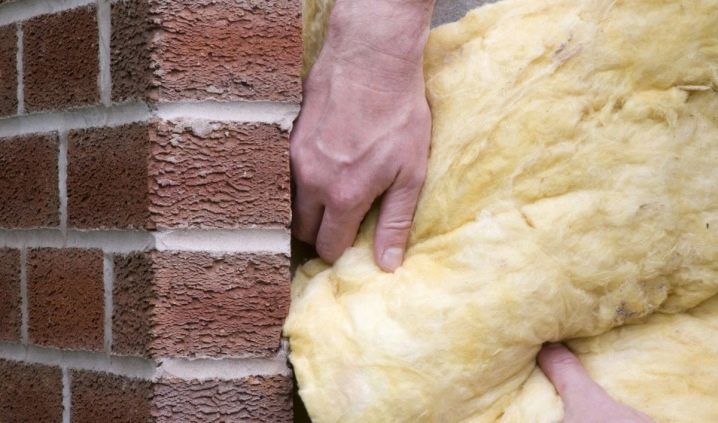
Before choosing an insulation material, you need to understand the variety of heat insulators produced, taking into account their basic properties and characteristics. By the type of installation, thermal insulation products are divided into: roll, bulk and slab.



Roll
Mineral wool is produced in the form of soft rolls. This fibrous material comes in three varieties - rock wool, glass wool and slag wool. For raw materials in the production of stone wool, rock alloys are used. Glass wool is produced from sand, dolomite and glass waste. For slag wool, metallurgy waste is used - slag. Attics are insulated with basalt wool and glass wool.


Mineral wool has the following advantages:
- do not burn, melt at high temperatures;
- rodents do not start;
- available;
- convenient for laying;
- are lightweight.

The negative point when using cotton wool is its hygroscopicity and low environmental friendliness. Cotton wool absorbs water well, reducing its thermal insulation properties. When laying glass wool, you must follow safety rules and use personal protective equipment. The environmental friendliness of the material is low, since phenol-formaldehydes, which are harmful to human health, are used in the production of mineral wool.
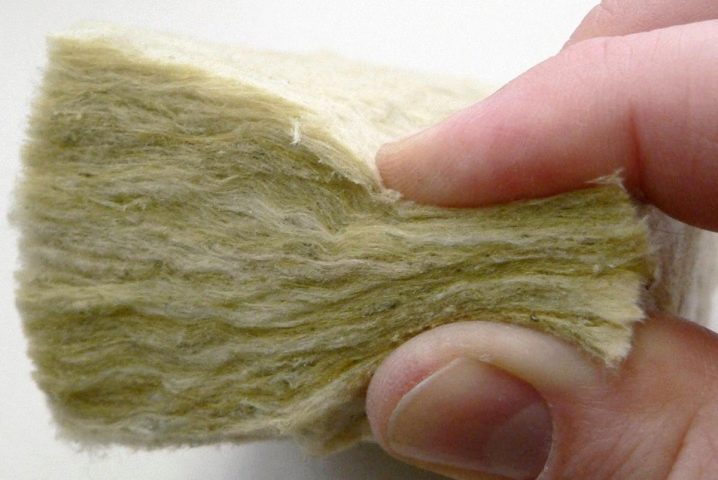

So that moisture does not penetrate into the cotton wool, it is necessary to strictly observe the installation technology with vapor barrier films and a waterproofing layer, leaving gaps for ventilation. With proper insulation with mineral wool and compliance with all technical requirements, you can achieve an economical and high-quality thermal insulation layer.
Rolled polyethylene foam, or izolon, is used for complex thermal insulation and as a hydro-vapor insulator. It is a foamed polyethylene with a thickness of 0.3-2.5 cm with a one-sided foil layer. Izolon has heat-dissipating, fire-resistant and hydrophobic properties.

Bulk
In the form of fractions of different sizes, the following types of bulk insulation are used:
- sawdust;
- straw;
- slag;
- vermiculite;
- expanded clay;
- foam glass;
- ecowool;
- polyurethane foam.



Houses were insulated with sawdust for a long time, until modern heaters were launched into mass production. The main advantages of sawdust are high environmental friendliness caused by the naturalness of raw materials, low weight and availability of material for a penny cost. The main disadvantage of sawdust is the flammability of the material. Also, when absorbing moisture, sawdust can become moldy. The sawdust layer is easily damaged by mice.


Straw insulation is a traditional rustic method of keeping your home warm. It is lightweight and affordable material. Due to the high thermal conductivity, the layer of straw should be large - up to half a meter.
The negative sides are obvious:
- straw serves as a good habitat for rodents;
- lights up quickly and burns well;
- gets wet and rots;
- cakes, reducing the layer of insulation.

Slag is a raw material obtained from metallurgical waste. Slag pumice and blast furnace slag have long been used as a cheap backfill insulator. It is non-flammable, durable and cheap material.
As a result of the swelling of mica, vermiculite is formed - a natural, lightweight, durable insulation. The thermal conductivity coefficient is comparable to that of mineral wool. Its absorbent qualities make it possible not to install water protection. Vermiculite is not affected by fire.

Expanded clay is a light clay granules. Natural mineral material is environmentally friendly, durable and non-combustible. Among the advantages of warming with expanded clay, it is worth noting the ease of installation - the granules are simply scattered in the attic with the required layer thickness.In order to achieve reliable thermal protection in different regions, expanded clay is laid with a thickness of 20-40 cm. A large layer of expanded clay is heavy, therefore, the possibility of loading on wooden floors is taken into account.
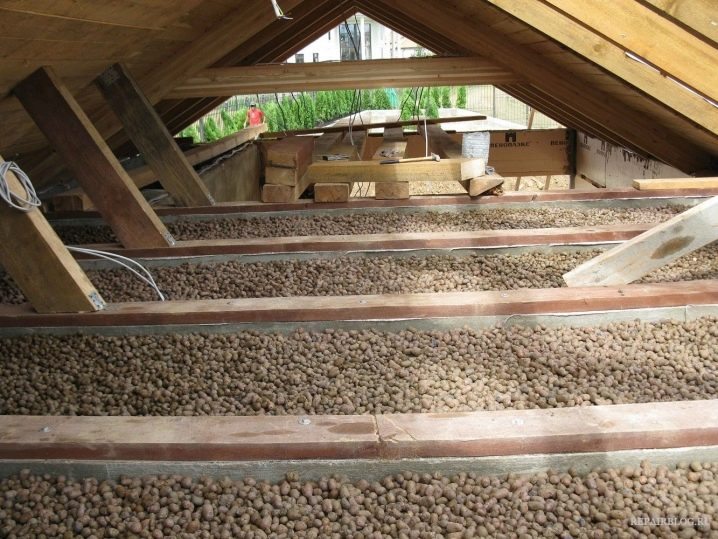

Foam glass belongs to the filling low-heat insulation. In production, the waste of the glass industry is foamed, obtaining a high-quality insulator. Foam glass is characterized by moisture resistance, strength, environmental friendliness and durability. The high cost of foam glass is a limitation for widespread use.


Ecowool is a modern cellulose insulation.
Pros of using ecowool:
- natural antiallergenic composition;
- flame retardants give fire resistance;
- does not lose thermal conductivity when wet.
Polyurethane foam belongs to the category of bulk insulation. Polyurethane foam is a liquid plastic that does not need a vapor barrier and waterproofing. It has the lowest coefficient of thermal conductivity, imparting high heat-insulating properties to a small thickness of insulation. The coating is applied in a continuous layer without seams, covering all the cracks. Water-repellent qualities prevent fungi and bacteria from multiplying in the attic space. The solidification strength does not give rodents a chance to start. The composition contains substances that give polyurethane fire resistance.


Polyurethane has only one drawback - the high price. This is due to the use of professional compression equipment for spraying foam. We have to resort to the help of specialized companies.
In slabs
Plates and mats of different sizes are produced:
- Styrofoam;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- mineral wool;
- reed;
- seaweed.



Styrofoam boards are composed of polystyrene granules.
Polyfoam has the following features:
- low thermal conductivity makes it an effective heat insulator;
- very lightweight, easy to install;
- highly flammable, emits toxic substances when the temperature rises;
- waterproof;
- not resistant to mechanical stress;
- the popularity of foam is due to its cheapness.


Extruded polystyrene foam is the same foam produced by extrusion. This allows you to preserve all the advantages of foam, acquiring an increased density that can withstand heavy loads. In the expanded polystyrene plates, grooves are provided, which facilitates installation without gaps and creates a continuous coating.
One of the options for the production of mineral wool is slabs, often one-sided coated with reflective aluminum foil. Foil acts as a vapor barrier and reflects heat from the house. The miniplate is convenient to use for self-assembly.


Reed mats and algal ladders are produced in the form of compressed briquettes. Natural, natural, light materials - reeds and algae - are used as raw materials. High ecological and vapor-permeable properties make them suitable for wooden buildings. The problem of fire safety is helped by the processing of raw materials with fire-resistant compounds.

How to choose?
When choosing thermal insulation materials, the type of overlap and the features of the insulation are taken into account. The characteristic qualities of a thermal insulator become a decisive criterion.
A number of factors are taken into account:
- Thermal conductivity level. The best insulation has a low thermal conductivity with a small layer thickness.
- The weight. The load on the floors depends on the weight.
- Fire resistance and frost resistance. The material must not catch fire.
- Ease of installation.
- Durability. The insulation must be durable, not collapsing under the influence of adverse conditions.
- Ecological cleanliness. The more natural the composition of the material, the safer it is for human health.
- Price. In private construction, price often becomes the main criterion.

Taking into account all the features of the material, you can choose the right insulation for your home.Mineral wool insulation is often the best choice. Compliance with the installation instructions will allow you to perform high-quality thermal insulation work.
Calculation of the thickness of the insulation
In accordance with the SNiP requirements for building insulating materials, the thickness of the insulation depends on the type of thermal insulation, the duration of heating and the average temperature in winter in a particular region.

The thickness of the insulation is calculated based on the thermal conductivity coefficient of a particular material. This indicator is indicated on the packaging of the purchased insulation. Moreover, the upper limit of the norm is selected for a humid environment.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity of material | Insulation thickness |
0,03 | 12 cm |
0,04 | 16 cm |
0,05 | 19 cm |
0,06 | 24 cm |
0,07 | 29 cm |
Features of work
The type of overlap determines the peculiarity of the thermal insulation work. Thermal insulation installation methods differ depending on the type of insulation.
On reinforced concrete slabs
It is easy to insulate an attic with a reinforced concrete slab overlap, since the attic floor is flat. As a heater, rolls of mineral wool, a slab version and any bulk varieties are suitable. The weight of the material can be disregarded, since reinforced concrete slabs are able to withstand heavy loads.
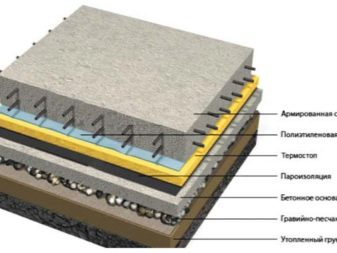
You can install the insulation by scattering the material over the surface. In this case, expanded clay, foam glass, vermiculite and slag are suitable. The attic space is preliminarily covered with a vapor barrier film. Then scatter the granules on the calculated layer. The top layer can be a cement screed. If the attic is used as an attic, then a concrete floor is supposed to be installed.


The second method of laying involves the use of lathing. Wooden blocks are located at the distance of the width of the roll or slab of the insulation used. The size of the timber should correspond to the thickness of the insulation layer. The correct arrangement of the attic space involves the flooring of the subfloor on the lathing joists. If foam or foam slabs were used, then a concrete screed is made. When using rolls of mineral wool, plywood or plank floor is laid.
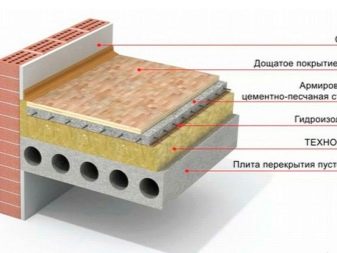
On wooden beams
In private houses, it is advisable to make a joist floor. On the underside of the beams, a hemmed ceiling is made between the first floor. From the side of the attic, beams remain, between which insulation is placed. For a wooden house, the best insulation will be ecowool, basalt wool, reed mats, foam glass and polyurethane foam.

A vapor barrier is laid on top of the beams with a continuous cover. Insulation is next laid. If the height of the beams is not enough for the thickness of the material, then they are built up with slats. A prerequisite is the insulation of the beams themselves. This will help prevent freezing of the structure. A waterproofing film is laid on the insulation. A rough floor of wood-based panels or boards is laid on the logs.


Useful Tips
The thickness of the roll and plate heat insulator is selected taking into account the installation in two or three layers. This will help avoid cold bridges. Each subsequent layer is laid with overlapping joints of the previous one. Multi-layer mounting reduces heat dissipation.
When laying insulation boards, it is necessary to achieve solidity. To do this, the material is accurately cut off, the location of the slats is calculated, all seams and joints between the minelite and the crate are sealed.
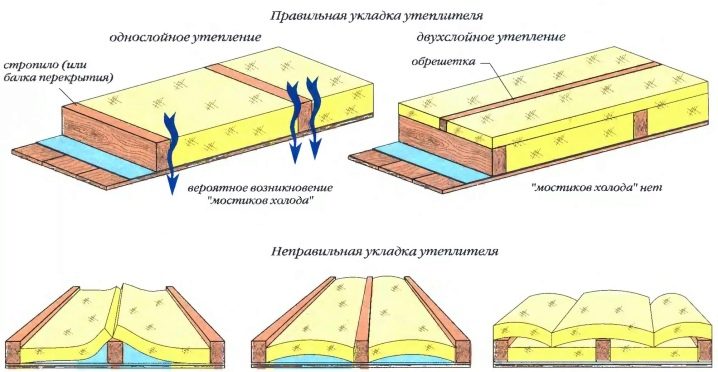
When deciding to insulate the attic on your own, you must not forget about waterproofing and a vapor barrier, as well as use materials that absorb water. This will lead to a decrease in insulation characteristics and rapid deterioration of the insulation. The shelf life will decrease with improper installation, it will be necessary to replace the heat-insulating layer, which will entail unnecessary expenses.
During the installation of the vapor barrier, it must be checked that the vapor barrier film or membrane is installed on the correct side. When using insulation with a foil layer, remember that the reflective side is laid down.Foil reduces heat loss.

For the features of the attic floor insulation, see the following video.













The comment was sent successfully.