Cement: types and features of production

Cement is indispensable for construction work. It is literally a basic element for many types of repairs. It is able to take on the function of other materials, while it is difficult to find a worthy alternative to cement itself. This material is made universal by the types and features of the production of cement mixtures, thought out in terms of the component composition.

What it is?
Cement is a mixture of limestone rock with the addition of minerals and synthetic substances, which are called plasticizers, which has repeatedly passed through a crusher and a firing procedure at temperatures above 1500 degrees. They are necessary to increase the strength, and also slow down the process of moisture loss from the slurry.

A mixture of minerals is often confused with another building material - concrete.
There is a fundamental difference between them on several points:
- Cement differs from concrete in that it can already be used for repair work by adding water. Concrete mixtures consist of 4 components, one of which is cement.
- In the cementitious mixtures there are no components of the coarse fraction, and sand, crushed stone, gravel, expanded clay are added to the concrete.
- Due to the absence of large fillers, cement sets faster and turns into a monolithic joint under any conditions.
- Various applications. Although both materials are used in construction, they serve different purposes. Foundations and elements of load-bearing structures are formed from concrete. Cement often acts as a masonry and leveling material.
- Technical characteristics and composition are regulated by different GOST.

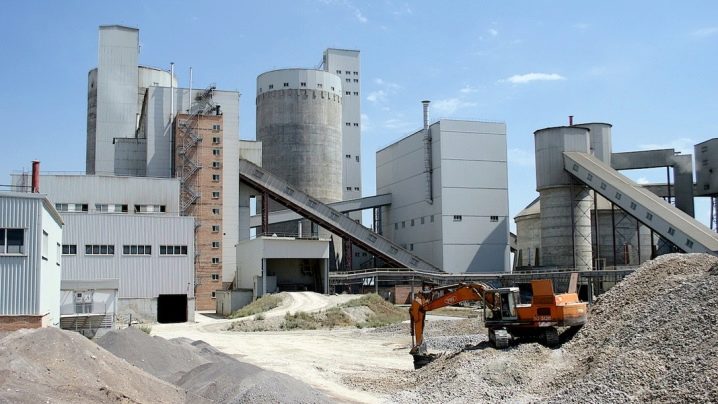
Manufacturing and packaging
Production and packaging of cement is a long process that requires high-tech equipment and control. Its origin lies in limestone quarries. Two types of limestone are used. The first is located close to the surface, at a depth of several tens of centimeters. This is the so-called "second-rate" limestone, but it already contains iron, aluminum oxide, silicon and other minerals. They give unique properties to cement mixtures.




The second layer is located at a depth of several meters. It is cleaner, almost free of other minerals (with the exception of calcium carbonate), and is considered top-notch.
Both types are used in production, both pure and combined in different proportions with each other and additional components. The ratio of the first-class to the second-class substance, as well as the type and quantity of additives, determine the brand and cost of the cement. Limestone rock in its natural state is a solid monolith. It is broken into small fragments with explosives, laying them in layers of limestone in the quarry, and then collected by loaders. The size of the fragments can be of different sizes, from small pebbles to an entire building block. In this form, they go to cement plants.


At the plant, the raw materials are primarily sent to the “primary crusher”. In it, large fragments are crushed to the size of a tennis ball. In the process of grinding large fragments, water enters the crusher so that dust does not rise, and together with it, the mass of limestone is not lost. The crushed stones are conveyed to the secondary crusher via a conveyor belt. In it, the rock is "rubbed" to fragments the size of crushed stone. The first and second grades are crushed separately.

Then a raw mix is formed for cement of different grades. After mixing, the finished "heaps" are sent to the roller mill. In the process of grinding limestone, additives are used: powdered magnesium, silicon and aluminum oxide, if they are contained in the limestone rock in insufficient quantities. The mill grinds the rock to stone flour. This stone meal then goes to the preheater. In less than a minute, it heats up from 80 degrees Celsius to 800.

This procedure is necessary in order for all the components of the composition to move and acquire the ability to solidify to a solid monolith when combined with water and in contact with air.
Unnecessary components are separated in the heater, lime remains suitable for construction. She goes to the cylindrical firebox. The bottom of the firebox heats up to 1700 degrees. The mass inside the kiln is melted into small "glass" balls called clinkers. When leaving the oven, they are quickly cooled with a flow of cold air to 70-80 degrees. Fast is key. If it cools slowly, the mixture is of poor quality. This is the raw material for quality cement.

The cooled "glass balls" go through the last stage of processing - the final crushing. In fact, this is the grinding of hard clinkers between steel balls of different diameters, of which there are about one and a half tons in one crusher. When grinding clinkers, lumpy gypsum is added to the stone flour. It slows down the hardening process of the slurry. The powder mixture leaving the crusher is cement. Some manufacturers add plasticizers to it to increase strength.

The finished powder mixture goes through the packaging procedure. For this, specialized machines with a dispenser are used.
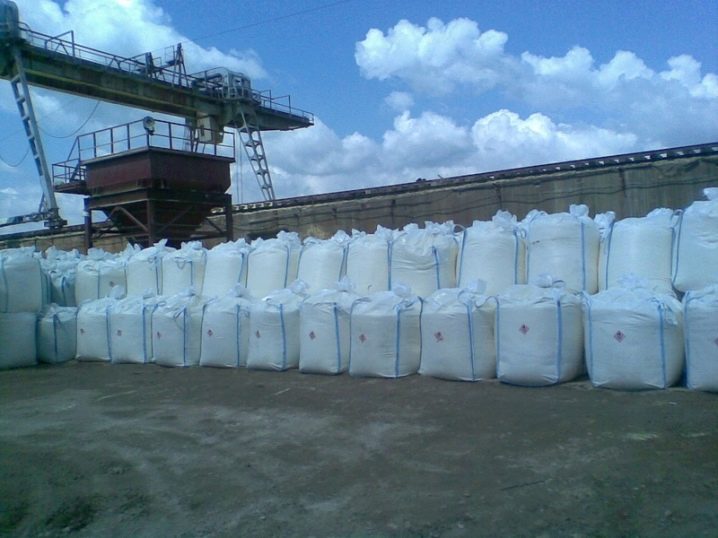
Cement bags rarely have a small volume of 10-15 kg. Usually the minimum weight is 25 kilograms, and the most running one is 50 kg. Bags of 50 kilograms are called slimbegs. Sometimes there are non-standard volumes of 30, 35, 42, 46 kg. The packing bag consists of several layers (2 to 5) of craft paper. Also common are packaging containers for construction on an industrial scale - big bags. These are soft containers made of polypropylene or nylon of high strength with or without stiffening ribs and linings. The weight of cement in big bags is from 300 to 3000 kg.
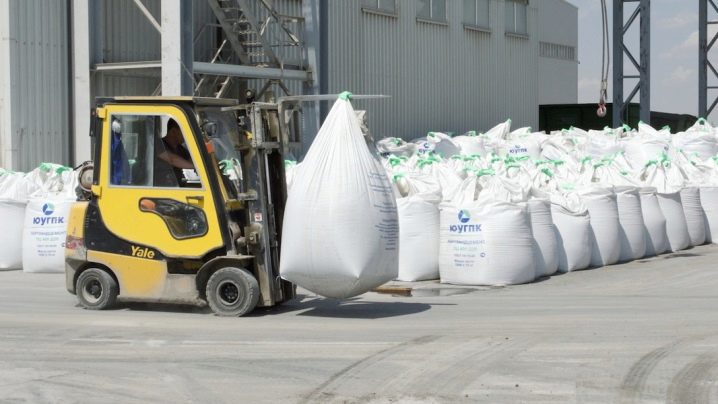

Big bags have a number of advantages over conventional packaging:
- wholesale purchase of cement reduces the price for 1 kg of the mixture;
- soft containers have slings for loading;
- They are heavy-duty, reusable and recyclable;
- polypropylene shell extends the shelf life, since it protects the cement from the negative effects of the external environment;
- containers can be completed with liners for heat resistance, anti-static, waterproof, UV protection.

Varieties
The definition of "gray powdery substance" is not entirely correct for cement. It also comes in a different color. Color is given to it by various additives that affect its technical characteristics, and colors. In addition to shades, the material also differs in other criteria. The classification is made according to the component composition, purpose, appearance of the powder and solution, and the country of origin.
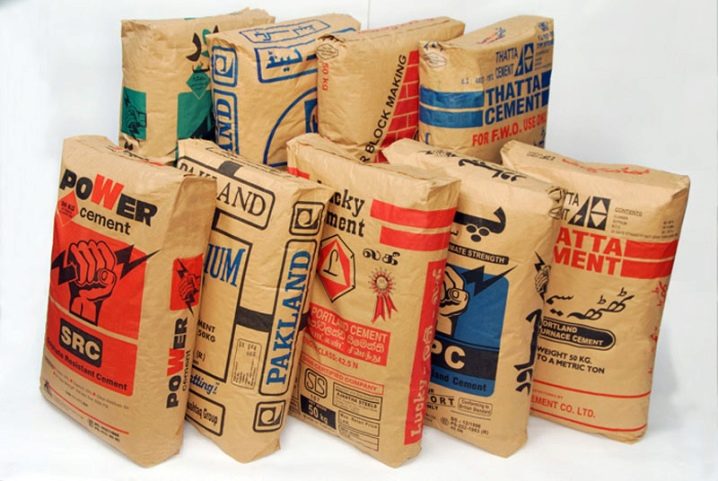

In terms of composition and properties, one can distinguish:
- Sulfate-resistant mixtures. They are obtained by grinding clinkers, but without adding mineral components. Also, in the manufacture of such cement, 90-92% of calcium aluminates are removed from the composition. They are added to concrete when a substance is needed that will be evenly distributed in the pores of the concrete without causing internal resistance.




- Portland cement. On the contrary, a large amount of powdered minerals is introduced into it. The result is a fast-hardening, durable layer. The strength of the layer is normalized not only for the "matured" substance on the fourth week, but also on the third day.This contributes to the fact that the cement, when hardened, acquires greater strength and resistance to damage. It does not crack and withstands various mechanical shocks and loads. Such mixtures are added to the composition of concrete in the manufacture of reinforced concrete structures. They are also used in home construction.




- With PAD additives. These include synthetic substances and plasticizers, the amount of which can reach three-tenths of the total mass. They are necessary for the absorption of cement sand, that is, they envelop each cement grain with a film that does not allow the substance to adhere to each other. As a result, both the cement mortar itself and its connection with concrete acquire elasticity and are easier to fit, leveled on the working surface.




- Hydrosulfoaluminate. This fast drying cement is often referred to as expandable because of its ability to expand in volume during the "setting" process. This happens due to the fact that calcium sulfatoaluminates are added to the dry mixture, which, as a result of reaction with water, increase in volume by one and a half or 2.5 times (relative to the original solid). When dry, the mass increases by 2%. Despite this "yeast" effect, it has a good density.
- Gypsum or stress cement. The same as self-expanding, only the component composition in it changes. What it is, it is clear from the name of the material.




It is optimal to work with such cement in wet conditions. So it expands more efficiently and gives the maximum effect. Expanding types of cement are used to level the joints between elements of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures. It creates good waterproofing, which is especially important in the construction of hydraulic structures and pressure pipes.
- Aluminous. The name of this type of cement speaks. It is obtained from limestone, which is laid close to clay deposits in the soil. In the process of roasting and grinding, a large amount of limestone rock with a proportion of alumina is added to the mixture. It, in turn, contains aluminates, which convert the cement into a fast-setting, viscous substance with hydraulic properties. Such a product is unique in its technical characteristics. It is used in rare cases when it is necessary to carry out urgent repair work in conditions of high humidity, precipitation, sub-zero temperatures. Alumina cement is not capricious in this respect and is equally effective under different conditions. This leads to its high cost.




- Hydrophobic. It is obtained by grinding mineral clinkers with various additives. Suitable water-repellent substances, such as asidol (extracted from the processing of kerosene, solar and oily waste of oil production with the addition of sulfuric acid). The use of soda soaps and mineral oils, oleic acid, and synthetic fatty acids is widespread.

The advantages of hydrophobic cement are its high frost resistance and water resistance, as well as its ability to be stored under any conditions without losing its properties. It is less durable than other types, so it is not suitable for supporting concrete structures. It is used to produce lightweight porous concrete blocks.
- Shrink-resistant. It is a mixture of three components: gypsum, lime and alumina limestone. Gypsum is used semi-aqueous, lime is slaked. During the drying process, it does not expand and does not shrink. They are used in the construction of building foundations, tunnel tracks.
- Magnesian. Received in a way that is radically different from the production of conventional cement. These are compounds of magnesium oxide and an aqueous solution of magnesium chloride. Such a mixture is heated only to 800 degrees Celsius, and then, when it solidifies into a whole mass of white color, it is crushed.Such cement is similar in its properties to gypsum and is used more for interior decoration, floor leveling and for architectural purposes.

- Pozzolanic. For its production, active mineral substances (burnt clay, fuel ash) are added to the stone flour from clinkers. These materials are readily available and cheap, and their share in the composition of cement is significant, therefore the cost of the total mass is lower than for "pure" cement. In solid form, it is resistant to water washout and leaching. The area of application is underwater and underground structures. The hardened cement should be in the water environment or on the surface at all times, without the variable influence of moisture.


- Silicate. Everyone who has dental fillings is closely familiar with this material. A finely dispersed mixture with a large composition of sodium and calcium fluorides is used in dentistry. It is very similar in structure to tooth enamel. Water is not used as a liquid; special compounds are needed for its dilution. It can be diluted with water for use in interior finishing works as a material for decorative finishing. The cost of such cement is very high.
- Polycarboxylate. Substance with a high level of adhesion to organic tissues. Like silicate cement, it has little to do with construction and is used for medical purposes. In particular, for filling milk teeth.
- Slag. Powder mixture of cement, gypsum and blast-furnace slag. The slag accounts for 20 to 60% of the total composition. The more it is, the less active the cement. Its strength increases over time. Resistant to stable aggressive environmental influences, but does not tolerate temperature extremes and humidity levels.
- Lime and slag. In it, in addition to the components of slag cement, there is a proportion of lime. The strength of the material is not very high, therefore, a solution is used when laying and making low-grade concrete. Can be added to plaster.
- Backfill. Its specific field of application is plugging oil and gas wells. The composition contains many components responsible for plasticity, hydrophobicity and high strength.



Manufacturers
Chinese manufacturers occupy a significant share of the cement market. The state standard in China and Russia for this material differs, therefore the Chinese products, which are offered on the market as cement of 500 brands, are actually closer to 400. From the assortment there are no additives, Portland cement and quick-hardening.

A serious competitor to Chinese manufacturers - turkish cement... It fully complies with European quality standards. With impeccable technical characteristics, Turkish materials benefit from several more criteria. They are not overpriced, since the dry method of processing raw materials prevails at factories in Turkey. It is more economical and faster than the wet method, which is still popular in Russia. Products are transported to the markets of other countries in big bags with all possible means of protection. It arrives at the place safe and sound and can be stored in this form for a long time.




The assortment of Turkish cement is from 300 to 500 brands. It is recommended to purchase it in branded packaging. In "nameless" bags, cement powder, which has already been ground up again and packaged after the expiration date, may be sold, possibly that has nothing to do with Turkey. Indian cement was unexpectedly of high quality for the Russian consumer. In the sales ranking, it consistently occupies its position in the first five lines. All raw materials comply with standards, and the products cope with their tasks 100%.

More of the unexpected manufacturers on the list - Iran and Egypt... Cement of domestic production is also of good quality. Its advantages include a wide range of products, compliance with state standards, and a cost that is lower than that of manufacturers from other countries.This is explained by the fact that the price does not include the cost of transportation across the border. Russian cement is mainly produced in slim-bag format in paper and polypropylene packaging without protective layers inside, which reduces its shelf life in some conditions.


Products manufactured by in brazil... No experimentation with the component composition (up to the recycling of ceramic materials) makes it worse. In the product line, you can find a material suitable for specific needs and operating conditions. The product of American production has established itself.
The competition is made by materials from the countries of the Asian region - Japan, Vietnam, South Korea... German goods are popular among European manufacturers.

Colour
The usual color of cement is dark or light gray. Some species may already have a different shade (magnesia and silicate) during manufacture. They are white by nature. Part of the cement is painted in graphite, almost black color. This is the effect of the presence of additional components and dyes. Colored cement is less common. It is mainly used as a decorative and functional additive in concrete mortars and floor leveling mixtures. A colored leveling layer facilitates decorative finishing when using self-leveling floor mixes.


Cement is colored in two ways: directly during production (the method is more reliable and economical) and with the help of a pigmented powder during dilution of the solution. The free-flowing pigment makes it possible to dye the mixture in any color, be it red, blue or purple. But such a variety is required in exceptional cases, when the cement coating serves immediately and decorative. Combined grinding and firing of clinkers with an oxide of some metals gives more effective coloring, but the range of colors is limited to green, yellow and black colors of varying degrees of brightness.

Such mixtures are added to concrete to give it a colored texture. Its color will not wear out and fade over time, in contrast to the solution dyed with color.
When using colored cement, it is important to take into account that the addition of coloring pigments is insignificant, but still affects its technical characteristics. Basically, this affects the shrinkage of the solution. It is more pronounced than that of an uncolored substance.


Brands: how to choose?
It is not easy for a non-professional in the field of repair and construction to understand what the mysterious letters on the cement packaging mean, how to choose the right material based on the alphanumeric markings, who installs them and how to find the right material to fill the foundation. Cement marking is carried out in accordance with GOST. Since a little more than 10 years ago, the generally accepted standard for Russia was changed to the European one, confusion may arise. Not all manufacturers have switched to the new designation system, and sometimes it is difficult to determine the required sulfate-resistant M500 under their outdated numbers.

The old standards had only two designations: PC (Portland cement) and SHPC (slag Portland cement). The quality was determined by the brand from 300 to 500, and the amount of additives was determined by the letter D. For example, ПЦ300Д20 meant that there was Portland cement in the bag with 20% additives of various substances. The common European standard has made significant changes to this system. Now the package indicates the name of the cement (as on all European packaging with cement - CEM (from cement), strength class, type and amount of additives, additional characteristics.

The compositional classification has expanded to five positions:
- CEM I is equal to Portland cement (PC).
- CEM II - PC with additives of mineral origin. This class has subclasses A and B, showing the amount of additives in the mixture. On the packaging, the numbers are indicated without%, but the ratio is measured in them.
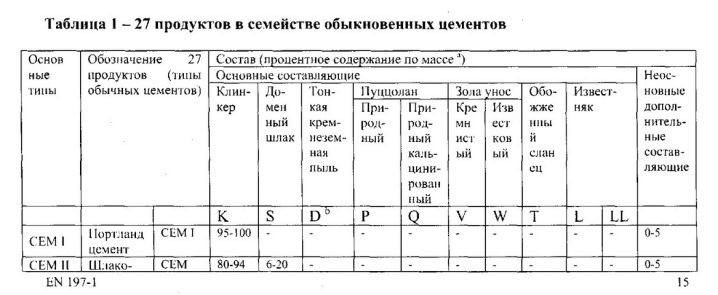
The exact name of the additive is indicated through a dash.W means slags, I - lime content, Z - ash, MK - silicon derivatives. Burnt shale, silicate dust, pozzolana can be added.
- CEM III - PC with slag. It also has a subclass, but only one - A. It denotes the percentage of slag in the composition.
- CEM IV - pozzolanic.
- CEM V - compositional.
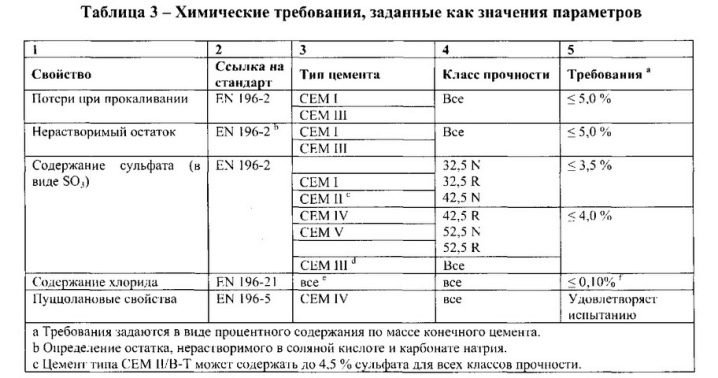
The strength class is followed by the detailing of the component composition. The indicator is measured in kilograms of weight per cubic centimeter. Accepted norms: 22.5-32.5, 42.5-52.5. The information line ends with the determination of the rate of solidification of the solution. H - normal, B - fast-setting cement. For the second option, the layer strength for 2-3 days should be additionally indicated.
What to do for those who are accustomed to the old type of marking, and how to choose the one that is best suited for specific purposes? Relate the strength of the old standard to the strength of the new standard.
Cement of the M100 and M200 brands (strength - 12.5 kg per square centimeter) was used for all kinds of construction and repair work in private construction. The load on him was not as big as on a production scale, so he coped with a number of functions. Mortar M100 or M200 was suitable for rough floor screed, brickwork of partitions indoors, leveling walls and sealing complex defects, plastering. In the past few years, these brands have been phased out due to poor quality.


Now the minimum acceptable is M300 (strength - 22.5 kg per square centimeter). It can be used for brickwork of residential premises, stoves, fireplaces, in large-scale construction, renovation work, pouring screed, foundations, for mixing with concrete components. He also participates in the production of reinforced concrete structures. The products have a permissible strength of SNiP, they are suitable for use at different times of the year, they are resistant to moisture and sulfates, and are convenient to use in the form of a liquid solution. But the M300 falls short of ideal performance. If possible, you should pay attention to higher brands.

М400 (32.5 kg / cm2) high strength, does not corrode, is resistant to moisture and low temperatures, wear-resistant. It is considered affordable and versatile in quality. Depending on the additives, it can be used in private and large-scale construction. Foundations, including prefabricated ones, as well as structures in contact with water are produced from pure cement of 400 brands. Hydrophobic additives make it suitable for the construction of wall panels from high-strength raw materials with additives to make curb blocks, floors, foundations.

M500 and M550, which are often put in one line, have a strength index in the range of 42.5-52.5 kg / cm2. These types of cement are highly resistant to atmospheric influences, are not afraid of water, frost, temperature changes, sulfates, almost do not shrink, and are easy to use. They are used for the manufacture of high-class prefabricated reinforced concrete structures.

Cement М600 (52.5-62.5 kg / cm2) mainly used under unfavorable conditions for recovery work in emergency situations. It has improved characteristics in relation to the M500. For private use, there is no need to use this high-strength and fast-hardening material. You can limit yourself to M400-550. It will withstand everything from building the foundation for a two-story cottage to laying a fireplace inside this cottage. M700 - M1000 brands refer to purely professional materials.


Storage
There are several ways and options for storing dry cement:
- At home. It is by no means the most reliable way to keep the material suitable for construction and repair. A common mistake is to think that cement is dry enough in a warm living space and does not need additional protection. This is especially true for craft packaging. Even in the house there may be too much air humidity, which is why the cement loses some of its characteristics.And if water gets on it, then it begins to clump in the package. Also, its operational state is affected by interaction with oxygen. It is a catalyst for many elements. Its effect on cement also reduces the quality characteristics.

- Outside. Here, all the dangers are obvious: the impact of environmental factors can spoil the material in less than six months. Of course, it will not cease to become a viscous substance when water is added, unless it solidifies the entire bag, but poor storage conditions affect the main quality of the material - its activity. These are its actual bonding properties and brand compliance. At best, spoiled cement will lose 10-15%, and instead of M300 it will behave in operation like an unsuitable M200.
- In the spring and summer. In the warm season, cement is threatened by high humidity, exposure to ultraviolet radiation from direct sunlight, and the risk of a greenhouse effect under polyethylene.

- Winter-autumn there is a risk of rainfall, and for some mixtures severe frosts and temperature changes are harmful. Even before turning into a slurry, cement already loses its useful qualities.
- In bags (paper or propylene). Both paper and polypropylene are capable of allowing moisture to pass through, so any container needs additional protection.
- In bulk. The most problematic option for long-term storage. Bulk cement is a dry powder that is delivered to the buyer in sealed containers, and then simply poured into one heap without any storage container. You need a special approach to it, and it is better to order such cement at all immediately before the start of construction or repair.



The approximate shelf life of cement under favorable conditions is 1.5-2 years. So that it does not lose its important qualities with different storage methods, it is important to follow the recommendations of professionals. It is advisable to purchase cement immediately before use in the amount that will go away for several applications.

If, for some reason, construction work was interrupted, and the cement remained in a small volume, it can be stored at home. A suitable room must be dry, away from rooms where water is constantly used (not a balcony or loggia, not a basement), and ventilated. From time to time, the bags need to be turned over so that the cement does not cake. Unstable packaging can be protected with heavy construction waste bags (made of PVC foil). It is not advisable to overfill if the shelf life exceeds 6 months, since chemical reactions occur in the open air. The room temperature should not exceed 20-25 degrees in order to avoid the greenhouse effect inside the package. Condensation can also spoil the material.

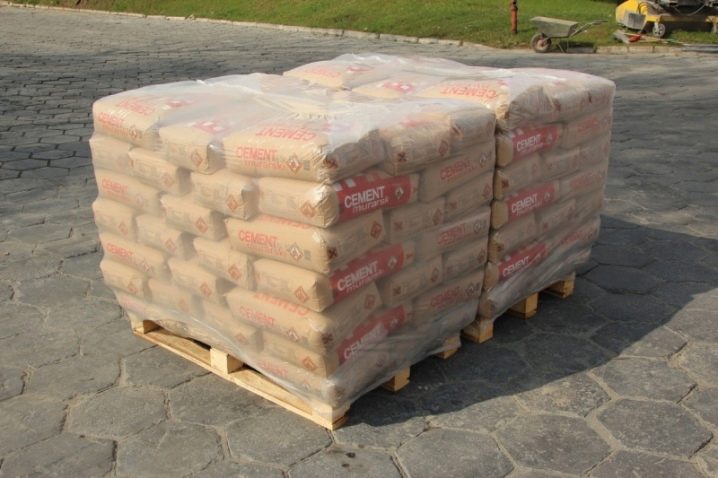
It is difficult to place a large stock of material in a residential area; it will have to be taken out into the street.
To protect it from dampness, you need:
- choose the most dry place;
- cover the base (ground, floor) with PVC film in one layer so that the substance does not absorb moisture from the soil;
- set wooden pallets on top. It is advisable to treat pallets with a primer and varnish or paint, since wood is also very absorbent. In the future, they will come in handy on the farm more than once;

- rewind each bag with cling film;
- place in extra strong trash bags for 120 liters, seal on top with mounting tape;
- insulate with old clothes, hay or sawdust;
- place under a shed or in an outbuilding. In this form, the cement will be preserved for several seasons without losing its properties.

A nuance is important: the higher the activity of the cement, the faster it is lost.
Bulk cement is stored in so-called cement pits. Organizing them will take a lot of time and effort. It is necessary to dig a deep hole, reinforce its walls so that they do not crumble, take care of several layers of waterproofing and high-quality thermal insulation, and organize a canopy.Mineral wool, foil sheets and PVC film for these purposes will cost no less than a new batch of cement, therefore, bulk building materials are not purchased in advance.

Application
With the help of cement, many construction and repair tasks are solved. In some cases, it is effective on its own, and in some it forms a symbiotic substance with additional components or becomes part of the building mixture itself.
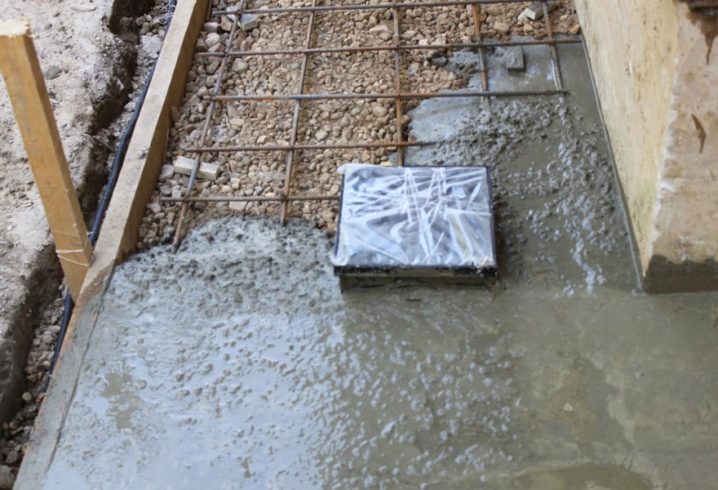

Common uses for cement:
- Pouring the foundation for a private house or garage. It is not used in its pure form due to its too large weight. To do this, it is introduced into a concrete composition in which there is dry alluvial sand, stone or crushed stone, ASG, water. Cement here plays the role of a binder and elastic component.
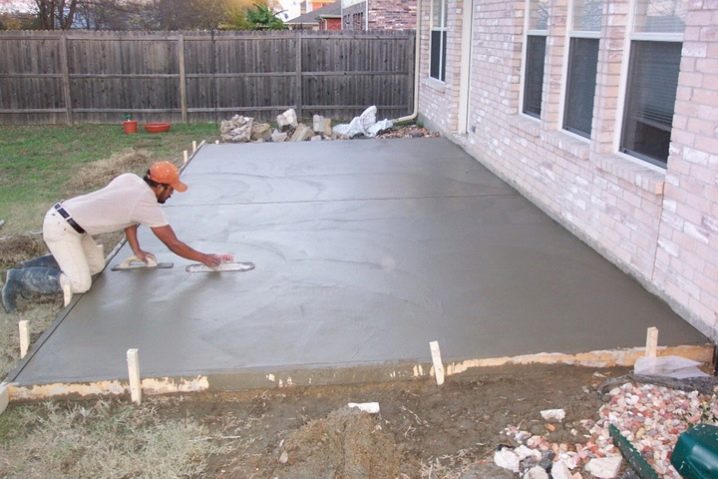
- Filling the floor screed. It is essential in almost any room. With a relatively flat surface of the subfloor without defects and large differences in height, a thin cement screed of 30-40 mm can be dispensed with. For more problematic areas, it is used in two layers. Also, with the help of cement, you can make an inclined screed in rooms where a drain is needed, or fill in the contour of a water-heated floor in order to avoid damage to the system from temperature differences inside the pipes. It is important to use acid-resistant cement and cement-sand mixtures for screeds.


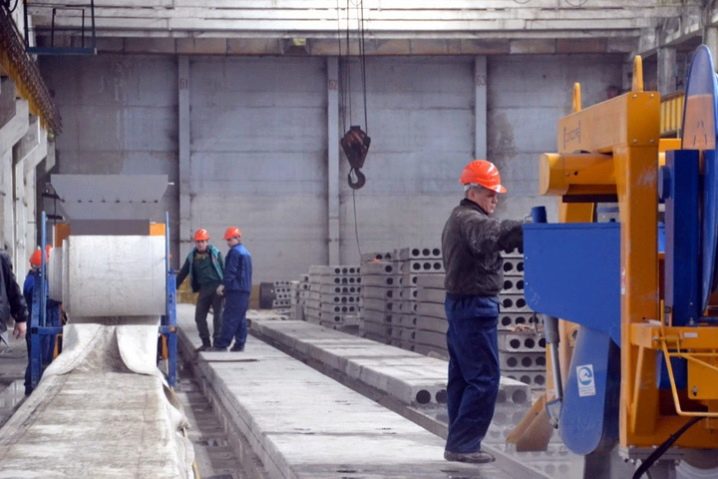
- Production of reinforced concrete structures and prefabricated foundations, floors and wall elements of the house. Stressing (stressed) cement is needed here.
- Construction of structures in water, road construction, construction of bridges, tunnels, multi-storey residential buildings.
- Brickwork. In this case, liquid cement plays the role of mastic, connecting bricks, blocks, natural and decorative stone, and other laying materials. Masonry is used not only for the construction of partitions and walls in the room, but also for the construction of fireplaces and stoves. In the last two cases, refractory cement is needed, not lower than M400.

- Plastering and leveling of ceilings and walls inside and outside the premises. A solution of finely dispersed limestone with the addition of gypsum cements problem areas, making them suitable for decorative finishing. Since the process is long, PVA glue is added to the finished composition, which slows down the evaporation of moisture and improves adhesion to the working surface.
- Waterproofing. A sheet of insulating material can be "planted" on the cement mortar so that it does not float when the screed is poured.
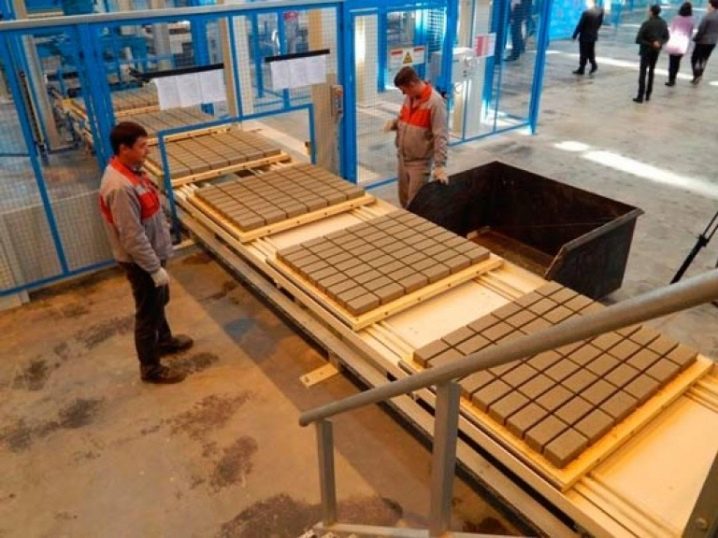
- Manufacturing of paving slabs and other decorative items. Colored cement with high aesthetic qualities is used here.
- Organization of garden paths using a reinforcing mesh.

- For the blind area. This structure plays the role of removing liquid sediments and melt water from the building. In this case, 30-40% of the components of the bulk fraction of the type of expanded clay, broken brick, slag are added to the cement mixture.
- "Ironing". It works as a protective "shell" on the concrete surface. A thin layer of liquid cement mixture is applied, and after hardening, it is rubbed to smoothness.
- Decorating. Cement perfectly replaces gypsum for creating sculptures, park and garden decor in the form of flower beds, pots and flowerpots.

For how cement is made, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.