Hawthorn breeding methods

All methods of propagation of hawthorn are reduced to two: seed and vegetative. For varietal hawthorn, the best way is grafting.

How to propagate by cuttings?
The choice of breeding method for hawthorns primarily depends on the species.
Large-fruited varietal garden hawthorn is more often propagated by grafting and cuttings, only when picking up you need to carefully select the material so as not to cut the branches of the stock. The seed method in this case can give unpredictable results.

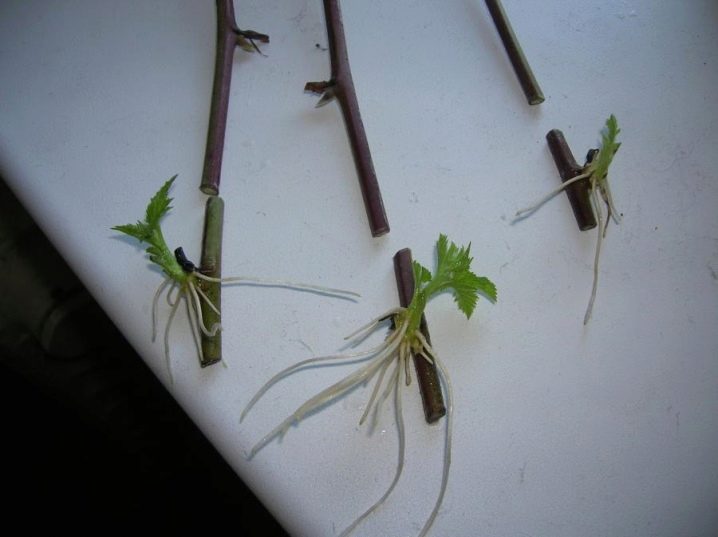
Common hawthorn reproduces well by root shoots or root cuttings. Seed propagation has its advantages - you can get very hardy material. But this will take time and patience from the gardener. The common and monopedic hawthorn species act as a rootstock for cultivated forms. Hawthorn cuttings can take root, but they do it tightly and reluctantly.

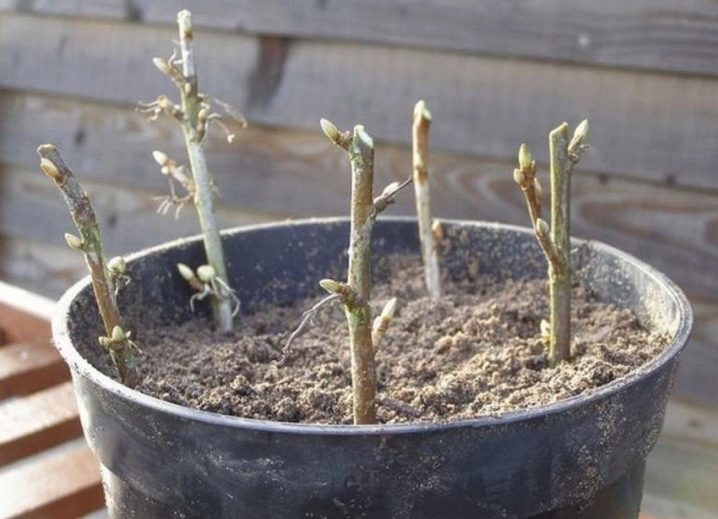
It is better to take cuttings for long-term storage in spring., before the start of sap flow, or in the fall, after the leaves fall. Summer is the worst period. However, green cuttings are best harvested in late June or early July. During this period, the shoots are just beginning to lignify, but they are still plastic and actively grow.
Optimal propagation by cuttings will come earlier if the weather is hot and dry.
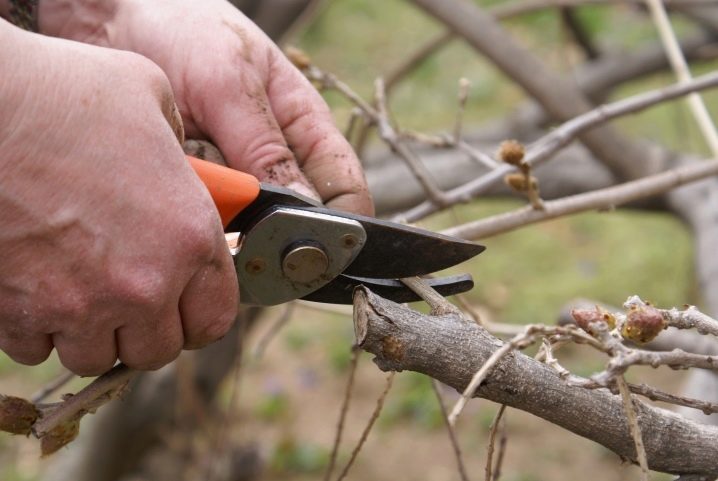

Selection and cutting of material
Shoots should be taken only from lateral, not too active branches. When cutting the material, you should select the middle and lower parts of the shoots that were closest to the roots. The upper ones take root worse. And also do not take the vertical central fatty shoots - they form roots very weakly.
This is how the shoots should be.
-
Clean, without damage and stains (disease, burns, traces of frostbite) on the bark.
-
Best age - annual shoots. Slightly worse - biennial.
-
Length each cutting should eventually be 10-15 cm, thickness 7-8 mm.
It is best to pick branches for cutting cuttings from the middle level of the branches, on the south side of the crown.

From below, greenish cuttings are cut off under the kidney - here immature cuttings are the least vulnerable to infections. Lignified - cut strictly in the center between two nodes.
The top cut of any cuttings is made as close to the bud as possible, at an angle of 45 degrees.
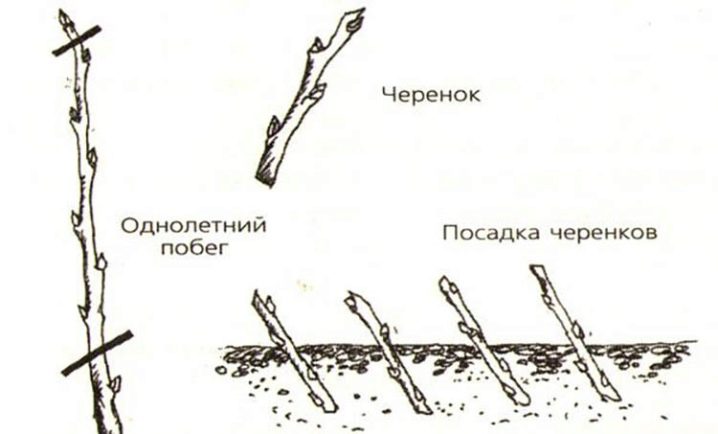
Variants
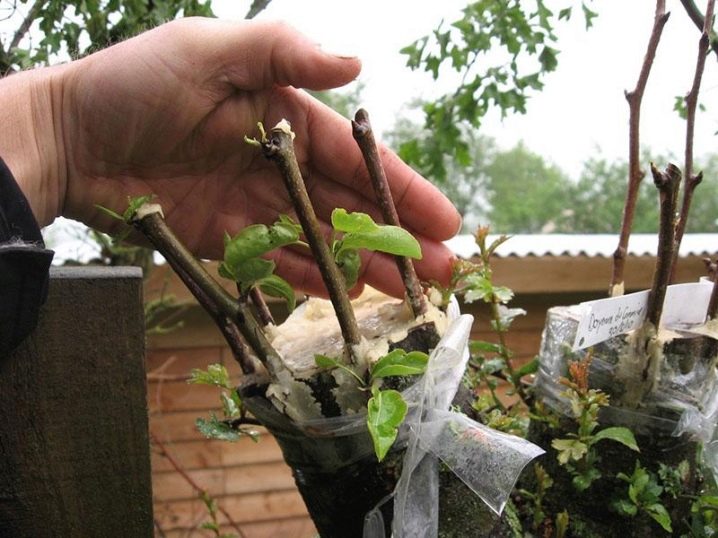
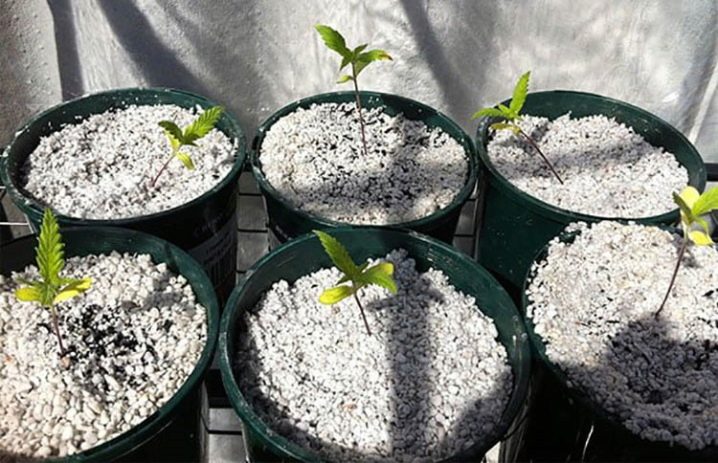
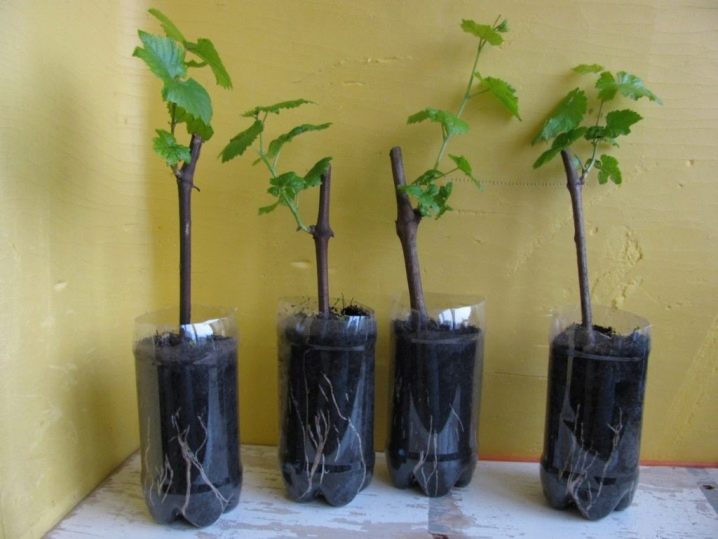
It does not matter if the cuttings are collected green or lignified, it is advisable to process them in a stimulant. It can be "Kornevin", "Zircon", "Epin". The cuttings are kept in a stimulant solution for 1 hour, then planted in sand mixed in half with peat. A stimulant solution is poured into the plantings, the cuttings are covered with a glass jar.
Another variant of the mixture is 1 part of sand to 1 part of perlite.
Cuttings will need careful care: constant airing, careful watering.

The roots will not give the cuttings themselves, but young daughter plants under the lower bud. As soon as they appear, they begin to remove the glass jar - first for 20 minutes, then the time is increased.
Watered abundantly, achieving complete wetting of the soil, but only when the top layer dries out. The next year, young bushes can be planted in open ground. The distance between the landings is 2 m.

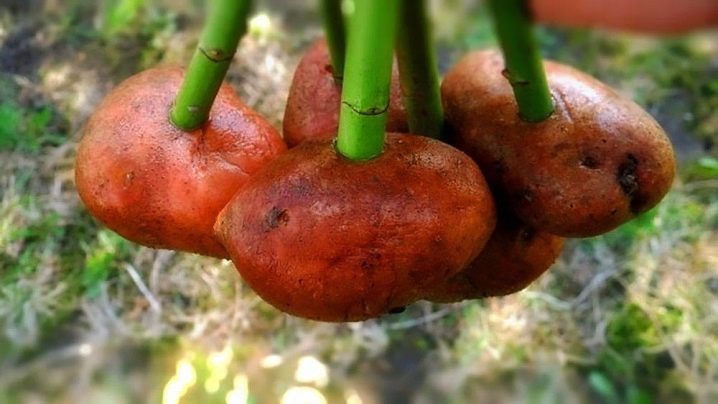
Rooting hawthorn cuttings can be carried out in potatoes, similar to roses. Cuttings are treated with weak potassium permanganate, kept in a solution of "Heteroauxin" or another stimulant for 24 hours.You can take aloe juice. Take a large healthy potato, remove the eyes, let it dry. Use a screwdriver or a knife to make a "hole" in the potato.
The stalk is inserted into the hole, the potato is immediately planted in the ground. The place is chosen warm, protected from the winds. In a potato, the stalk receives the necessary nutrients. The tuber holds moisture well, it is created by nature not to deteriorate in the soil for a long time, protects hawthorn cuttings from infection by bacteria, and the tip of the cuttings from temperature extremes.

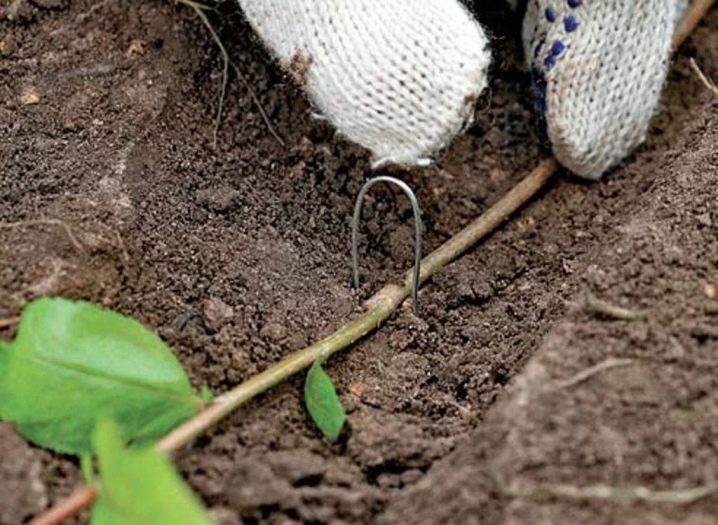
Breeding by layering
The method is not suitable for standard plants, only for bush hawthorns. Instruction.
-
In spring or early summer, small grooves are dug next to the bushes.
-
You need to prepare metal staples.
-
Young 1-2-year-old shoots are laid so that the place under the lower bud is in the ground.
-
Pin the shoot with a staple, and sprinkle it with earth (preferably peat, dry humus, hay).
-
In the future, the layers are looked after as full-fledged plants. Fertilize once a month.
-
In the fall, the layers are separated from the mother plant, and planted in a permanent place.
If the roots of the new seedlings are small, the transplanting of cuttings can be postponed until spring.

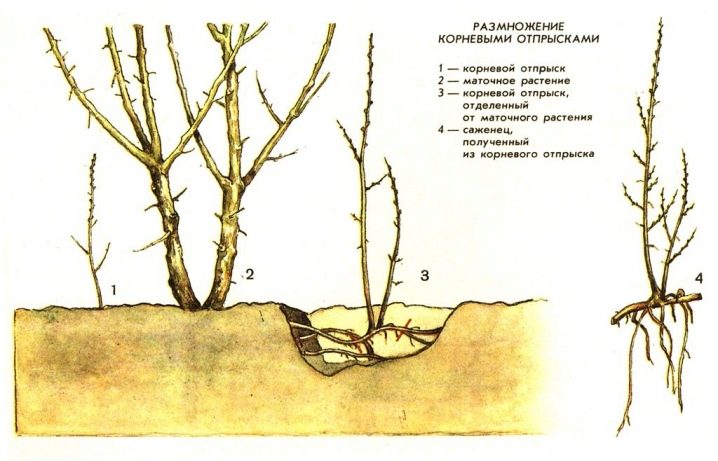
Using basal offspring
Hawthorn actively gives root shoots. Usually, especially in grafted plants, it is cut out so as not to deplete the main plant. Several of the strongest daughter plants are left for reproduction. They are separated from the main bush with an ordinary bayonet shovel or secateurs, chopping off the root connecting the offspring and the mother bush. At the same time, they act carefully so as not to damage both plants.
Shoots that have reached 10 cm are separated in spring and early summer, until early July.
There is also a method of propagation by root cuttings. In the spring or autumn, dig in the roots 2 cm thick, cut into 10 cm segments in length. Dip cuttings in a warm place obliquely with thick ends up, so that there is 2 cm above the soil.
Seed propagation
The complexity of seed reproduction of hawthorn - in the need for long-term stratification... Like any mid-latitude plant, the hawthorn lives in cycles. Its seeds are also adapted for long wintering and awaken due to the complex effects of time and temperature.
Hawthorn seeds are stratified within 7-8 months. at a temperature of + 4 ... 7 ° С.
Stratification option: the seeds are wrapped in gauze, kept in a warm place (+ 20… 25 ° С) for 4 months, then the same period is kept in a refrigerator or basement at a temperature of + 4… 7 ° С.
When sown before winter in the first spring, only 20-30% of the seeds germinate.
Slightly unripe seeds are harvested, because the ripe shell is very hard, reminiscent of a stone.
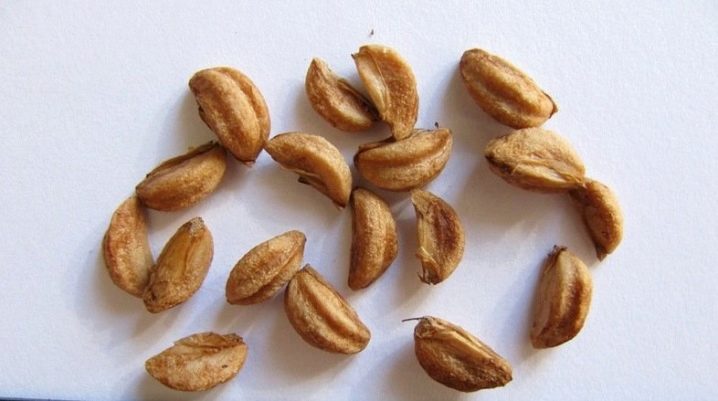

Scarification will help speed up germination - this is a treatment that allows you to get rid of the hard outer shell of the seeds, and the seed will be able to germinate faster.
Methods for scarification of hawthorn seeds.
-
Soak the seeds in warm water for 3 days. Wipe them with sand, rinse. Soak in a solution of potassium nitrate 1% for 2 days.
-
Rinse the seeds with water, soak in a solution of 3% sulfuric or hydrochloric acid for 20 minutes, rinse, then rub through a sieve with sand. Another option: soak the seeds in water, add acids on top, and stand for 12 hours. Under natural conditions, hawthorn seeds often undergo natural scarification in the gastrointestinal tract of birds, therefore, such treatment with a crop is perceived positively.
-
Processing with a nail file, file, sharp knife. Cuts or cuts are made on the hard crust of the seeds. The difficult way, the seeds of the hawthorn are quite small.
-
Sanding. The seeds are clamped between two sheets of fine sandpaper and rubbed with palms, rolling back and forth.
-
Scald the seeds with boiling water, and immediately put them in cold water. Withstand in it for a day. Repeat the procedure.For convenience, the seeds are wrapped in a thin cotton cloth and dipped alternately in glasses with boiling water and cold water.
After scarification, seeds are sown in open ground. Seedlings will appear in spring, by the second year the seedlings will reach 1.5 meters.

Graft
The vaccination is performed at the beginning of August. It will take skill and a sharp tool - the hawthorn has hard bark and wood.
The stock is a common hawthorn or one-pistil, red rowan, pear, chokeberry, irga. Hawthorn is a tolerant culture that gets along well on all the listed trees.
Inoculation is carried out on mountain ash by the method of improved copulation. Shafts of equal diameter are aligned along oblique cuts so that the tissues of the cuts coincide. The place of inoculation is 80-100 cm. The stock is a hawthorn seedling at the age of 2 years, with a root collar diameter of 1 cm.
The best time for copulation is late March, early April, until mid-June. It is important to catch the moment when the scion (varietal hawthorn) is still asleep, and the stock (mountain ash) has already begun to wake up.
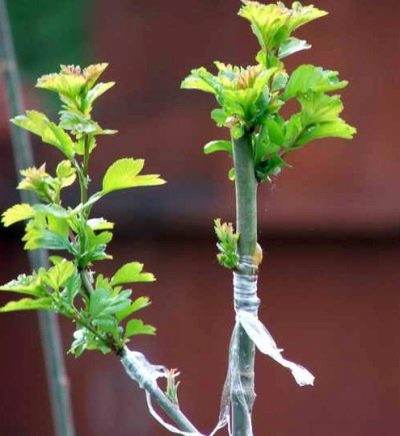

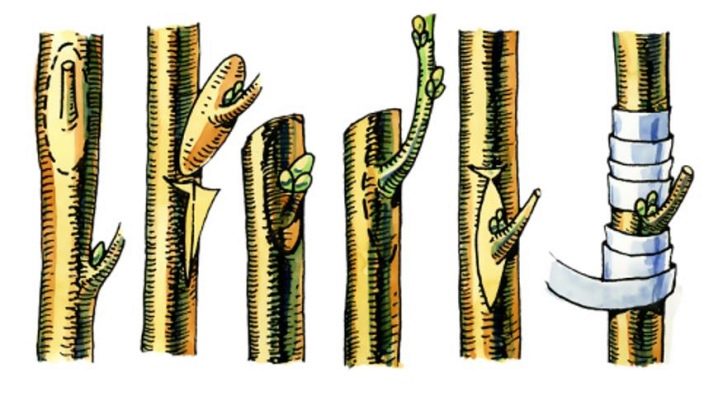
Piping is used less often. In hawthorns (as well as cherries and cherries), the buds are difficult to preserve until spring. To do this, you need to cut the cuttings for leading and store them in cool conditions. Therefore, the method of "grafting with a sprouting bud" in early spring is not very effective. It is safer to vaccinate with a wintering kidney. Such buds form in the current year after the plants leave the period of spring growth.
These kidneys can be harvested any time of the year before vaccination, in the early morning or evening. They are cut from the middle of suitable shoots. The leaf plate is removed, the petiole is left for convenience. The shoots are wrapped in a damp cloth and kept in a cool place.
Then carry out budding in the butt. This method is good because it can be carried out at any time of the year, regardless of the movement of the juices. At a distance of 1-1.5 cm from the kidney, a cut is made, cutting out a shield, which is a kidney with a piece of bark and a thin layer of wood. It is desirable that the layer of wood is not thick, otherwise the shield will take root worse. On the rootstock, the bud is removed, trying to repeat the shape of the shield. The lower part of the cortex is not removed. It turns out a kind of "tongue". The shield is applied to the cut site, covered with a tongue. The scutellum together with the tongue is carefully and tightly tied to the stock, so that the bud looks outward.
Piping can also be performed in a T-shaped incision.
And there are also innovative ways of breeding hawthorn. Cloning allows you to get thousands of plants in six months. The plant bud is placed in a special nutrient medium. The method requires special equipment.




































































The comment was sent successfully.