What does common hawthorn look like and how to grow it?
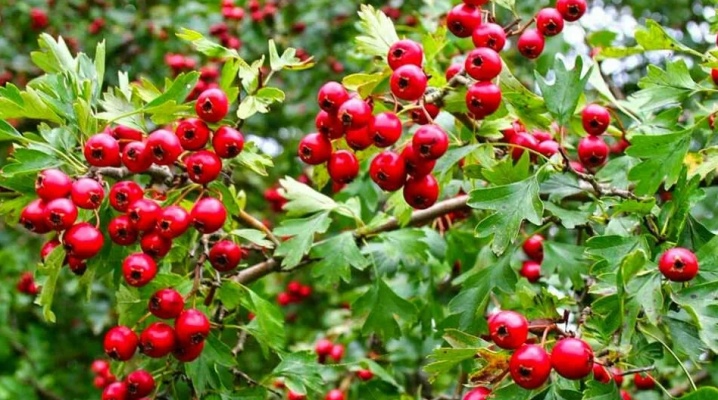

Common hawthorn has many names. It is also called prickly or smoothed hawthorn. A shrub plant, which belongs to the pink family, is very widespread, has excellent decorative qualities and a lot of useful properties. In the article we will tell you what the common hawthorn looks like, and how to grow it correctly.
general description
The distribution area of the plant in question is the territory of Western Europe. In natural conditions, today there are over 200 varieties of this culture. The hawthorn was introduced to the eastern part of Europe at the end of the 19th century. In those days, it was considered as a cultivated plant. Over time, hawthorn again turned out to be a wild crop, which can be found on the edges, in plantings or in forest areas. The plant can thrive in marine and humid climates, as well as in stony soils.
Hawthorn is a well-known plant that is difficult to confuse with other crops. The height of an elegant bush can reach an impressive mark of 3 meters. The characteristics of the plant largely depend on how it was cut. The crown of common hawthorn is usually lush, dense and spherical. Slightly less often, the crown has an asymmetric or ovoid structure. The thorny details on the shoots of hawthorn are most often characterized by a length of 5 cm.


It is necessary to take into account the fact that the common hawthorn produces white flowers on the branches. The form of this plant is most often multi-stemmed.
-
The bark of a gray or brown shade on a dense stem of a plant can be covered with characteristic cracks or grooves.
-
The shoots of the common hawthorn most often grow in a forward direction, but weeping varieties of this popular culture can also be found.
-
Young twigs of common hawthorn attract attention with a rich red hue. They are often covered with small thorny elements.
As for the leaf blades of common hawthorn, the following botanical description is relevant here.
-
The leaves of the plant are medium in size. Most often, the plates have the characteristic shape of an egg, rhombus, circle or ellipse.
-
In addition to solid leaf blades, common hawthorn can produce blades with dissection or notches at the marginal areas.
-
Usually the foliage surface of hawthorn is smooth. And you can also find such plant varieties, the leaf blades of which are complemented by characteristic pubescence.
-
Against the background of the autumn season, the foliage of common hawthorn acquires a beautiful golden hue, and can also turn orange or purple. You can also meet such species that do not change their original color at all. A similar tree, right up to the very fall of the foliage, shows a green crown.


Consider what features and external characteristics the flowers and fruits of common hawthorn have.
-
The flowering period of the plant in question falls on the last spring days, or at the beginning of the summer season.
-
The common hawthorn blooms quite brightly. The inflorescences of this popular culture most often have an umbrella or small shield structure.There are varieties that only produce single flowers.
-
Every flower of a plant has 5 petals. The color of the buds is usually snow-white, as well as pink or reddish.
-
During flowering, hawthorn gives off specific aromas. Sometimes the smell resembles rotten fish. A similar phenomenon is due to the fact that in the flowers of the culture there is a special substance that provokes unpleasant odors.
-
Fruiting of hawthorn most often occurs at the very beginning of the autumn season.
-
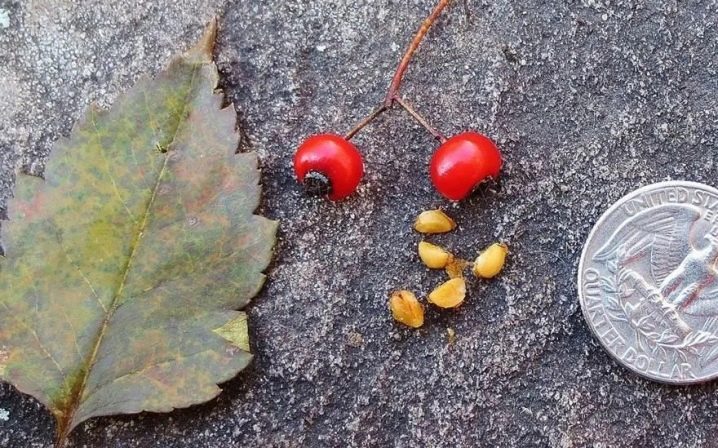
The fruits of the common hawthorn look like small apples. The diameter usually reaches 0.8 cm. Their shape can be pear-shaped or spherical. Elongated infructescences can also develop.
-
The colors of hawthorn berries can be different. The colors range from light orange to burgundy. After the 10th year of life, the culture begins to bear fruit in full force.

The root system of common hawthorn becomes very long when the crop reaches more than 5 years of age. That is why replanting the plant during this period is no longer recommended, since too long rhizomes will be extremely difficult not to damage.
The growth rate of common hawthorn varies. On average, the annual growth of the crop is about 25 cm. The same value is relevant for the width of the plantings. The plant reaches its final indicators and maximum size in 7-10 years of life.


Varieties and forms
Let us consider what features and distinctive features characterize the most common varieties and forms of common hawthorn.
Pear
In this plant variety, the leaf blades are composed of three lobes. Due to this feature, the tree in its external characteristics is very similar to viburnum. In the wild, pear hawthorn usually grows in the west of the North American continent. The tree can reach impressive heights - about 12 meters.
The branches of the pear variety are covered with sharp thorns. The inflorescences of the culture have a corymbose shape, consist of a large number of flowers. The fruits of the plant are characterized by a dark red color. Since the hawthorn variety in question cannot boast of frost resistance, it is usually not grown in our climate.


Semi-soft
Under natural conditions, this plant grows in North America. Its size can be up to 8 meters. The tree has a tent-like crown. The leaf blades of the culture show a rich green color and an 8-lobed structure. The ovoid shape is characteristic.
Initially, the outer side of the semi-soft hawthorn foliage is covered with light pubescence., after which it remains visible only in the area of the veins. In the autumn, the foliage acquires a brown color with a slight reddish tint. Large corymbose-type flowers hang down on elongated legs.
In appearance, the inflorescences of this variety strongly resemble a real downy cloud. Small fruits are orange in color and have a slight reddish tint. The fruit taste is very pleasant.


Pinned
This hawthorn variety is Chinese. It appears to be a branched tree that loves moisture very much and is not afraid of frosty weather conditions. In addition, this plant does not impose special requirements on the condition and characteristics of the soil in which it grows.
The diameter of the crown of the variety in question can be up to 6 meters. The bark develops dark, has long spines and a gray tint. The foliage of the crop grows dark green, showing a glossy sheen on surfaces. The plates are dissected. Small bright red warty berries can be pear or ball shaped. The variety in question looks especially impressive both during flowering periods and during fruiting.


Crimson cloud
This variety can grow both as a shrub and as a tree with a height of 4 meters or more. The culture easily tolerates shading, tolerates drought without problems. Crimson cloud feels best on loams, as well as on heavy clay-type soils. The plant can grow on talus and rocks. It thrives best in humid climates.
For the species of hawthorn under consideration, thorny branches are characteristic. The flowers of the culture are large, with a bright crimson color and a snow-white core. Fruits are medium-sized, red and rather sweet.


Landing
Common hawthorn is an ornamental shrub that does not impose special requirements on the composition of the soil mixture. The culture is easily adaptable to a wide variety of external conditions. The plant is not afraid of frost or drought, and is also shade-tolerant.
Common hawthorn is often planted against the background of the spring season. However, many experts recommend doing this in the fall, not in the spring. During this period, the seedlings do not need a lot of maintenance due to the sufficient amount of rainfall. If the weather is relatively warm, the rooting of the culture will be noticeably accelerated. Despite the fact that in autumn the common hawthorn is in a state of "rest and rest", its roots can still actively grow and develop at soil temperatures up to +4 degrees Celsius.
The main thing is to start planting the culture in a timely manner. In this case, the young rhizome system will have time to complete its formation before the first frost: in bushes planted in autumn, it grows much more slowly.


It is important to choose and prepare the right place for planting the plant. Common hawthorn is allowed to be planted in almost any type of soil. However, it is best to opt for drained and fertile land that receives ample light. The landing itself should be made in not too deep pits 50x50x80 cm.
The bottom of the holes must be filled with a drainage layer of gravel, gravel or broken brick. A drainage of 15 cm is enough. To prepare the optimal planting mixture, you can use leaf flour, sand, peat and humus. Lime can also be added to the formula, but this is not recommended if the shrub is in the early stages of its development.

Let's figure out the basic rules for planting common hawthorn.
-
First you need to prepare 2-year-old seedlings. It is best to buy them in proven nurseries.
-
Future bushes must be located, maintaining a distance of 1.5-2 meters from each other.
-
Before starting planting procedures, special attention should be paid to the tips of the roots. All dry or damaged areas must be removed immediately.
-
Good drainage needs to be taken care of. For this, fine gravel is laid out at the very bottom of the planting hole, 10 cm of sand is poured on top, ½ a bucket of humus is taken, superphosphate (100 g) and 500 ml of wood ash are added to it. The combination of components is mixed well, and then the hole is filled with the mixture by 1/3.
-
As soon as the seedlings are placed in the soil layer, they must be well watered, and then sprinkled with a dense layer of dry grasses, peat or straw.
Do not plant hawthorn seeds or seedlings in the vicinity of apples, cherries or pears. This is due to the fact that the listed fruit trees suffer from the same pests. To form an original hedge around the entire perimeter, a culture is planted in a trench 50 cm wide, keeping a distance of no more than 0.5 m.


Care
Plants planted on the site will definitely need proper and regular care. We will understand the basic care measures that will be necessary for common hawthorn.
Watering and feeding
The plant in question will grow and develop much more actively if you fertilize it regularly.From the second year after planting on the site and until the first moment of fruiting, fertilizers are applied 2 times during the year. The first time the culture is fertilized against the background of blooming leaf plates. Nitrogen compounds are suitable for this. The second dressing is added in September.
Ripe bushes should be fed 3 times during the season. The following types of dressings are required.
-
Spring. To do this, mix 10 liters of water, 3 tbsp. l. sodium humate. This mixture is poured under one plant (at least 30 liters per position). When the flowers bloom, take 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water. One plant will need 10 liters of funds. Hawthorn is fed either early in the morning or late in the evening.
-
The plant is also fed during the ripening of its fruits. For this, 4 tbsp is diluted in 20 liters of water. l. sodium humate. The prepared mixture must be very carefully watered with the bushes.
Watering the plant also needs to be done correctly. In hot summer seasons, watering is carried out once a month for rich fruiting. For 1 bush, you will need to spend 1 bucket of water. If there is no rain for a long time, watering can be done a little more often - 2-3 times a month. It is important to ensure that there is not too much moisture in the soil mixture.


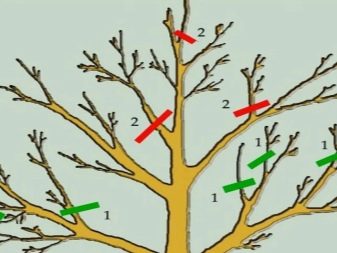
Pruning
The culture in question survives the molding procedure without any problems. At the same time, the thickening of the crown is significant. Thanks to this, the plant can be used to create a beautiful hedge.
Common hawthorn needs only one obligatory pruning - spring sanitary cleaning. Through this operation, all dried and damaged parts on the plant are removed.
The haircut should be carried out on the basis of the planned structure of the crown. If you need to make a hedge, then the shoots are most often pruned to 1/3 of the total length.

Wintering
Common hawthorn appears to be a fairly frost-resistant plant species. He does not need thoughtful insulation for the winter. As for the decorative varieties, they still need to provide at least light cover to cover the protruding roots. For this, it is allowed to use a dense (up to 10 cm) mulching layer made up of dry foliage.
It must be remembered that any hawthorn may freeze buds or shoots against the background of the winter season, but with the onset of spring everything usually quickly returns to normal.

Reproduction
Common hawthorn can reproduce in various ways:
-
seeds;
-
layering;
-
root suckers;
-
cuttings;
-
grafting on a stem.
Most often, the plant propagates precisely by the seed method. First, the seeds are properly prepared, then sorted and placed in suitable containers, where there is a possibility of moisture removal.

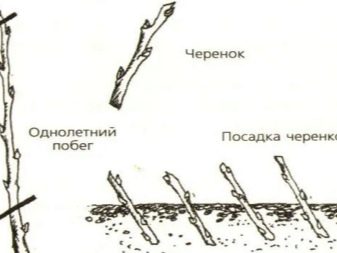
Plant propagation by cuttings is also carried out very often. For this, in late autumn or early spring, crop segments are prepared with a thickness of up to 15 cm. After that, they are added dropwise. In the spring, these components are divided into pieces of 7-8 cm and planted obliquely in a greenhouse with fertile soil. In this case, 1-2 cm of the cutting is always left on top. The earth will need regular moisture.

Diseases and pests
Like many other fruit crops, common hawthorn can be subject to various diseases. Most often these are:
-
fungal;
-
viral;
-
bacterial;
-
non-communicable diseases.
Most often, it is the diseases of a fungal nature that are spread.
Often, the hawthorn is affected by powdery mildew. Because of this, the plant becomes covered with a whitish bloom, which over time becomes denser, becoming gray. In later stages, this plaque takes on a brown tint. Powdery mildew can parasitize the crop in question, causing serious harm to it.
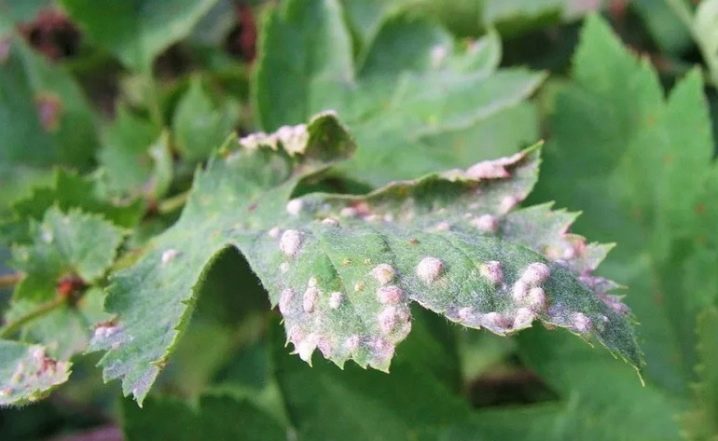

And also the plant can suffer from spotting. This multi-colored disease can affect a wide variety of cultures. The disease is fungal, carried by insects.
The foliage of hawthorns is often rusty. The disease also attacks the branches and fruits of the plant. The defeat of integumentary tissues provokes another disease - scab. It leads to the rupture of these tissues, and can manifest itself in the form of burns.
Very dangerous fungal infections often lead to curly leaf blades. They inflate, create unusual bulges and concavities, and become covered with a brownish tint.


In addition, common hawthorn in many cases turns out to be a "target" for harmful insects. Usually, the culture in question is attacked by those pests that move from apple trees, plums and pears, as well as ornamental plantings. Basically, common hawthorn is affected by:
-
mealybug;
-
shield;
-
hawthorn;
-
fruit sawfly;
-
flat-bodied;
-
weevil;
-
false shield;
-
green aphids and others.
It should be noted that the common hawthorn itself cannot act as a carrier of the listed parasitic insects.


Application in landscape design
Landscape designers love the common hawthorn, as it is characterized by unpretentiousness and does not need complicated care. In addition, the plant demonstrates beautiful and rich colors that can effectively decorate the backyard area. The curious structure of the hawthorn crown can serve as a decoration for any garden.
Most often, the plant in question is used in landscape design for the following purposes:
-
for landscaping those areas that are still empty and not occupied by anything;
-
to form beautiful hedges;
-
as aesthetic combined landings, coupled with spireas;
-
to create spectacular alleys.
As mentioned above, the culture easily tolerates the cropping procedure, therefore it can be subjected to the formation of any patterns and shapes. At the same time, sharp thorns of plants can serve as an excellent protection of the territory from animals and rodents.






































































The comment was sent successfully.