Types and sizes of bolt holes

There are all kinds and sizes of bolt holes. Many of them are enshrined in GOST, but it is imperative to know a number of subtleties without referring to it. It is useful to study the diameters of holes for bolts M6 and M8, M10 and M12, M20 and M24.
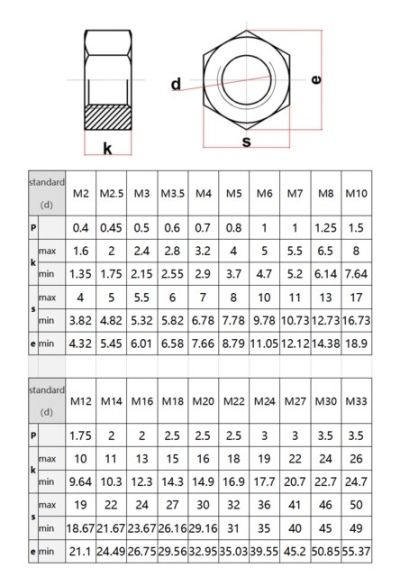
Requirements
The main standards are enshrined in GOST 11284, adopted back in 1975. The document is devoted to various kinds of holes for any type of fasteners. The standard prescribes three rows of diameters for the passages for fasteners. In each subsequent row, the channel cross-section must be larger than in the previous one - provided that the size of the hardware itself is identical, of course.
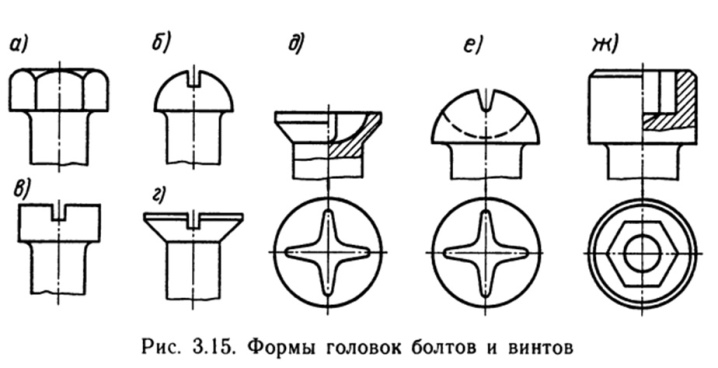
Quite often, the bolts are made under the head.
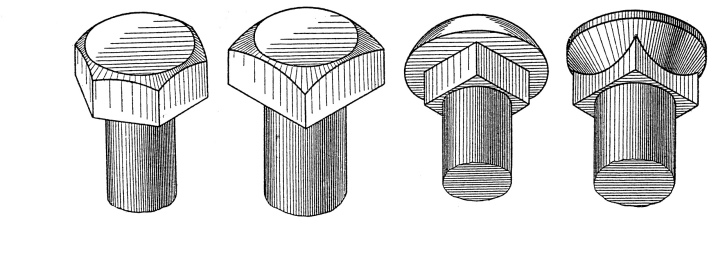
Mostly such heads are made in the form of a hexagon. But sometimes there are options:
-
with turnkey flats;
-
with the location of the hexagon inside;
-
with triangular splines.
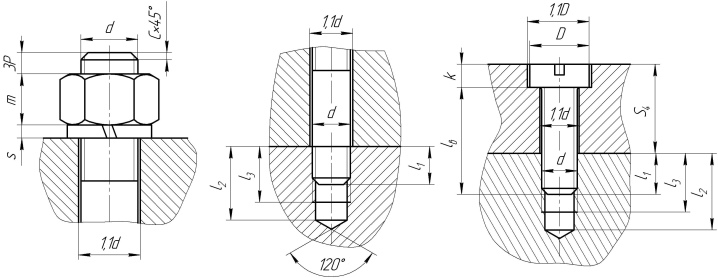
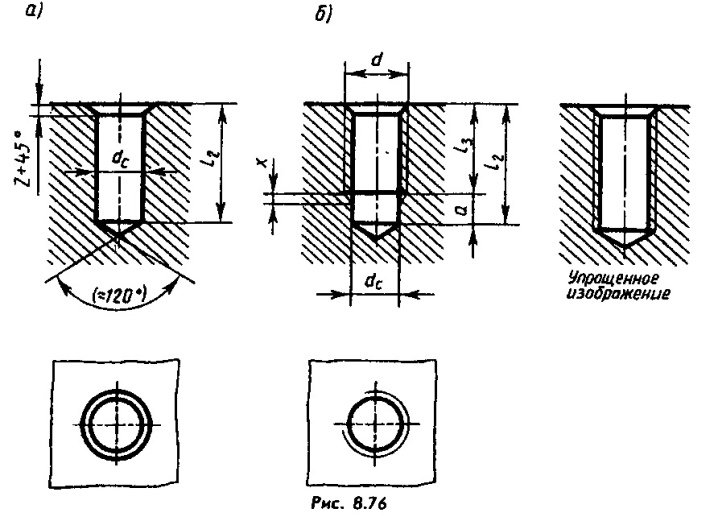
Holes for high strength bolts must be countersunk. It is not allowed to push the channels through the full diameter of the fastener. This limitation applies in the following cases:
-
construction of bridges;
-
work with steel, designed for temperatures from -40 to -65 degrees;
-
work with steel grade C40 or C52.

A very important technological parameter in a large number of cases is the roughness of the products. The choice of its appropriate values, as practice shows, baffles even those who begin to study the course of engineering sciences. But without plunging into these "jungle", it is worth noting the main thing - with a roughness size of 20 to 80 microns, it will already be perfectly visible visually. This circumstance makes it possible to well distinguish between different levels of unevenness of the holes. In general, roughness is described in accordance with GOST 2789, adopted in 1973.

A number of key properties are set there:
-
high-rise;
-
stepper;
-
high-altitude stepping (it is also customary to distinguish 14 categories of roughness).

Views
Through holes for bolts can have a cross-section for rods from 0.1 to 16 cm. Passages for fastening studs, rivets and screws have exactly the same dimensions. However, the dimensions of the "blind" passages can be exactly the same. Important: when laying through holes, special measures must be taken so that the drill does not hit the workbench or other support. For this purpose:
-
use special workbenches with recesses;
-
place a wooden or combined (wood-metal) gasket;
-
reduce the rate of drilling at the very end;
-
put a steel bar with a hole.
By shape, the bolt heads themselves are divided into:
-
oval;
-
hex;
-
square;
-
round configuration.
Dimensions (edit)
The holes for the M6 fasteners are as follows (in centimeters):
-
for the first row - 0.64;
-
for the second row - 0.66;
-
on the third line even more - 0.7.
But in practice, there are also smaller fasteners - M5. In this case, the sequential layout of the sections is as follows:
-
5,3;
-
5,5;
-
5.8 mm.

At the same time, there are many holes for larger bolts. So, under the M8 you have to make channels:
-
first 8.4 mm;
-
then 9 mm;
-
and finally, in the third row it is already 10 mm.

The next dimension in diameter is M10. For this type of hardware, the following dimensional norms apply:
-
on the first line - 1.05;
-
on the second line - 1.1;
-
on the third line - 1.2 cm.
Of course, there are also much longer attachment devices. First of all, we are talking about the M30 category. For holes for such bolts, the following standards are established (by row):
-
3,1;
-
3,3;
-
3.5 cm.

The largest bolt type allowed by the 1975 standard is the M85. To use it in the first row, channels of at least 87 mm are required. At the second and third levels, 91 and 96 mm are required, respectively. True, in a domestic environment, this size is very rarely required.
It is typical mainly for construction and industry.

Quite often in the industrial sector, bolts of the M45 type are also used. To use them, you need to prepare a hole:
-
in the first row - 4.6;
-
in the 2nd - 4.8;
-
in the 3rd - 5.2 cm.
But, again, this is all too large for a common household fixture in most cases. There, however, the M12 bolt is in demand. And with him the situation is much more interesting. In the initial size group, the value is very rigidly set - 13 mm. But in the next two there is a choice - 1.35 / 1.4 and 1.45 / 1.5 cm, respectively.

The same applies to M14 (15, 15.5 / 16, 16.5 / 17) and M16 (17, 17.5 / 18, 18.5 / 19 mm). The next product on the list - M18 - has the dimensions of suitable passages in metal (in order):
-
1,9;
-
2;
-
2.1 cm.
But of course, fasteners of the M20 category also deserve attention, or rather, the holes for their placement. Everything seems to be relatively simple here - 21, 22 and 24 mm, depending on the specific row. For the next position - M22 - the typical dimensions of the fixation passages are 2.3, 2.4 and 2.6 cm. Finally, for another popular option - bolts of the M24 category - the same indicators will be pretty much:
-
2,5;
-
2,6;
-
2.8 cm.
The variation in the size of the holes, at least in some cases, is very easy to explain. This is due to the fact that the bolts themselves differ in accuracy class. If they meet the requirements of category A, then it is possible to form the channel without a gap. However, the problem is that it is quite difficult. And therefore, in real building structures, category B compounds are predominantly used.
For friction hardware with a cross section of 12 mm, the nominal dimensions of the technical channel are from 13 to 15 mm. For shear and friction-shear, the same restrictions are set. But with a larger diameter of the rod, the differences between these two groups begin (for 20-mm fasteners - 21-24 and 21-23 mm, respectively).
Another important topic is the choice of the length of the fasteners used. It is calculated by summing the dimensions of the thickness of the elements to be joined.

Next, you need to add another thickness of the washers and nuts used. Additionally, a correction factor of 30% is introduced to the cross-section of the hardware. When this calculation is made, it is necessary to select the closest size among the assortment of fasteners. (As necessary, the calculation is rounded up so that the bolt protrudes from the nut by at least one thread turn). The above is enough to estimate the basic parameters of the holes.

But there are a few more subtleties that you should definitely remember. Some bolted connections are shear. If the thickness of the outer part is more than 0.8 cm, then the thread should be outside the package to be joined. In other cases, it should be at least 50%, but not less than 0.5 cm outside the products to be joined. If the length of the fastener does not fulfill this condition, you need to choose a longer one or shorten the hole - only making sure that the fastener does not lose reliability.
In the next video, we suggest that you visually familiarize yourself with the types and sizes of bolt holes.













The comment was sent successfully.