Diseases and pests of beets

Beetroot is a crop that is prone to a wide variety of diseases. Most of them can be successfully dealt with if the necessary measures are taken in a timely manner.
Diseases and their treatment
Different beet diseases manifest themselves in different ways. Due to some ailments, the leaves turn yellow, from others the foliage becomes covered with noticeable spots, the fruits deteriorate. Consider the most common diseases that can affect this popular culture.

Fomoz
Serious fungal disease. Phomosis can strongly affect only the leaves of a plant, but also its fruits. If you do not start to treat the damaged crop in time, then an even more serious problem associated with lagging rot may arise.
Most often, the main symptoms of phomosis are several signs.
- Well-visible light brown spots are formed on the leaf plates of the plant. Stems and peduncles are distinguished by noticeable zoning.
- Root crops have characteristic patches that are very similar to lesions resulting from dry rot. However, in the case of phomosis, these areas do not have a formed superficial mycelium.
- In the cut, the tissue of the fruit turns dark brown.
- The affected tissue will certainly begin to rot. The formation of pycnidia begins on their surface.
The main reason for the occurrence of this ailment is associated with the use of initially infected crop seeds. In addition, phomosis can appear if you neglect the removal of infected plant debris from the site. Acid and dry soil types are a suitable environment for the active development of the disease.

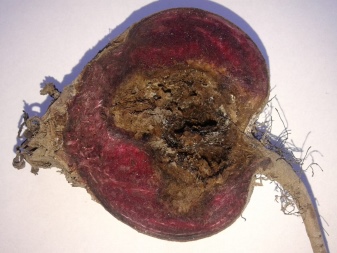
The disease in question can and should be treated. It will be possible to fight against phomosis by using special fungicidal agents. For these purposes, the best suited drugs "Altazol", "Alpari", "Benazol". The popular Bordeaux liquid can also demonstrate high efficiency.
It makes sense to turn to the unscheduled introduction of appropriate dressings.
Cercosporosis
This disease is also fungal. Its main source is contaminated seed or diseased areas on surrounding plants. Once on the beetroot foliage, the fungus begins to multiply very quickly. After a short time, clear signs of its activity on the plant can be noticed.
- Characteristic gray spots usually appear on the beet leaves. They have reddish-brown edges, which are also clearly visible. Over a short period of time, these spots begin to decrease in size, which is why they become more like ordinary dark spots.
- First, the dying off of large and mature rosette leaves begins. Following them, the small foliage of the plant also dies.
- There is a noticeable change in the sheet plates - they twist downward.
- The tops of the plant begin to wilt quickly. Because of this, the summer resident can immediately notice the opening of the row spacings. Usually it catches the eye immediately, so it is difficult not to notice it.
- Under the influence of the disease, the development of root crops slows down sharply.
- Beets are no longer "sugar". The sugar level in fruits drops by 20-50%.


The active development of this serious fungal disease on beets occurs due to a sharp change in humidity levels during the growing season. Usually such events are directly related to changes in weather conditions.
Cercosporosis is a serious condition, but it can be treated. The highest efficiency is demonstrated by such drugs as "Gamair", "Pseudobacterin", "Benomil", "Alirin-B". You can also use all sorts of folk remedies. For example, it can be a soapy solution, which is often supplemented with ash.
Of course, such homemade formulations help in the fight against fungal diseases, but they are not as effective as the above drugs.


Powdery mildew
A very serious disease that can cause great harm to plants. Many summer residents are well aware of this ailment, because its symptoms make themselves felt when growing a huge number of various crops. The main causative agent of powdery mildew is a fungus belonging to the ascomycete class. It spreads rapidly throughout the site if the weather is dry and hot.
Let's find out what are the main symptoms of powdery mildew on beets.
- Due to this disease, a white powdery coating forms on the lower and middle leaf plates. At first, it looks like small spots, which after a while begin to grow to the size of the foliage itself.
- Brown, and then black dots may form on a white coating. They are also called clestothecia.
- There is a sharp disruption in the synthesis of sugars in the leaves, and the outflow of plastic substances to the roots is also disrupted. Due to such events, the leaves age much faster.

To overcome this dangerous ailment, you can use such highly effective drugs:
- Alto Super;
- "Abacus";
- Rex Duo.
It is worth noting that treatment with folk remedies against powdery mildew, as a rule, does not bring the desired results. Such measures can only be used as ancillary measures. It makes no sense to expect a greater effect from them.
Rhizomania
And this ailment is of a viral nature. It is caused by a virus of necrotic yellowing of veins. The main carrier of this disease is a unicellular parasite belonging to the order of plasmodiophores. Its activity level rises sharply against the background of high temperatures as well as high levels of humidity. When growing beets in areas in dry regions, the likelihood of rhizomania is significantly reduced.


However, the summer resident still knows better how this serious disease manifests itself.
- The original shine and elasticity of the beetroot foliage is immediately lost.
- The growth of culture is markedly reduced.
- There is an indispensable crushing of the size of the fruit. Their lower part is noticeably shortened. The inside of the fruit becomes much harder.
The course of this disease may well be completely asymptomatic. In this case, it will be possible to notice the fact that beets suffer from rhizomania only by a sharp decline in yield, a decrease in the quality of fruits.
Those plants that have managed to become infected with rhizomania should be treated with special fungicidal preparations. For example, effective is "Fundazol" or "Benazol". But the greatest results are brought by direct spraying of uterine fruits with the composition "Rovral".
Ramulariasis
Summer residents often confuse this disease with the ailment discussed above. Ramulariasis manifests itself in much the same way. The main difference between these whitenings is that the color of the spots with ramulariasis is much lighter, closer to white. In addition, with these diseases, spots of different sizes are formed.

If we consider the general symptoms of ramulariasis, then it is worth noting certain signs.
- On the foliage, gray-green spots are formed, which are distinguished by an irregular shape.Over time, these spots become brown, covered with a snow-white bloom.
- The tissues inside the stains begin to crack. Some time after this, the leaf plates themselves begin to fall off the plants.
- The characteristic specks extend down to the petioles.
- Beetroot fruits begin to shrink.
These symptoms are hard to miss. So that a serious illness does not continue to develop further, all plants that have managed to become infected need to be thoroughly treated with special preparations. These include the Rex Duo fungicide. If there are damage in small areas, then all diseased specimens can be simply removed, and then be sure to process the soil.
Peronosporosis
This name is a disease that very often affects garden crops, including beets. Otherwise, downy mildew is also called downy mildew. This disease affects beets most often. This is especially true of those plants that grow in a humid climate.


Downy mildew is a fungal disease. As a rule, it has a particularly strong negative effect on beet tops. Because of this, a whitish bloom first forms on it, and after a while yellow spots break through. The latter begin to grow rapidly, spreading over the entire leaf plate of the plant. The main signs of the appearance of peronosporosis are other events:
- foliage deformation occurs;
- leaf tissues become much denser and thicker, rapid dying off occurs;
- peduncles are also deformed, their development is noticeably inhibited.
To effectively combat this disease, it makes sense to use the following popular drugs:
- Apron;
- Amistar;
- "Acrobat".
The same funds are allowed to be used as preventive measures. You can also turn to certain preventive procedures, which provide for the timely removal of affected plants, a more careful selection of planting materials.
Fusarium
This disease often affects beets planted outdoors. The disease is fungal. Pathogenic fungi can penetrate into the body of a root crop through rhizomes. Gradually, Fusarium will move from roots to foliage, changing their appearance.

The main symptoms of the onset of the disease will be as follows:
- the leaves turn yellow, first the older ones change, and then the young leaf plates;
- petioles begin to darken and rot;
- there is a blackening of the vascular bundles of the roots, auxiliary roots appear in large quantities.
If beets are severely affected by Fusarium, they die even in the first stages of their development. Sometimes dry rot can persist in the flesh until harvest. There are no highly effective means aimed at combating fusarium. The summer resident can only resort to certain preventive measures:
- it is necessary to clean the site of all plant residues, dig up the ground;
- for planting, it is best to choose beet varieties that are resistant to fusarium;
- plants should not be planted in the same places for 2-3 years;
- make sure that the roots do not receive mechanical damage;
- planting must be processed during the growing season, the preparation "Kagatnik" will do.
Rust
Rust can be safely called an agricultural pest. Its pathogen settles precisely on beets. The fungus is actively developing in spring and summer. Its appearance is immediately reflected in the state of the sheet plates. A variety of preparations can be used to effectively combat rust. The most effective are usually shown by "Abacus", "Alto Super", "Amistar Extra".


Jaundice
Viral disease. Most often it affects beets in the first year of its life. We will learn about the characteristic symptoms of this disease.
- The lower and middle leaves turn yellow.First, they turn yellow in the upper part, and then along the extreme zones between the main veins.
- A noticeable necrotization of the veins appears on young leaves.
- Diseased leaves change their shape, look shorter than healthy foliage. Their surface becomes less smooth. Brittleness increases.
To fight a dangerous virus, it is advisable to resort to competent preventive measures. First of all, it is necessary to process plants from aphids. If the plants have already been affected, they will need to be burned.


Good results are also shown by the treatment of beets with insecticidal preparations. For example, you can use "Phosphamide".
Mosaic
Viral disease. It often affects not only beets, but also broad beans, spinach and cabbage. It manifests itself in a noticeable mosaic type pattern on the foliage. After some time, the foliage deforms and dies off. Leafhoppers and bedbugs can carry the disease, so you always need to get rid of them on the site.
Beets affected by the mosaic lose their former sweetness and produce much fewer seeds. Effective methods of treating this ailment have not yet been developed.

Gray rot
Disease of a fungal nature. It can affect not only beets, but also completely different crops on the site. Often, gray rot begins to actively develop precisely at the time of planting vegetation or during storage of root crops. In particular, such problems often arise if the storage is kept at an elevated temperature along with high air humidity. Symptoms of gray rot are as follows:
- root crops are covered with round brownish spots;
- gray-green mold forms on the affected areas;
- the fruits soften, the green mass fades.

To prevent the development of this ailment, the fungicide "Glyocladin" is used. In addition, the site is scrupulously cleaned of all plant residues.
White rot
Another name for this disease is sclerotinosis. The disease is fungal, spoils not only beets, but also carrots and other vegetable crops.
It can be recognized by its specific symptoms.
- The affected areas soften, become covered with abundant mycelium, become like cotton wool to the touch.
- The affected areas are denser. Initially, white, and a little later, black hard bumps are formed on them.
- Then there is an absolute softening of the root crop.


In the fight against the problem, the following means are often used:
- "Akanto Plus";
- "Absolute";
- Alpha Standard;
- "Amur".
Red rot
It is also called felt disease.

Consider the main signs of the development of this ailment.
- On root crops, subcutaneous spots of a lead-gray shade are formed. Above them you can see the mycelium.
- In the future, many black sclerotia are formed on the harvested fruits.
- Affected tissues are both soft and hard.
- Leaves wither soon with profuse lesions.
In order not to lose the beet crop, it should be treated with fungicides, for example, "Alirin-B" or "Gamair". Folk remedies in this case will be useless.
Blackleg
This ailment is also called root-eater. It affects many cultures.

Because of it, the roots darken and rot, the seedlings grow very slowly, the leaves wither. Rapid growth of seedlings with such a disease can not be expected.
You can treat a black leg with fungicidal preparations or dusting with ash. Seedlings are often watered with soda solution.
Common scab
Fungal disease. It leads to the appearance of rough patches on root crops, forms a dark brown crust.


Beet growth slows down due to scab. The following remedies can be used against this disease:
- "Discor";
- "Pure color";
- "Speed".
Bacterial cancer
A very serious bacterial disease. Not as common on table beets, but can have a significant impact on the condition of the crop. Forms smooth neoplasms, leads to the appearance of growths on the beet neck, to thinning of seedlings. Tumors can even appear on the leaves.
To fight bacterial cancer, you must follow the appropriate rules of agricultural technology. Of the chemicals, Fitolavin and Fitoverm are ideal.


Pests and the fight against them
Consider a description of the most dangerous pests for beets, and also find out in what ways you can fight them.
- Beet fly. Slows down the growth of plants, feeds on their sap. You can spray the beets with an onion peel-based solution against flies.
- Wire beetle and bear. The roots of the plant are devoured. To combat them, beets can be sprayed with Bordeaux liquid.
- Shield-bearer. Insects gnaw out visible holes in the foliage without touching the veins. You can fight them by weeding weeds, processing biological products, spraying with insecticides.
- Aphid. Often planted crops are eaten by these harmful insects. They take away all the juices from the plants. You can fight aphids by spraying with soapy water. You can use drugs "Karbofos", "Iskra", "Commander".



Prevention measures
We will learn how you can protect beets from diseases and pests through preventive measures.
- It is imperative to adhere to the norms of crop rotation.
- It is necessary to regularly cultivate the soil to protect plants from diseases. For these purposes, use special disinfectants. You can feed the culture with manure or specialized vitamin and mineral components in the complex.
- It is necessary to liming the soil. For this, slaked lime, wood flour or ash are used.
- Requires the most scrupulous selection and proper preparation of the planting material itself.
- It is imperative to remove all weeds and plant debris. Damaged plants must be burned so that the disease does not spread further.
- You must always monitor the condition of the beets on the site. At the first signs of the appearance of any disease, it is important to water or spray the crop with suitable means on time.


See the next video for more details.













The comment was sent successfully.