Review of diseases and pests of peppers

Pepper is a nightshade crop, which, unfortunately, like all garden dwellers, is susceptible to pests and diseases. It is worth noting that quite serious problems can be encountered when growing peppers both in greenhouses and in the open field. That is why an overview of the most common diseases and the most dangerous parasites, as well as ways to combat them and preventive measures, will be relevant.

Description of diseases and their treatment
Before processing plants using folk remedies and modern drugs, it is necessary to find out the causes of the problems that have arisen. If you do not decide on a specific disease of sweet (bell pepper) or bitter pepper, then the treatment is likely to be ineffective, and sometimes it can be harmful. Modern gardeners have to deal with a whole list of diseases belonging to various categories:
-
fungal;
-
bacterial;
-
viral.



In addition, the ailments of peppers are also of a physiological nature. So, the plant is often affected by apical rot, which many mistakenly classify as infectious diseases caused by fungi and bacteria. This attack manifests itself at the stage of formation of fruits that are in dire need of calcium. An indicator of the development of the disease will be the appearance of whitish, yellow or brown (similar to rust) spots on the tips of the peppers.
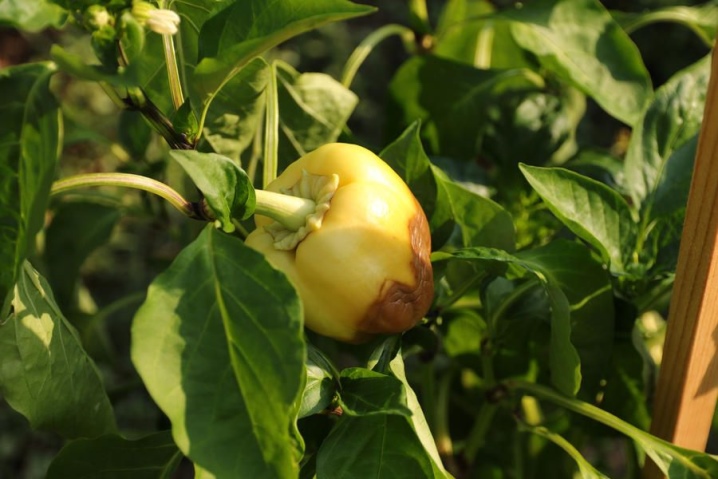

To effectively treat apical rot, you first need to know the causes of calcium starvation in plants. Most often, the following factors prevent the assimilation of this element:
-
peat soil, which is characterized by an acidic reaction;
-
use for irrigation of water with a high concentration of iron;
-
regular feeding based on ash;
-
sharp temperature fluctuations;
-
drought.





As a rule, the increased content of the peat component in the soil becomes the reason for the lack of calcium due to acidification. Dolomite flour and, of course, ordinary chalk are the sources of this element. But it is worth considering that they contain it in a form that is difficult to access. Given this feature, chalk and flour are used in tandem with table vinegar.


Often, gardeners choose calcium nitrate, but this remedy is recommended to be used as a preventive measure, before the first ovaries appear.
Fungal
This type of disease of the described vegetable crops occurs most often. The main of the favorable conditions for their development is predictably excessive moisture. In this case, the methods of treating a plant that is sick are largely determined by the type and characteristics of the pathogen.
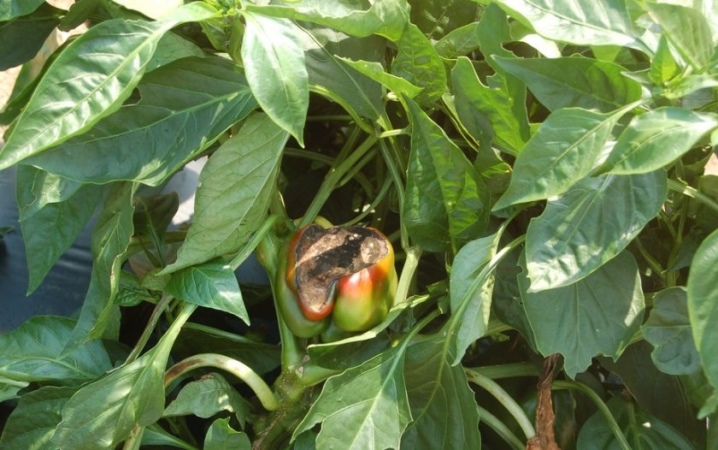
One of the most common fungal diseases is late blight, which is popularly called "brown rot". The first symptoms of damage to the plant will be yellow spots on the foliage, which turn brown rather quickly, in parallel with this, a mealy bloom forms on the inner side of the plates. As a result of the progression of the fungus, the affected plant tissues die off, and the leaves curl and dry out.

At the same time, dark segments appear on the fruits, which, growing, become the cause of rotting.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, late blight threatens vegetables grown in the open field, and the peak of diseases occurs at the end of the first summer month. The chance to save plants from an epidemic exists only at the initial stages of the development of the disease. To do this, you will need to carefully process all the leaves and stems and spray them with saline (1 glass of sodium chloride per 10 liters of water). And also experienced gardeners successfully use "Trichopol" at the rate of 20 tablets for the same 10 liters.
And also it is worth paying attention to other dangerous fungal infections and methods of countering them.
-
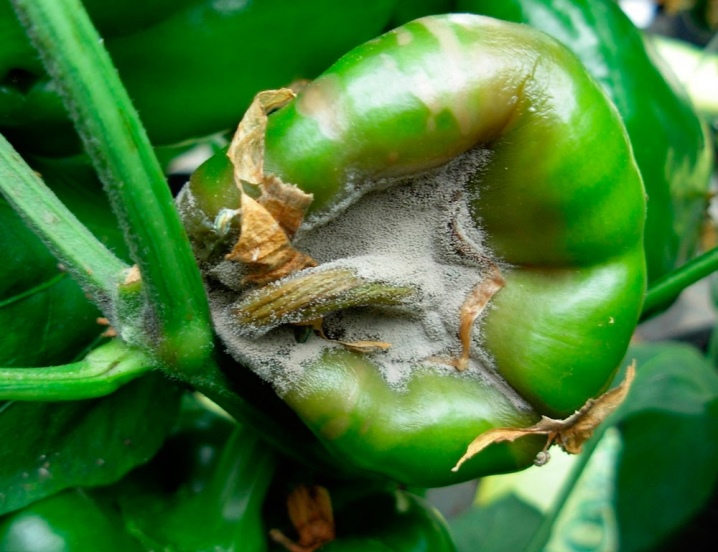
Gray rot caused by a fungus of the genus Botrýtis Cinerea. It is one of the most common diseases in greenhouse peppers. The phytopathogen in this case affects stems, foliage, flowers, ovaries and fruits. The latter eventually begin to rot, and a gray fluff appears on them. When the first symptoms of a fungal infection are detected, it is necessary to treat with such fungicides as "Luna Tranquility", "Fundazol" and "Switch".

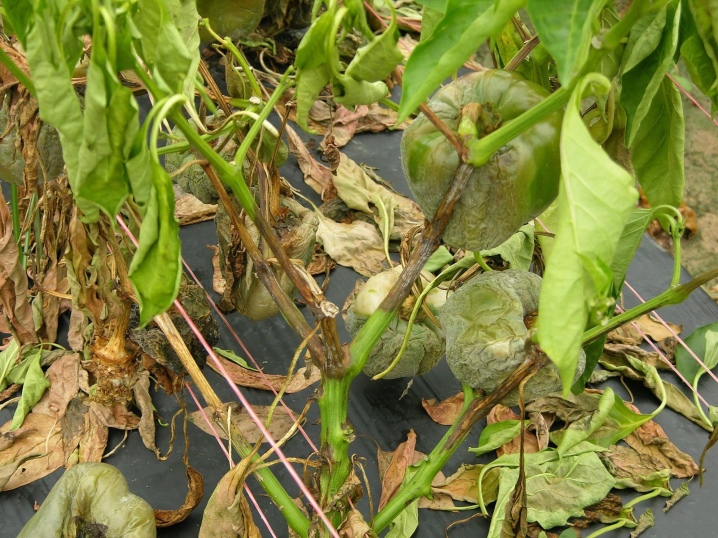
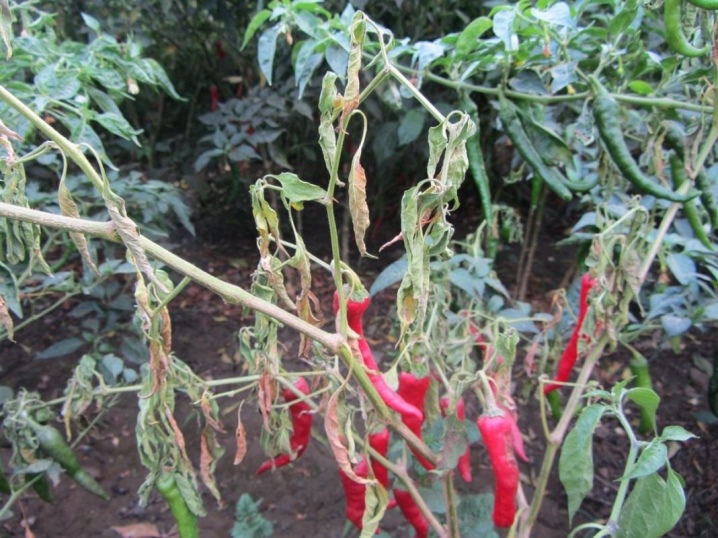
- Wilt (wilt or fusarium) - a disease that is dangerous primarily for seedlings of peppers, but also capable of harming grown bushes after they are planted in a permanent place. Initially, the fungus affects the lower leaves, after which they begin to turn yellow, dry and fall off. Such bushes lose the ability to form ovaries, and the fruits that have had time to form cease to develop. In such cases, diseased plants must be removed together with earthy clods and burned, and healthy individuals must be treated with Topsin-M or Maxim.

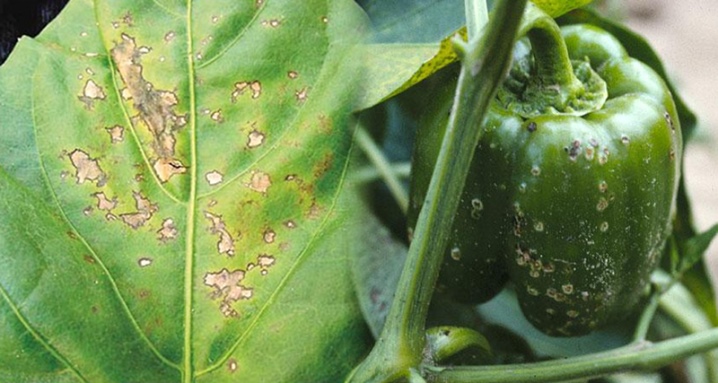
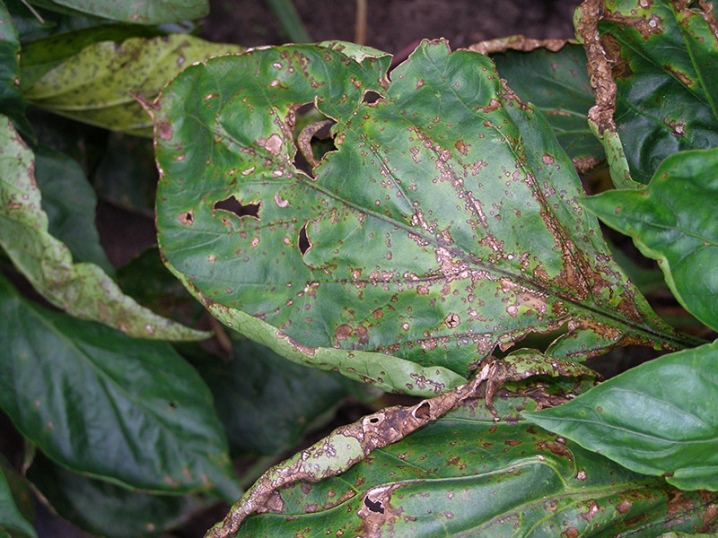
- Alternaria or black spot - a fungal disease, the outbreaks of which are more likely in rainy and rather cool weather, as well as noticeable differences between night and day temperatures. The main sign of infection is the appearance of necrotic formations on the leaves, which quickly merge into one whole, which leads to the death of the leaf plates. Sick bushes must be removed and burned, and uninfected plants must be treated with copper oxychloride or Bordeaux mixture.


- Anthracnose - the consequence of seed and soil contamination. This fungal disease can affect all aerial parts of the nightshade crop. In this case, spots and ulcers will appear on the bushes, having a purple border with an orange or pink tint. Effective means of treatment and prevention of disease are 1% Bordeaux liquid and the drug "Tiram".


The most affected parts of the plants must be carefully cut and burned.
- Cladosporium - a fungal infection that poses a danger to greenhouse peppers. Its development is observed during the period of flowering and the formation of ovaries. The lower leaves are primarily affected by pathogens. Yellow spots appear on them, which then acquire a brown tint, as well as a gray bloom. Treat infected plants with fungicides "Zaslon" and "Barrier".
Bacterial
Diseases in this category are similar in many ways to the fungal infections described earlier. It is for this reason that in some cases it is quite difficult to correctly identify the problem.... Taking into account such nuances, many experienced gardeners, when fighting phytopathologies, prefer to use universal means. This refers to drugs that have both antibacterial and antifungal effects.
The most common diseases of this type are primarily bacterial cancer of bell pepper. Its pathogens are bacteria known as Clavibacter Michiganensis. The disease most often affects crops grown in the southern regions, as well as in greenhouses and greenhouses. It is possible to determine the defeat of peppers by discolored leaves and necrotic spots on the fruits themselves, the size of which reaches 3 cm.Plants can be saved by processing at the initial stage of cancer development "Fitolavin" and means containing copper.
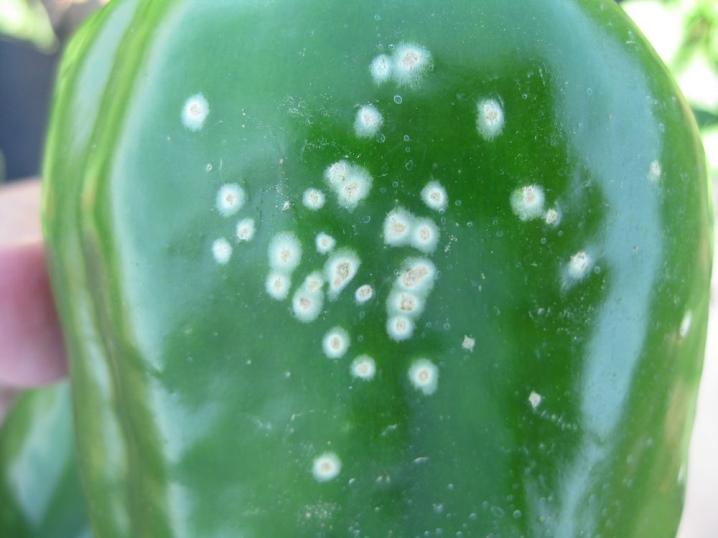

Another dangerous disease is black bacterial spot, provoked by the bacteria Xanthomonas Vesicatoria. Watery black spots appear on the stems and foliage of the diseased plant. Most often, the affected segments are located along the veins of the leaves. In addition, the appearance of convex points on the fruits is recorded, which will increase in size over time.

In this case, the surface of the infected peppers will become rough, the spots will eventually transform into ulcers, and the fruits will rot.
Active and, one might say, with a record rate of reproduction of pathogenic bacteria in this case occurs at high humidity and air temperatures in the range of 25-30 degrees Celsius. The main and most effective methods of dealing with black spot will be fungicidal agents. And first of all we are talking about about bordeaux mixture and the drug Abiga Peak. For prophylaxis, it is necessary to treat the seed material in a timely manner before sowing. In addition, it is important to follow the rules of crop rotation, and also not to forget about the need for spraying using the popular "Fitolavina".


Viral
In this case, we are talking about diseases that maximally negatively affect the yield of peppers, reducing it by 50% or more. In terms of the degree of danger, viruses differ significantly from the bacterial and fungal diseases described above, in which in the early stages there are chances to save infected plants. Viral phytopathologies, as a rule, lead to the death of nightshades and other vegetable crops. In this case, the following viruses become the most common sources of problems:
-
cucumber and tobacco mosaic - PTO and TMV, respectively;
-
soft mottling;
-
bronze;
-
stolbur.





Aphids, thrips and some other pests are among the distributors of viral diseases of peppers. The list of the main symptoms of the tobacco mosaic virus includes:
-
spots on the upper leaves in the form of a mosaic;
-
twisting of sheet plates into "boats";
-
the development of dwarfism in affected bushes;
-
sterility of flowers;
-
formation of chlorotic sites on fruits.
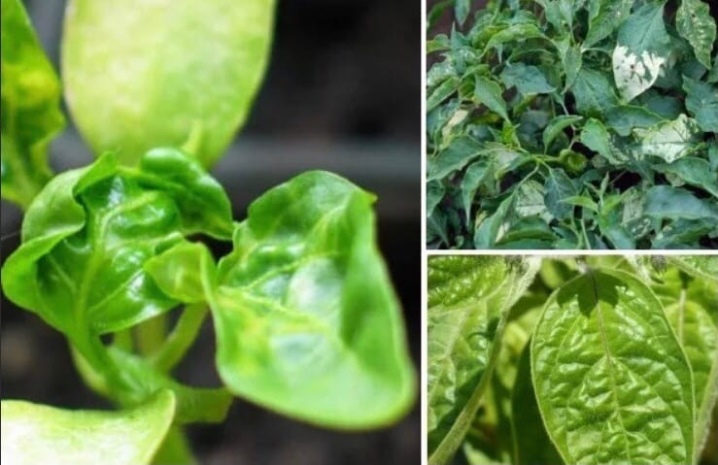

If the plant has become infected with the cucumber mosaic virus or soft mottles, then the symptoms of the disease will be similar. When the bronzing virus is infected, spots of a brown or olive shade will appear on the foliage and fruits. In parallel, black and brown stripes appear on the stems.
Stolbur is characteristic mainly of the southern regions, and cicadas become carriers of the viral disease. The list of signs of the disease includes shrinking, yellowing and curling of the leaves.
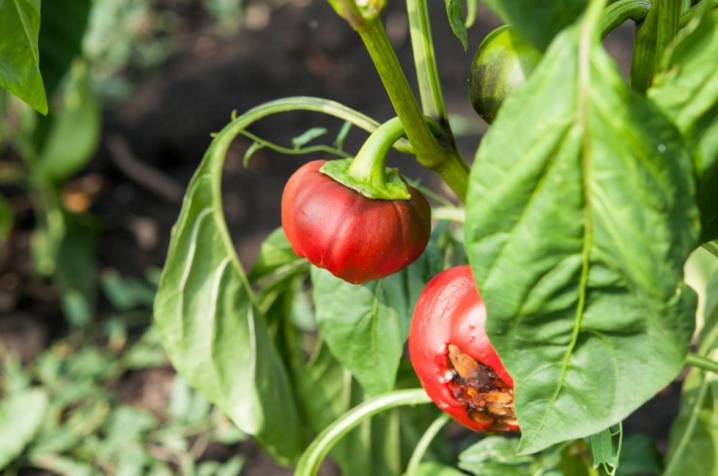

At the same time, the flowers of the peppers become sterile, and the fruits that have had time to form stop growing and begin to deform quickly. The bushes themselves wither.
Unfortunately, at the moment there are no effective methods of fighting viruses. It is impossible to save plants affected by such diseases. The only effective measure so far remains exclusively prevention.
Pest control
Both outdoors and when growing peppers in greenhouses, plants can be attacked by insect pests. As a result, gardeners begin to notice that someone is actively eating the foliage on which holes have appeared. Naturally, these are not the only signs of the presence of parasites. But in any case, it must be remembered that they are all capable of causing irreparable harm to peppers and all other crops in the garden and in the greenhouse.
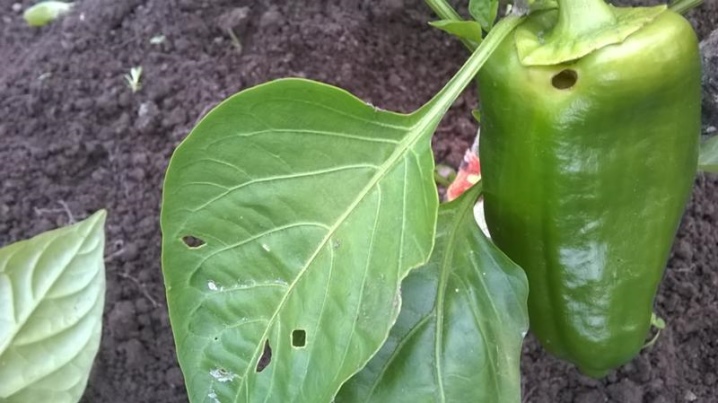

Given the potential danger and the importance of dealing with its sources, it is worth highlighting the following list of insect pests and ways to get rid of them.
-
Nematodes - representatives of roundworms that parasitize many plants, including sweet peppers. Today, three varieties are known: leaf, stem and root. In the overwhelming majority of cases, nightshades are attacked by the last type of nematode, which "gnaws" the roots.It is important to note that so far there is no effective means of combating this pest. Known insecticides and fungicides have little effect on it, since we are talking about roundworms. Gardeners can spray plants with drugs such as Nematofagin MikoPro and Vidat.


- Spider mitewhich appears on peppers mainly in hot weather. Signs of the presence of the pest are yellow specks on the leaves, a gray coating that resembles a layer of dust on the inner side of the plates, as well as a subtle cobweb covering the aerial parts of the plant. As part of the fight against harmful arachnids, peppers can be watered and sprinkled with appropriate means. Sunmite, Vermittek, Antiklesch, as well as Karbofos and other acaricides have proven their effectiveness.
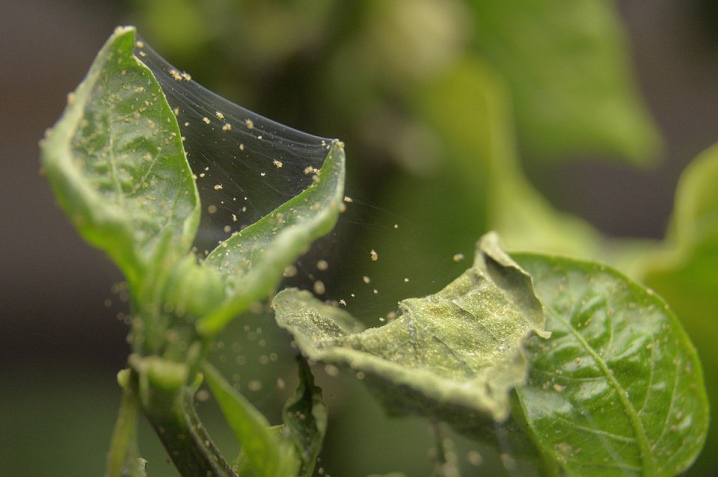

To ensure the achievement of results, it is recommended to carry out three treatments with an interval of 7-10 days, alternating the drugs used.
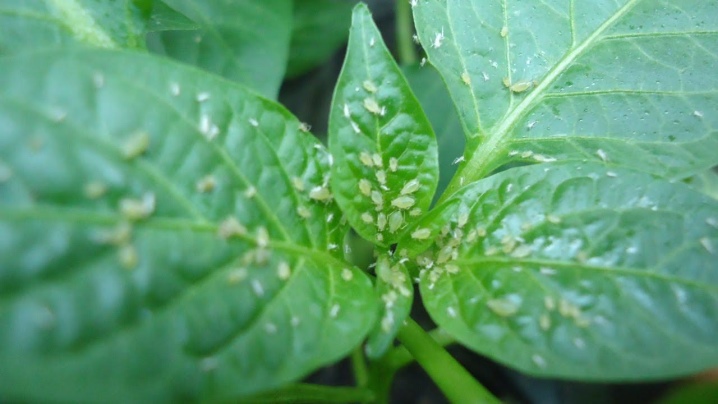
- Aphid - a pest that often attacks plants in greenhouses, and its spread is soil infested with larvae. Ordinary ants can also contribute to reproduction, which feed on insect debris, and therefore act as their natural defenders. Fighting this parasite, you should initially get rid of the anthills on the site. On the affected plants, the leaves are actively curled, the flowers that have had time to appear wither and fall off, and a characteristic sticky substance appears on the vegetative organs. "Karbofos", "Intavir", "Actellik" and other insecticides will help to destroy the parasite. The list of effective biological products includes "Aktofit", "Fitoverm" and "Entobacterin".

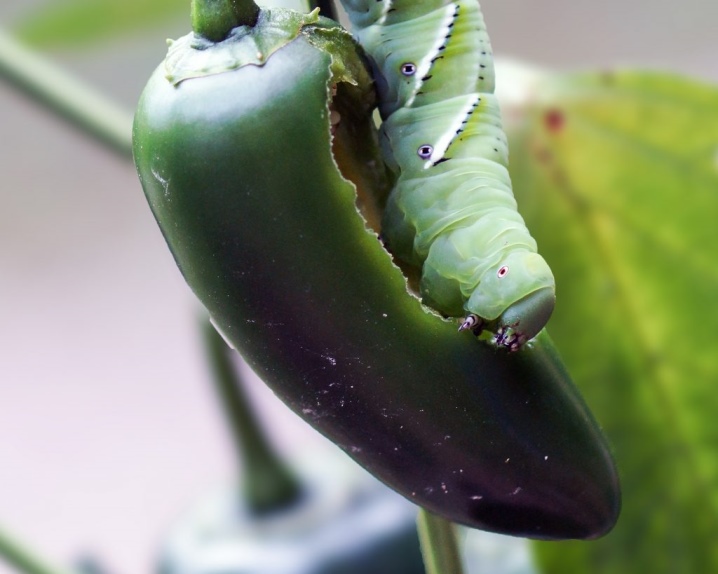
- Scoops - leaf-eating caterpillars, which also feed on the stems and roots of peppers. Pests are active at night, hiding in the ground during the day. High humidity is favorable for breeding. For the extermination of harmful caterpillars "Gerold", "Decis Profi", as well as "Initiator-200" and "Alatar" are successfully used.

- Thrips, the main symptoms of the appearance of which will be deformation of the leaves and the appearance of yellowish spots on them, as well as the falling of flowers. Three-time treatment with 10-day breaks with "Aktara" and "Fitoverm" will eliminate the parasites.

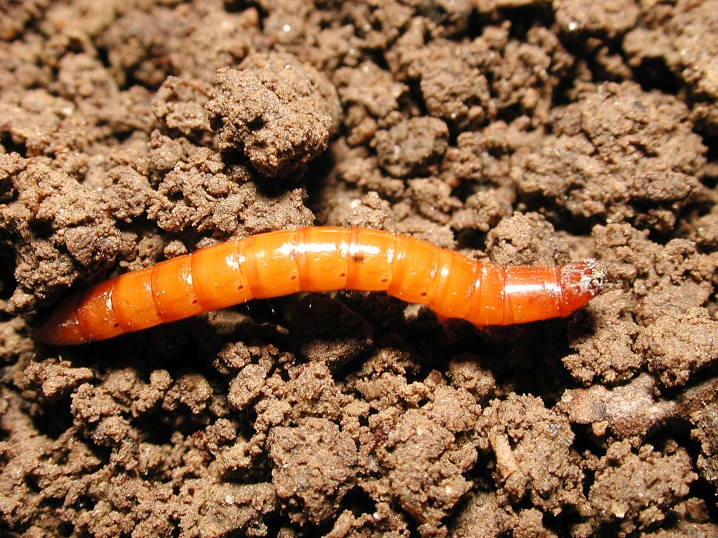
- Wireworms, which are the larvae of the click beetle, settle in the ground at a depth of about 12 cm and feed on the roots of peppers. Chemicals, as well as sowing green manure, will be effective measures to combat them. However, it should be borne in mind that the second option of action will give results only in the second season after the detection of pests. After harvesting and removing all plant residues, it is recommended to sow mustard or rye on the site.

It will remain in the spring after germination and dig up the beds before planting nightshades.
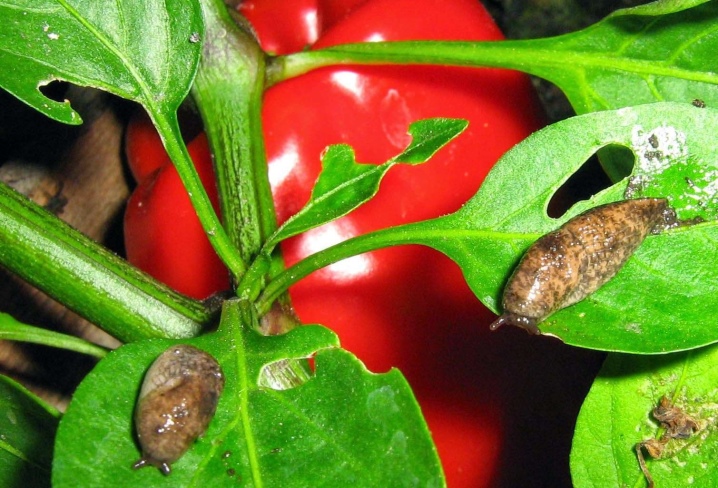
- Slugs, which most often appear at high humidity and temperatures within +25 degrees. The pest eats at night and gnaws at the leaves, leaving holes of different sizes in them. For the destruction of slugs, use the "Slime Eater" and "Thunderstorm Meta". The list of effective folk remedies includes slaked lime and wood ash, which are sprinkled on the soil around the bushes.

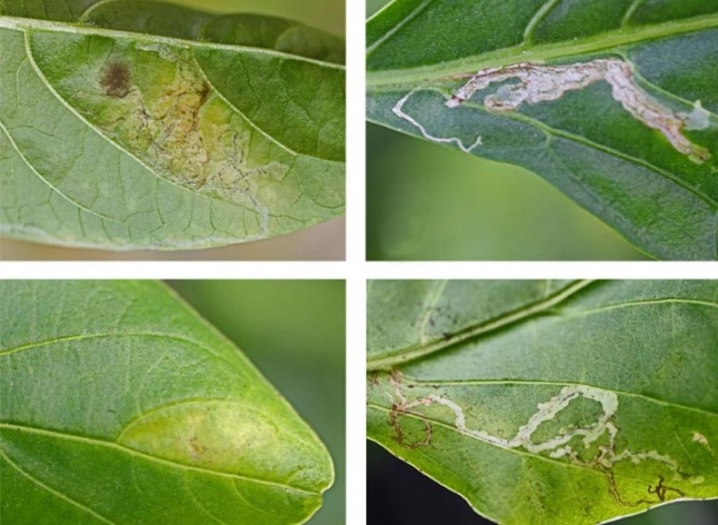
- Solanaceous miner - a parasite that actively infects both sweet and bitter peppers in the open field, as well as in greenhouses and hotbeds. The main source of danger is precisely the larvae that penetrate the foliage and gnaw through the passages there. A comfortable temperature for a mineral ranges from 25-30 degrees. Effective means of fighting this pest will be "Tianid", "Varant", as well as "Vermitek" and "Spinosad".

- Bedbugs - insects that bite through developing fruits and inject toxic liquid into them. As a result, such peppers become unsuitable for human consumption, as they become bitter in taste and acquire a specific "aroma". In addition, the fruits of the vegetable crop quickly begin to rot.You can resist bedbugs with the help of insecticides used to kill aphids and whiteflies.

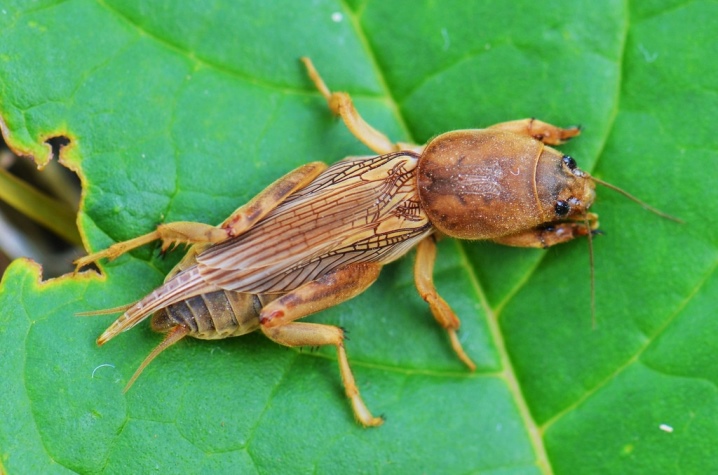
In addition to all of the above, do not forget about such a dangerous pest and enemy of all gardeners as bear... Its adults eat ovaries, buds and leaf plates of peppers. The bear larvae cause irreparable damage to the root system of vegetable crops. To get rid of the pest quite quickly, tools such as Zemlin, Vallar and Antikhrushch.

It is worth noting that the arsenal of effective fighting tools is constantly being updated and expanded.
Prevention measures
Of course, it is much easier to prevent the development of diseases and the appearance of pests than to deal with the consequences later. As a rule, the treatment of plants and the removal of insects is time consuming and labor intensive. Moreover, there is a risk of being left without a crop at all.
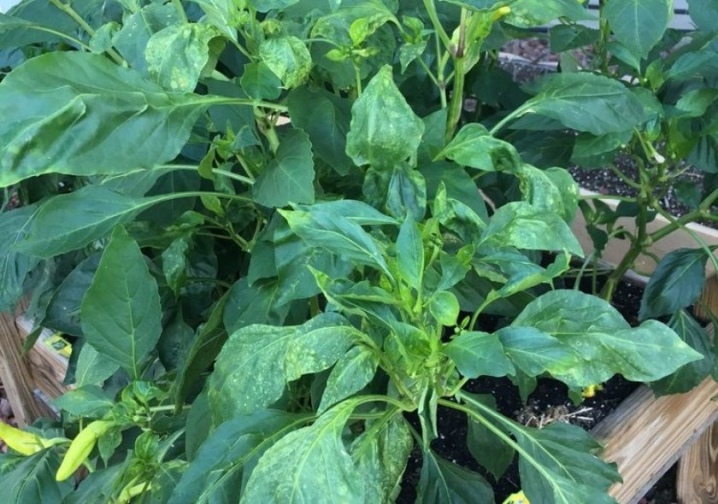

Based on this, it is necessary to highlight the following preventive measures to prevent many dangerous diseases:
-
strict adherence to agricultural technology;
-
careful study of the theory and recommendations of breeders;
-
the correct choice of varieties resistant to infections, the acquisition of exceptionally healthy seed material;
-
alternation of crops cultivated on the site every year;
-
soil disinfection;
-
strict adherence to the rules for caring for seedlings;
-
obligatory processing of the used inventory;
-
regular weeding;
-
removal of plant residues after harvest;
-
spraying plantings;
-
planting of green manure and analysis of crop compatibility.




Experienced gardeners successfully use the processing of plots and the peppers themselves serums, Bordeaux mixture and copper sulfate... These time-tested measures help protect plantings from most diseases and harmful insects. And you can also process plants "Fitosporin", which is a natural biofungicide.
This drug is considered one of the most effective antifungal and antibacterial agents.
To provide protection from insect pests, and ultimately to reap a decent harvest, it is highly recommended to follow simple rules.
-
Dig up the soil in a timely manner.
-
Apply both organic and mineral fertilizers correctly and on time.
-
Plant peppers where onions or legumes were previously grown.
-
Water the plants weekly with settled water.
-
For prophylaxis, treat the bushes with soapy water.
-
Inspect peppers regularly to see if pests have appeared.
-
Apply periodic sprays to keep ants and snails away.
-
To prevent the appearance of a bear on the plots, use rotted manure at least 2-3 years old.




The listed rules of care are extremely simple. However, ignoring them can be truly disastrous.













The comment was sent successfully.