Cabbage moth: description and methods of struggle
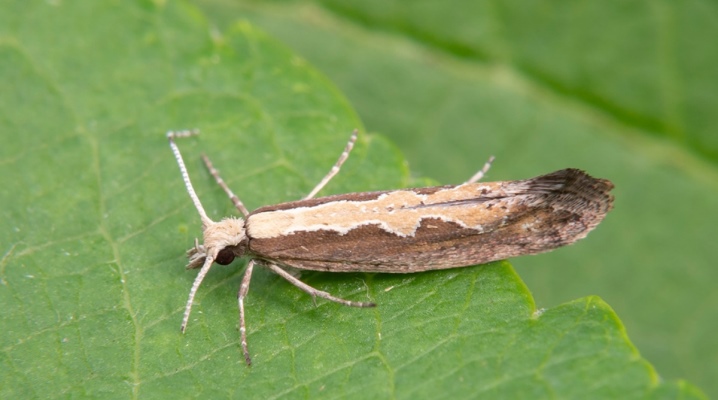

The cabbage moth is a parasitic insect that costs nothing to spoil the entire crop. She lives, develops and procreates due to this. There may be nothing left of the seasonal cabbage harvest if you let things take their course and do not come into opposition with the moth. And this can and should be done if the pest is already visible on the plant.


Description of the pest
The cabbage moth is an insect of the genus of butterflies, has wings up to 8 mm long, light brown in color. She looks rather faded, therefore it is far from immediately striking. And from a distance it will not work at all to see the moth: it successfully disguises itself as ordinary brownish twigs. The moth lays eggs from which caterpillars hatch.
And now they are happy to eat cabbage leaves, and adult insects are not averse to feasting on flower nectar. At one time, an adult moth can lay a maximum of 5 eggs, they are very small, only 0.4 mm. The eggs are greenish and unrealistic to see.
They lay them right in the cabbage, and after 3 days you can expect caterpillars, which will pupate in 3-4 weeks.


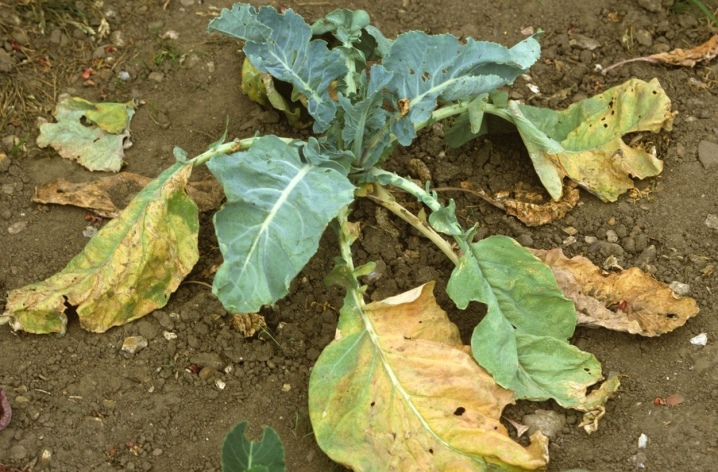
The main type of insect pest is called the cabbage moth, but it is the caterpillar that has the most formidable effect on the harvest. As soon as they are born, they begin to eat the leaves and quite quickly seriously injure the plant. To destroy 1 head of cabbage, for example, only 2-3 caterpillars are enough! And if a whole family settled in the head of cabbage, needless to say, how quickly they will destroy the crop. The affected plant will slow down in growth, and then completely begin to rot. And all because of the small and nondescript moth and its larvae.
When the caterpillars eat one head of cabbage, they will not calm down and start after another, calmly crawling to the next one. And when the caterpillar is reborn into a moth, it will stop eating cabbage, but will gladly lay offspring in its leaves. That is why this vicious circle must be broken and not allowed to continue the process of laying eggs, hatching, maturation, etc.


Reasons for the appearance
The appearance of this parasite is cyclical. It depends mainly on the climatic context, on the level of temperature and humidity indicators. It is believed that this type of moth en masse spreads in years with warm and rather humid, so-called mild winters. Thanks to this weather, cruciferous weeds develop earlier than usual, and it is they that become the fodder base of the first generation of the parasite. And if then the dynamics of positive temperatures is stable, then the first generation of moths will develop actively and without hindrance, and then the time of the second generation will come, and a full cycle will start.
Heat, dry summers are also very good conditions for the parasite. In such a season, it is the cabbage moth that can become the leader in pests that massively destroy cruciferous plants. Another risk factor that the summer resident can definitely influence is the permanent cultivation of crops in one place. If cabbage grows at the same point on the plot for 6-8 years in a row, the risk of such a misfortune as cabbage moth increases significantly.
In a warm climate, the pest can produce up to six generations, in more severe climatic conditions - no more than two or three generations.


Control methods
If a pest is found on the site, then all cruciferous plants need to be processed, not only cabbage. If mustard, turnip, rapeseed, radish or arugula grow in the garden, they are also at risk. The butterflies themselves start flying over the plants late, after sunset, so fixing them is problematic. But if damaged leaves were found, with a high probability we can talk about moths.
If you turn the inside of the leaf, you can see the caterpillars eating it. A superficial inspection of the plant from above may yield nothing. It is obvious that the plant will suffer from the attack of parasites - general lethargy, weakness, the appearance of yellow spots on the leaves are very characteristic signs of damage. If the yellowing has covered the entire head of cabbage, this is almost the death of the plant.

Chemicals
Of course, few summer residents or gardeners want to use "chemistry" on their site. It is logical that you want to get rid of the pest as gently as possible, without any risk to the crop, but this is not always possible. If it is noted that more than 10% of all plants are already affected by the cabbage moth, then it is the chemical agents that should be used. If there are more than 3-5 larvae on a cabbage bush, you cannot hesitate.
"Chemistry" of which classes can be used:
- neonicotinoids;
- pyrethroids;
- organophosphorus compounds.
These groups include Karbofos, Chlorofos, Karate, Aktellik, Nurell, Ambush, Fury, Ripkod, etc. known to summer residents. Any of these drugs requires strict observance of measures security.
These are toxic agents, conditionally dangerous both for the user himself and for the crop. If you exceed the dosage, dilute the composition incorrectly, you can destroy the plant.



One of the most popular chemical products against cabbage moth is Actellik. It is a hazard class 2 chemical insecticide. The drug is considered very toxic, but due to its strong action, it shows such effectiveness. It is released in ampoules, each 2 ml. The product is to be dissolved in water. A ready-made solution from special equipment is already being sprayed. The person performing the treatment must be protected: glasses, a respirator, gloves are required. Otherwise, you can get a strong allergic reaction, etc. The processing of the crop must be postponed to the day when the weather is clear, stable, and the next couple of days do not promise rain. During these days, all pests that are firmly entrenched in the cabbage will die. They will not have time to move to other heads of cabbage and other crucifers.
But chemical insecticides also have disadvantages: it leaves no chance for caterpillars and butterflies, but it may not affect pupae and adult larvae. To destroy them, you will have to carry out a new procedure after some time (play "finishing off"). Before using any proposed chemical, you need to carefully read its instructions (there may be nuances provided by the manufacturer) and make sure of the processing time. Chemical treatment is not possible during every period of plant growth.

Bacterial agents
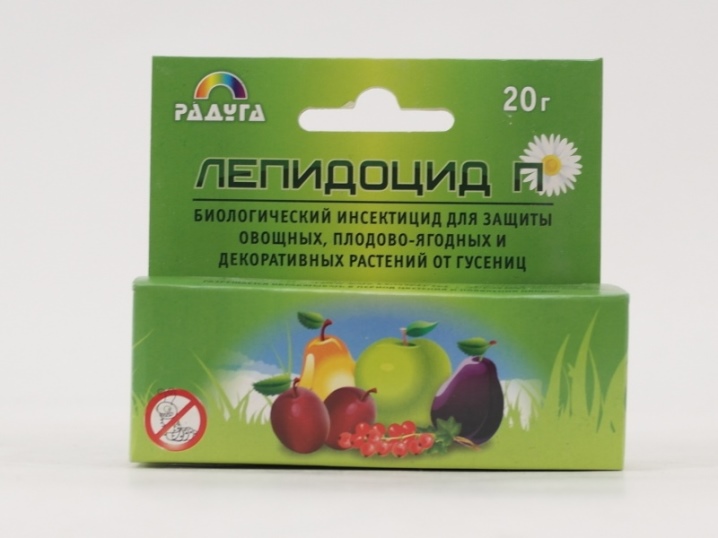
Otherwise, they are called microbiological insecticides. They are based on bacterial spores and their toxins. A caterpillar eating a leaf of a cabbage or other cruciferous plant does not suspect that it has been treated with such a bacterial "weapon", and it is fraught with paralysis for it. The preparations of this cycle are effective only if the temperature outside is above +16, at this time the food activity of the moth increases. Insects, by the way, do not die immediately, only after 3, or even all 5 days. It should be noted that bacterial preparations have no effect on humans and animals, they are not toxic to them, which makes them more preferable.
Bactospein, Lepidocid, Dendrobacillin, Gomelin, and also Entobacterin will be on the list with these funds. Take, for example, "Lepidocide" - bacteria in its composition kill the cabbage moth in 2 days. If you spray the plants with this preparation, their protection is prolonged for 2 weeks. And this significantly affects the level of yield.
But bacterial agents are not without their drawbacks.Cabbage moth develops immunity to them, therefore preparations must be alternated in case of repeated use.

Folk methods
Many problems in the garden can be dealt with with the so-called folk methods. For example, physically, you can also cope with moths, but only if there is very little of it on the plant. If you aim at the manual collection of a few cabbage eaters, it is possible to stop their attack. But still it is difficult, because only some pests sit on the surface of cabbage leaves, no more than 30%, the rest, alas, cannot be approached.
Other popular measures include infusions. If you spray the plants with an infusion of tansy or celandine, wormwood, and maybe potato tops, the moth can also recede. For half a bucket of chopped greens of the listed plants, add the same amount of boiling water, necessarily equal proportions of the components. The grass is poured with boiling water and waited for a day. After that, the medicinal composition must be filtered and the plant is sprayed with this agent.

You can also treat cabbage with ash. They say that there is no better remedy for cabbage slugs, but it turns out that it can also fight moths. It is proposed to dissolve two glasses of ash in 10 liters of water, and throw a whole bar of good laundry soap there. And all this composition needs careful stirring, they are sprayed with damaged cabbage leaves.
A couple more recipes against cabbage moth.
- Take onion peel and tobacco, each ingredient for 200 g and pour 10 liters of water over them. The solution needs to be boiled for 2 hours and at the very end of boiling, add 200 g of finely chopped garlic cloves to the composition. The cooled composition is filtered, instead of boiled water, fresh water is added so that the liquid volume is 10 liters.
- Mustard powder in the composition of 100 g is poured into 10 liters of boiled water - the mixture is infused for 2 days. Before use, the solution is filtered and diluted with water one to one.
- A pound of fresh, finely chopped dandelion leaves (if not, you can replace 1 kg of dry ones) are poured with 10 liters of hot water. This solution is infused for 12 hours, after which it is filtered. To spray cabbage, the concentrate is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 3, 1 tablespoon of any liquid soap is added there.

Moth butterflies can also be caught using special traps. Cardboard or something similar dense is painted yellow (you can simply paste over it with bright yellow paper). Its surface must be greased with something sticky - petroleum jelly or just thick glue. And such traps are hung near the cabbage ridges: they are very attractive to moths.
However, this folk method can be replaced with a completely official one - purchase special pheromone traps. They are harmful only to insects, attract only them.
In the store, you should definitely clarify for which particular pest the trap is purchased.

Preventive measures
The main and reliable way to prevent the attack of the cabbage moth is to arrange a crop rotation. Even if the moth is not so terrible, then a decrease in yield due to a decrease in the concentration of minerals in the soil should alert the gardener. Every 3-4 years, the ridges need to be interchanged. What else can you do to prevent cabbage moth:
- thoroughly weed out all the grass in the fall, and then remove it from the site and only then dig up the soil;
- dig up the soil qualitatively, deeply, because the moth winters in the ground - after harvesting the parasite is dug into the ground and all the cold sits there;
- if you are engaged in planting early varieties and hybrids, proven and resistant, you can let the cabbage grow significantly until the moment of a potential attack by a moth, and a grown, stronger plant tolerates it better;
- inspection of emerging seedlings (especially during drought) helps not to overlook the pest, well-groomed plants have more chances to calmly go through the established life cycle.
So once, while in the garden, looking under the cabbage leaves, in broad daylight, you can stumble upon voracious young caterpillars. Either the summer resident attacks them, or they are the gardener's harvest. Carefulness and successful struggle for a rich harvest!














The comment was sent successfully.