What is wheat fusarium and how to treat the disease?

Wheat is one of the most important crops. A healthy rich harvest is important not only for the farmstead, but also constitutes an integral part of the country's food security. However, like many other crops, wheat can be sore. Fusarium is one of the most dangerous diseases.
Types
All cereals are susceptible to Fusarium. The disease leads to significant crop losses and a decrease in its quality. It is a known fact that in the 80s of the last century, due to fusarium, there was a shortage of marketable grain of the order of 20-50% in many regions of Russia, especially in the southern ones. In addition, the consumption of affected grain and products from it causes severe poisoning in humans and animals, and can lead to death.
The causative agent of the disease is a whole class of fungi that belongs to the genus Fusarium. They can affect different parts of the plant: roots and bases of stems, leaves, ears and grains. Fusarium head blight is a common type of disease for both winter and spring wheat.
It actively develops at temperatures above + 12 ° C and high humidity. The prognosis of the development of the disease will be especially unfavorable if such weather conditions coincided with the flowering phase.


Determination of the presence of a problem can be done by external signs. A typical description is as follows.
-
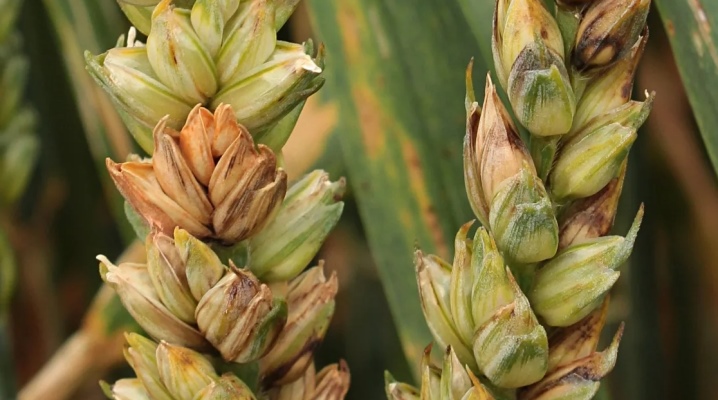
First, discolored scales appear on the spike, they are clearly visible when the background is still healthy green tissue.
-
Then the mycelium appears, which looks like a pink-orange or reddish-brick coating, depending on the type of fungus. Fungal spores are easily carried by the wind.
The susceptibility of the culture to pathogenic damage remains high from the beginning of flowering to harvesting the grain. The earlier the infection occurs, the higher the aggressiveness of the pathogen. The development of deformed and lightweight grains occurs in the ear. Affected grains, if they do sprout, are weakened sprouts prone to rot.
Some types of fungi do not form a colored plaque of the mycelium; instead, necrotic darkening, streaks, and eye spot can be seen on the scales of the spikelets. And it also happens that with fusarium, its visible signs do not appear. The contamination of grain and the presence of toxins will be revealed only by laboratory analysis.


Distinguish between early and late fusarium. With an early grain, it may not form, the grown grains are small, weak. Early disease leads to crop losses. When processing the crop, underdeveloped grains will be sifted out. They are not eaten, they are not suitable for future crops.
Late Fusarium blight will affect the quality of the crop. Since the disease began when the grains were already formed, it may not manifest itself outwardly in any way. Nice large grains will turn out to be toxic.
Another type of disease is fusarium root rot. Infection most often occurs through the soil. Pathogens can be found for a long time both in the soil itself and on the parts of plants remaining in the ground. Fusarium root rot is most often caused by poor agricultural technology, unfavorable climatic and weather conditions (for example, drought, crust formation on the soil). In diseased plants, few grains are formed, they are small in size. Grains may not form at all.


Treatment
It is very difficult to treat fusarium. You need to start fighting immediately, as soon as the first signs of the disease appear.It is very important to control the flowering phase. Today there are quite powerful drugs against fusarium, and the fight in the early stages of the disease can be successful. These drugs are fungicides. For example, the use of "Tebukonazole" will be effective.
There are methods for dealing with late fusarium. One of the main techniques is the use of additional fungicidal treatments. The first is the processing of seed crops. However, you will need to carry out a few more procedures. In this case, fungicides must be systemic. These are drugs that spread through the vascular system of the plant, suppressing the growth of the pathogen.
Fungicides can be used in many different ways.
-
Apply to soil. The product can be applied to the soil before planting or dissolved in water before watering.
-
Spray or dust with dry matter. If necessary, apply the fungicide over large areas in a short time using the aviation method.
-
Pickle the seeds. Both powders and solutions are used.

Means, as a rule, are taken different, alternating them so as not to reduce efficiency. The fact is that fungi can develop addiction to the components of the product.
To avoid the widespread spread of late Fusarium head blight, another method is used - desiccation. It is a method of speeding up the harvest. It consists in the fact that about 10 days before harvesting, wheat is treated with special chemicals. The culture is artificially dried to a state suitable for machine harvesting.
By reducing the amount of moisture in the grains, thereby increasing their ripeness, the procedure helps to reduce crop losses and increase its shelf life. Wheat is less exposed to wind and rain in the field. Especially important is the role of desiccation in unfavorable humid weather. However, you should be aware that a negative consequence may be the loss of the percentage of germination of seed wheat. Also, some chemical substances may remain in grain for food purposes.


Prevention measures
Like any disease, it is better to try to prevent fusarium than to use expensive (and not always subsequently useful for the consumer) ways to combat it. There are a number of necessary agronomic measures to protect against disease.
-
It is necessary to follow the rules of crop rotation. The most unsuitable predecessors are wheat, other grains and maize. Their remains perfectly accumulate and preserve the infection. Therefore, the fields must be thoroughly cleaned of the remaining plant parts.
-
It is necessary to carry out deep tillage.
-
Carefully select high-quality seed, purchase it from reliable suppliers. And also it is necessary to carry out pre-sowing preparation of seeds using dressing.
-
Observe the optimal sowing time and harvest on time.
-
Timely apply balanced fertilizer complexes containing microelements necessary for the culture. Carry out preventive fungicide treatment several times per season.
-
Avoid thickening of crops.
-
Refuse varieties with a long growing season. Use modern varieties that are as resistant to fusarium as possible.

Resistant varieties
Breeders are constantly working to develop Fusarium-resistant wheat varieties. However, this process is not fast, and Fusarium fungi are quite aggressive. Therefore, to date, it has not been possible to create varieties that would be completely immune to the disease. It is a known fact that soft wheat varieties are better resistant to fusarium disease, and winter crops are more resistant than spring varieties. By crossing frost-resistant species, scientists were able to obtain varieties that are quite acceptable in terms of resistance to infection.
They also have other beneficial properties.
-
"Thunder". Widespread winter wheat, frost-resistant varieties were taken to obtain it.It can be sown a week later than other winter varieties. Lack of lodging tendency allows harvesting with minimal losses.
-
"Stanichnaya". A variety with good yields and resistance to both frost and drought. Possesses high baking properties. It is a representative of varieties that are characterized by resource-saving technologies. When cultivating it, no pesticides are required.
-
Esaul. It belongs to the high-yielding early maturing varieties with excellent baking qualities. It tolerates frost and drought well, does not crumble. It does not lodge, except for fusarium, the variety is resistant to other diseases (yellow and stem rust, powdery mildew, head smut).
















The comment was sent successfully.