White bloom on currant leaves: causes and treatment of the disease
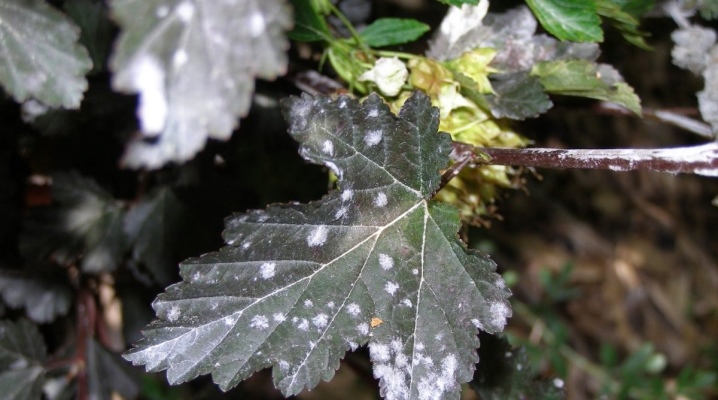

The appearance of a white bloom on a currant bush is a fairly common phenomenon. This is due to the activity of the fungus that causes a disease such as powdery mildew. This disease is very insidious and, if untreated, can destroy the currants in one season. In the summer, the infected bushes do not produce crops, and in the winter they freeze.
What is this disease?
Black currants are most susceptible to white bloom, while red and white ones suffer from it much less often. This is due to the low resistance of black varieties to fungal diseases, and therefore special attention should be paid to such bushes. Powdery mildew is caused by the fungi Podosphaera fuliginea and Erysiphe cichoracearum, which reproduce with the help of conidia. Fungal spores are quickly carried by the wind and insects around the area and affect not only currants, but also pumpkin crops, gooseberries and grapes.
Fungi are extremely tenacious: they perfectly tolerate the winter cold on fallen leaves and with the onset of spring they again move to plants.
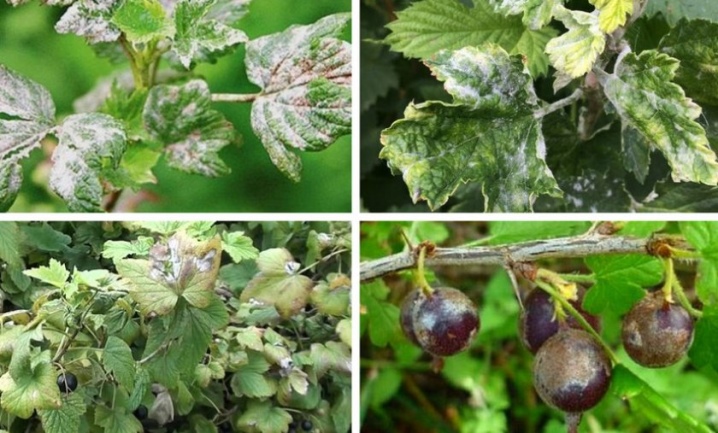

Causes of the disease
The reasons for the development of the disease are a combination of high humidity and high temperatures, thickening of the bushes, poor lighting and an excess of nitrogenous fertilizers. Infection is also possible in case of violation of agrotechnical measures, when, for example, sections after shortening the shoots are not treated with antiseptic solutions. Open wounds are the gateway for fungal infections, and the plant quickly becomes ill. Bushes affected by powdery mildew become very vulnerable to negative temperatures and, no matter how you protect them from frost, they almost always die.
The first sign of powdery mildew damage to currants is the formation of a white bloom on the back of the lower leaves and the appearance of liquid droplets. The fungus quickly spreads throughout the bush and if you do not start urgent treatment, then soon it will appear on the trunks and tops of the branches, and then it will begin to infect the shoots, buds and fruits. In a short period, the plaque becomes denser and becomes covered with black blotches - the fruiting bodies of pathogenic fungi. The defeat of the leaf plates slows down the process of photosynthesis, the supply of nutrients deteriorates, the leaves curl and, together with the ovaries, fall off. If the berries do appear, then they quickly become covered with a bloom, become dirty gray and inedible.
It is no longer possible to defend the harvest on a diseased plant, but the bush itself can still be saved.


How to fight?
The method of dealing with white bloom on currants depends on the degree of damage to the bush. At the initial stage of the disease, you can get rid of the fungus with folk remedies, and in advanced cases, the use of chemicals will help.
Treatment with drugs
It is possible to spray currants with chemical agents not only in order to treat the disease, but also for preventive purposes. At the first stage of the disease and for prophylaxis, smaller doses of light preparations are used, which allows not only to cure the bush, but also to preserve the harvest. Good results are obtained by processing currants with "Skor", "Fitosporin-M", "Quadris" and "Fundazol", however, the most effective remedy is Topaz.
All of these drugs are highly effective and fight white plaque well at any stage of the disease.

Quite good reviews have the compositions "Agrolekar", "Raek" and "Vectra", as well as an old and proven remedy - Bordeaux liquid. For its preparation, 10 g of copper sulfate is dissolved in 10 liters of water, the bushes are sprayed with the resulting composition. During the growing season, it is recommended to periodically change the preparations, which is caused by the rapid adaptation of the fungus to one or another agent. When using chemistry for processing currants, it should be remembered that preparations based on sulfur are the least toxic to the bushes. Berries after processing with such compositions can be consumed a week later.
As for the number of sprays, it depends on the degree of damage to the bush and the active substance of the chemical. Before processing, you must carefully read the instructions and in no case exceed the indicated dosage. Spraying should be done after sunset in dry and calm weather.
The interval between the use of chemicals should be at least 10 days.


Treatment with folk remedies
At the initial stage of damage to currant leaves with powdery mildew, as well as in order to prevent the appearance of fungal infections, folk remedies are used. Below are simple and proven options that can be applied to quickly rid the plant of white bloom.
- Wood ash well helps against fungal diseases. To prepare a solution, 1 kg of ash is placed in a bucket, add 10 liters of water, insist for three days, add 2 tbsp. l. liquid laundry soap, filter and spray the bushes. This should be done immediately after the appearance of the first leaves, watering young stems, adult branches and young leaves on both sides. Processing can be done up to 4 times with an interval of 7 days. The ash sediment remaining after straining is diluted with a small amount of water and poured under the bush.
- Soda also helps to get rid of white deposits. To do this, mix 100 g of soda with two tablespoons of grated laundry soap, add 10 liters of water, mix well and irrigate the bush.
- Cow dung fill a 10-liter bucket by 1/3, add water to the top and leave for 3-5 days. Then the solution is filtered, diluted with water in a ratio of 1 part of the manure mixture to 3 parts of water, the bush is irrigated.
- You can process the currants with potassium permanganate. To do this, dissolve 1.5 g of potassium permanganate in 10 liters of water, incubate for 10 minutes and irrigate the foliage from all sides.
- Milk serum has excellent antibacterial properties and copes well with fungus. To prepare a solution, 1 liter of serum is diluted with two liters of water and the leaves are copiously treated. Either 7 l of water is mixed with 3 l of whey, 25 g of iodine is added and the plant is irrigated. Processing is carried out 4-5 times over the summer.
- Iodine bred in a bucket of water in a ratio of 10 ml / 10 l, cultivate the land around the bush and the bush itself.
- Rapeseed oil well destroys fungal spores and frees leaves from white bloom. For this, 2 tbsp. l. oils are mixed with 10 liters of water and sprayed over the foliage. The result becomes noticeable after 2 weeks.



Mechanical methods
Such methods of dealing with white bloom are appropriate at the initial stages of the disease or to prevent it in the spring, especially if the bushes have already suffered from a fungus last season. Mechanical methods of dealing with powdery mildew include:
- mandatory cleaning and disposal of last year's leaves;
- planting closely growing bushes at a distance of at least one and a half meters from each other;
- removal of the top layer of earth in the near-trunk circle and its replacement with a new fertile substrate, pre-treated with fungicides;
- careful removal of weeds around the bush;
- timely removal of leaves and branches damaged by plaque, followed by their burning.

Processing rules
The order of processing currants depends on which parts of the plant are affected and how far the disease has gone.
- If the disease has just begun and the number of leaves with a bloom is small, then the damaged foliage is cut off and burned, and the bush is treated with fungicides or folk remedies.
- If the berries are covered with a bloom, then they are necessarily collected, poured with boiling water and disposed of.
- The defeat of shoots and upper branches suggests that the fungus has been present for a long time, since these parts of the plant get sick last. Most likely, it will not be possible to cure such a bush, so it is cut off as short as possible and what remains of the bush is poured over with a high pressure of water. Then the fungicide is diluted and the cut bush is treated along with the earth around it. In the spring, the top layer of the earth in the near-trunk circle is changed and preventive measures are taken. If everything is done correctly, then the bush recovers and quickly releases young shoots.
- In case of very severe damage, the plant is dug up along with the roots and burned. The top layer of earth is spilled with boiling water, removed and disposed of.

Prevention measures
In order for the currants not to turn white and bring a rich harvest, it is necessary to constantly engage in prevention and closely monitor the condition of the bushes.
- If there have already been cases of infection of currants with powdery mildew on the site or if the summer resident does not have much experience in growing fruit and berry crops, it is recommended to plant varieties that are resistant to fungal diseases. Russian breeders have succeeded in breeding several of these varieties that are immune to many fungal diseases, including powdery mildew. Among them, the following are worth noting:
- "Agate" - a variety bred in Siberia and represented by small bushes with straight shoots;
- grade "Black Pearl" widespread in the European territory of our country from the Urals to the Caucasus, it is highly resistant to powdery mildew and large fruits weighing up to 6 g;
- "Vernissage" is a very strong variety and is distinguished by large dark purple fruits;
- "Mystery" - a frost-resistant variety, practically not subject to the appearance of a white bloom.
- Before planting, it is imperative to disinfect the planting material. To do this, you can use funds that contain copper. If such drugs are not available, then you can use Bordeaux liquid.
- In autumn, the entire backyard area should be freed from damaged foliage and shoots., regardless of the nature and degree of their defeat.
- Currants should be treated for diseases in the evening, and the bushes should be watered in the morning. This is necessary so that the watered earth has time to dry out in a day and does not serve as a favorable environment for the development of the fungus.
- All garden tools are subject to mandatory regular disinfection.
- It is recommended to spray healthy currant bushes from time to time, using for these purposes harmless folk compositions prepared from improvised means.
- It is better to purchase seedlings in specialized nurseries, guaranteeing the absence of fungal infections in young animals.
- It is impossible to grow currants for more than 10 years in a row in one place. Before planting seedlings, a new site must be dug up and disinfected with fungicides.


For information on how to deal with powdery mildew on currants, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.