What is fusarium and how to treat plants?

Every gardener can face this disease. The main causes of fusarium wilting are waterlogged soil, damp weather and oversaturation of the soil with nitrogen fertilizers. Fusarium is a fungal disease. Without treatment, the plant affected by it may die. Therefore, it is important to immediately begin treatment at the first signs of illness. The disease occurs in all climatic conditions and affects both cultivated and wild plants.

What it is?
Fusarium wilting of plants is often found in plots not only among beginners, but also among experienced gardeners. Fusarium infects vegetable and flower crops. This is a fungal disease caused by the fungus Fusarium, which can support life for 5 years. The fungus adapts very well to environmental conditions and can live on various types of plants. Fusarium spores of the fungus can exist for a long time in seeds or soil, and under favorable conditions they will begin to develop and infect bushes.
Fungal damage begins with the root system in moist soil, and then spreads to the stem, leaves and even fruits. Fusarium mycelium gets inside the stem or roots and secretes the very toxic fusaric acid and lycomarasmin, which cause vascular obstruction. As a result the plant stops receiving nutrients, begins to weaken and gradually withers, and without treatment it can die.
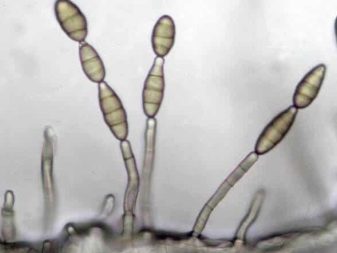

The first signs of the disease are wilting of the top of the plant and yellowing of the lower layer of leaves. In fruiting crops, the stalks are affected, they are covered with dark spots (almost black). According to the description, the diseased plant looks like wilting from lack of moisture. The leaves first hang lifelessly along the stems, then yellow or brownish spots appear on them, after which they dry completely. You can determine whether a plant is infected with a fungus by cutting off the affected stem. Inside it will be visible brown infected vessels with mycelium inside.
The main reason for the appearance and development of fusarium is high soil moisture... Stagnation of moisture in it can be caused by excessive watering, damp weather, improper planting of plants (thickening) and oversaturation with fertilizers. Very often the reasons are the inexperience of the gardener and his wrong actions when caring for plants... Also, fungal spores can appear on seeds or tubers when improper storage (in a damp place).
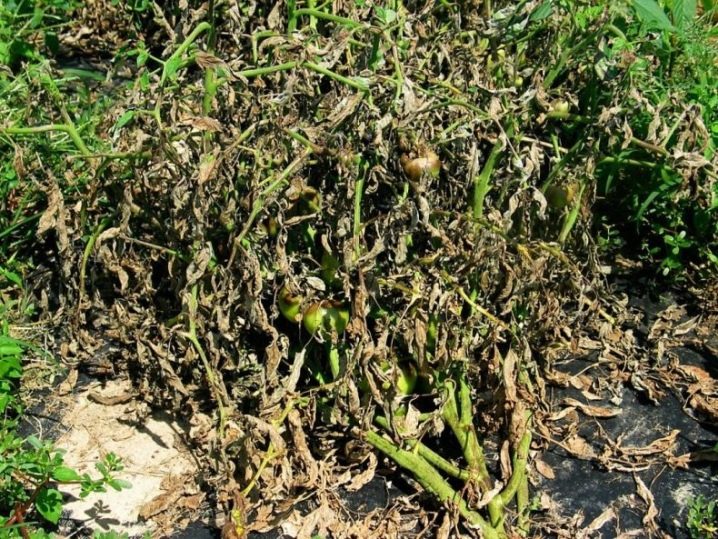

Treatment of garden plants
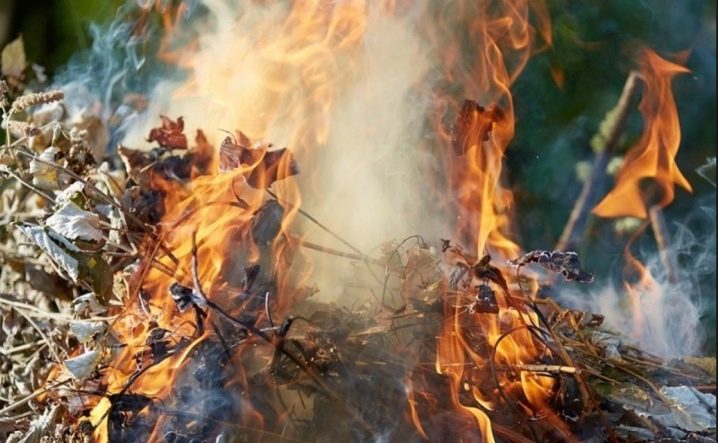
Unfortunately, Fusarium is considered incurable disease. It is almost impossible to save an infected plant, because the defeat begins from the root system, imperceptibly for the gardener. Gardeners discover a diseased crop only when it is already completely covered by the fungus. In this case, it must be removed from the garden and must be burned. And the latter must be well spilled with a solution of potassium permanganate or other fungicide. Plants growing nearby can also be sprayed with biological or chemical agents.
Any plant, even indoor, can get sick with fusarium. Physarium is capable of infecting an ear of barley, corn and peas. The fungus can only be resisted by varieties of cultivated plants bred by breeders.The treatment is the same for everyone, regardless of the type, be it cabbage, peppers, onions or parsley. In specialized stores, you can buy chemicals to fight the fungus and its spores. The latter can live in the soil for a long time, tolerate temperature changes well. Therefore, it is very important to burn all affected plants and not leave them on the ground as insulation for the winter or for compost.
Fizarium penetrates through the roots into stems, leaves, fruits, roots, even grains and seeds, completely affects the plant. When sowing infected planting material, the sprouts will already be infected, and in the future they will infect healthy plants.
Before sowing, carefully check seeds and grains for disease. They can be treated with chemicals and hardened. This will prevent contamination of all plants and soil on the site.


Fighting fusarium in the beds is more difficult. You can defeat him only by removing all affected plants. The bushes must be burned. And sprinkle healthy ones with a natural or chemical solution, be sure to shed the soil after infected specimens. Spraying should be repeated several times within 2 weeks.
For treatment, there are universal fungicides (Alirin-B, Agat-25K, Fitosporin-M, Baktofit, Trichodermin, Vitaros). They can be found in specialized stores. These funds are harmless to humans and animals, but destructive to fungal microorganisms. They can be sprayed on infected plants, shedding soil and used for preventive purposes.
Fungus and spores thrive in acidified soil. Therefore, before planting in the ground or directly at the bottom of the holes, gardeners add chalk or dolomite flour. This helps to reduce acidity and create an unfavorable (and even destructive) environment for the Physarium.


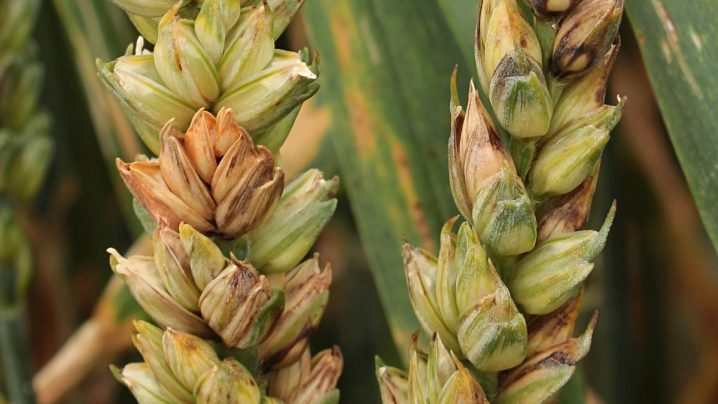
Wheat
Fusarium infection affects both the root system of wheat and ears. The defeat of the latter poses a great danger. Spores from the ears can be spread by the wind, and the farmer can lose up to 50% of the total crop. And eating contaminated grains leads to the accumulation of harmful (poisonous) microtoxins in the body. When the root system is damaged, the sprouts develop poorly and practically stop growing. Their color becomes pale, closer to yellow. Such plants do not yield crops.

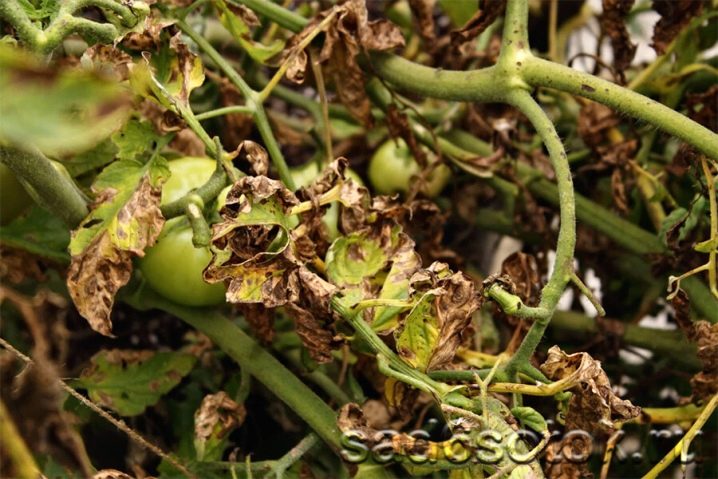
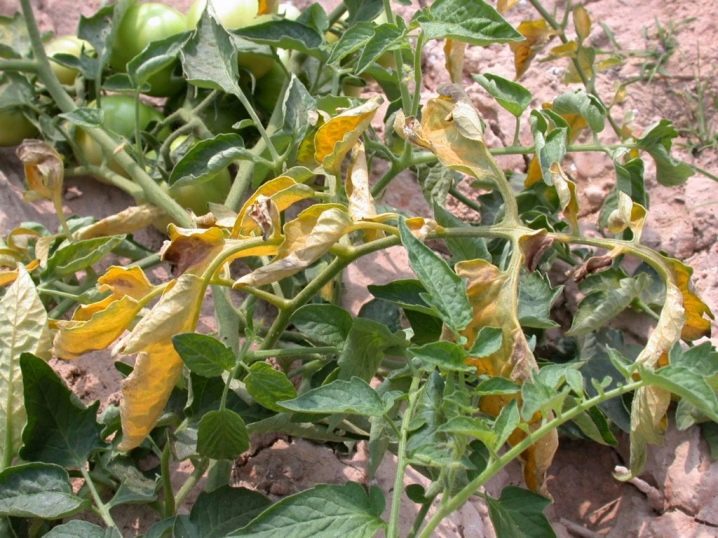
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are very often affected by Fusarium. Infection can occur at all stages of growth of the nightshade crop. The plant can get sick even at the stage of ovary formation, when all forces go to the growth of fruits, and the plant itself is weakened. In affected plants, the color of the stem changes, it turns dark brown, and the leaves turn yellow and curl. When such signs appear, you need to remove the plant with roots from the garden and burn it. To prevent the occurrence of fusarium, you need observe crop rotation, that is, to change the place of planting crops every year.
When infecting tomatoes, plants must spray with special fungicides (falcon). At the beginning of the formation of fruits, it is necessary to provide plant nutrition with phosphorus and potash fertilizers, regularly loosen the soil and limit watering. From the folk remedies, an infusion of garlic arrows with the addition of laundry soap can be distinguished. With this composition, you need to water and spray tomatoes. It will even help in the fight against fungus. With an early onset of the disease, wormwood twigs, which need to be placed at the roots of tomatoes, will help.

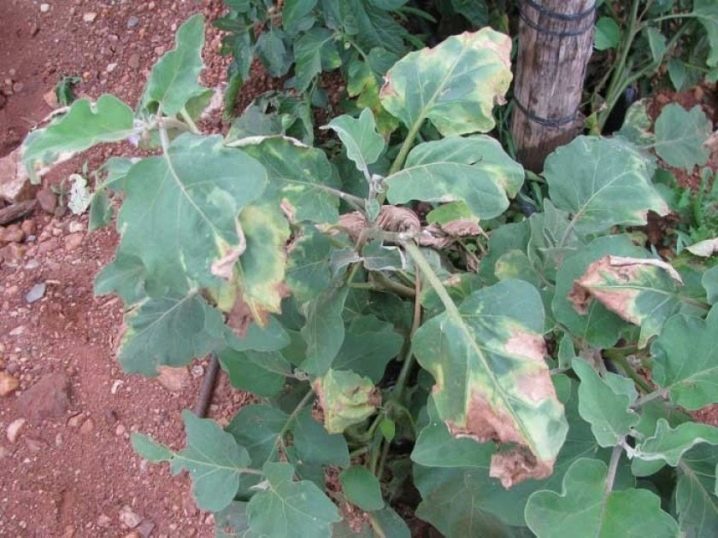
Eggplant
In eggplants, Fusarium appears at the beginning of flowering: the lower leaves begin to turn yellow and dry out. The fungus then spreads through the internal vascular system of the entire plant. Affected bushes may not die and will even form a small number of small fruits. But they lag significantly behind healthy plants in growth and look wilted.

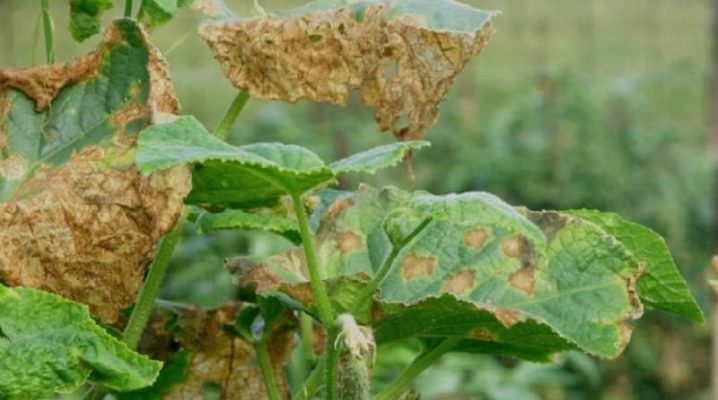
Cucumbers
In cucumbers, the disease is manifested by wilting of the upper shoots and leaves.And rot appears on the root part of the stem. Then the shoots darken and turn brown. Fusarium infects crops both outdoors and in the greenhouse.
It is very difficult to detect the disease in the early stages, most often this happens only when the entire vascular system of the bush is already affected, and it is almost impossible to save the plant.

Potato
Potatoes are most often affected by Fusarium during the flowering stage. The upper leaves of the plant become faded and wither. With increasing humidity, rot and pale pink bloom appear on the root zone of the stems. The bush begins to wither and after a few days may dry out completely. Fusarium rot also affects tubers. Soft dark brown stains appear on them during storage. And the pulp inside dries up and turns into dust. In the voids, myceliums begin to form, the tubers become pale pink, whitish or yellowish in color. One affected tuber is capable of infecting healthy tubers in a short period of time.


Garlic
If garlic is affected by Fusarium, the farmer can lose up to 70% of the crop. The fight is complicated by the large number of species of Fusarium fungi. Each has a different activity, and different fungicides are needed to destroy them. Fusarium can affect garlic not only during growth, but also during storage of the crop.

How to treat fruit and berry crops?
When fruit and berry crops are affected by Fusarium, not only the bush (tree) itself suffers, but also the fruits (berries). Most often, watermelon, melon, grapes, strawberries, apple trees and pears suffer from the disease. Under favorable conditions, the fungus spreads so quickly that the farmer can lose half of his crop, and sometimes more. It is impossible to eat fruits and berries from contaminated crops: poisonous acids from them accumulate in the body.
Fight the fungus in the same way as with other plants: you need to remove all affected specimens. If this is a tree, then it is necessary to cut off the diseased areas. And spray the remaining plants with fungicides and shed the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate. You can also use an infusion of wood ash with sulfur. Trimmed areas on trees and shrubs must be carefully treated with disinfectants.
In the spring, it is necessary to disinfect the roots and root area with a fungicide or potassium permanganate solution. And feed the shrubs with phosphorus fertilizers. With acidic soil, you need to use chalk or sand to deoxidize and create an unfavorable environment for the Physarium.


Experienced gardeners advise to plant only hybrid varieties of fruit and berry crops that are resistant to disease on the site.
How to save flowers?
Most often, Fusarium affects bulbous flowers, especially gladioli. There is not a single variety of the named culture in the world that can withstand this disease. If the flower has a weak crooked stem and yellowed leaves, then most likely its bulb is affected by a fungus. Such specimens cannot be stored, otherwise they will infect all other plants.
To prevent fungal disease, flower bulbs must be disinfected in special solutions before planting, which can be purchased at agricultural stores. The hardening of the bulbs also helps, when they are first heated in hot water (at a temperature of 50-60 degrees), and then sharply cooled.
Throughout the entire period of growth, it is recommended to spray flowers with solutions of fungicides against fungi ("Fundazol", "Tiazon"). The same composition can shed soil if you think that disease-causing spores could remain there.
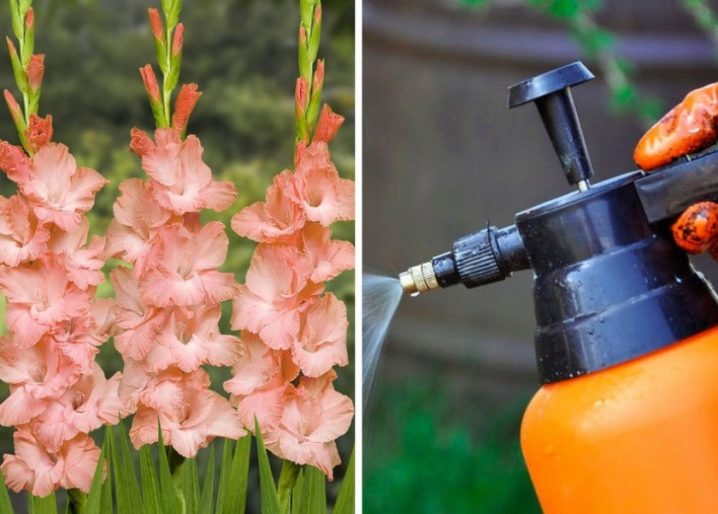

To save flowers (orchids, petunias, hydrangeas, brilliant cotoneaster, rose bushes, peonies and many others) when the first signs of illness appear you need to remove all affected stems and burn them, and treat the remaining shoots with fungicides. For spraying, a mixture of potassium permanganate with boric acid is suitable.The same solution can be used to treat the roots of perennial plants and bulbs dug out for the winter. When the first buds appear, spraying must be repeated.
In the fight against Fusarium for healthy flowers, only the merciless removal of all affected shoots (stems) and, if necessary, the entire plant along with the infected root system will help. When digging, the latter is removed along with a lump of earth: there are myceliums and spores. It is better to sacrifice a few plants than to lose an entire flower garden.

What other plants are affected?
Fusarium infects cultivated plants in closed and open ground, peppers, sunflowers, pumpkin, cabbage, soybeans, peas, beans are susceptible to it. Also, the fungus can overcome flax and corn. In grain and cereal plants infected with fusarium, the ears are covered with brown, gray or faded spots. The stems become frail, and the grains become small.
In coniferous trees and shrubs (thuja, spruce, juniper) needles turn yellow, then fall off. Dark spots appear on the trunks, and whitish or light pink mold appears on the root edge.
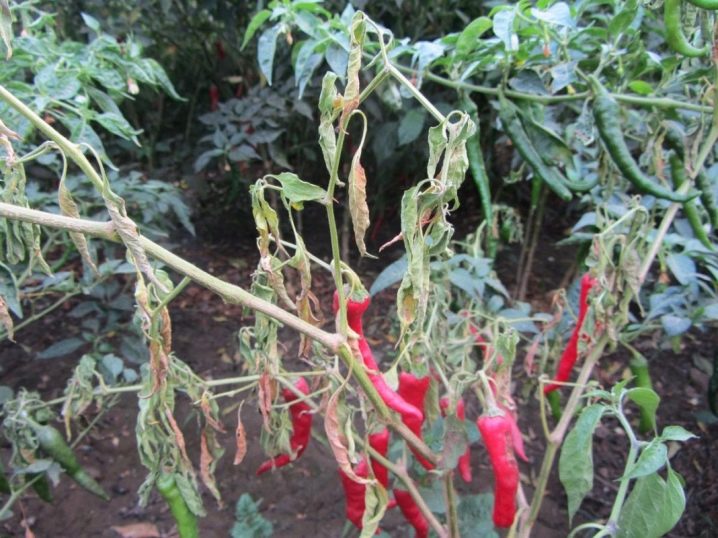

Prevention measures
As already stated, Fusarium is an incurable fungal disease, and it is impossible to completely get rid of it: the spores of the fungus, being in the soil, are viable for 7-10 years. Therefore, prevention of this ailment is very important.
First of all, it is important to observe the principle of crop rotation and to treat the planting material with antibacterial fungicidal agents before sowing or planting.
For prevention purposes, it is necessary to regulate watering and prevent stagnation of water in the soil. The soil under the bushes must be loosened after watering. Remove weeds, damaged stems and plant roots in time. Pathogens can enter them through the wounds.
When planting seedlings, be sure to leave enough space between them, do not allow thickening.

Folk remedies help only as a preventive measure against fusarium. They are powerless in treating affected plants. The most effective remedies for fusarium fungus:
- solution for spraying bushes from milk, iodine and laundry soap;
- infusion for spraying bushes and watering soil from wood ash and laundry soap;
- infusion for watering the soil from onion peel;
- garlic infusion for spraying bushes.
Shrubs and plants are treated with infusions and solutions throughout the growing season. They can be applied every 2 weeks.
Before planting seedlings or sowing seeds, the soil must be shed with one of the means. After harvesting, the land is also treated with disinfectants.







The comment was sent successfully.