Everything you need to know about bitumen
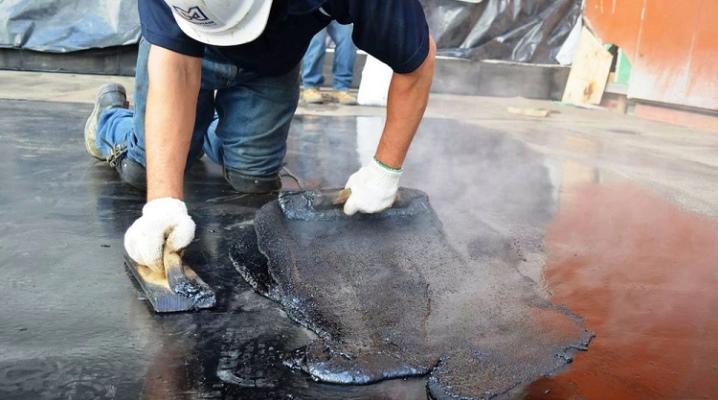

After reading this article, you can learn everything about bitumen, what it is in practice. It will be possible to understand what hot oil bitumen and other types are, to deal with specific brands and composition. And it will also become clear why a bitumen pump is needed, there will be answers to other questions.


What it is?
The overwhelming majority of people know about bitumen mainly that it is used in road construction and waterproofing works, and is made from oil. But in fact, bitumen is much more interesting than it seems at first. So, this is not one product, but a whole group of products that differ in solid or resinous consistency. Any bitumen does not dissolve in water, but can be completely or partially dissolved in chloroform, benzene and a number of other organic solvents. This name itself goes back to the Latin word resin.
The density of bitumen varies widely from 0.95 to 1.5 grams per 1 cubic meter. see The exact properties are determined by the quality of the oil involved, primarily the sulfur content and the level of oxidation.


The overwhelming majority of natural reserves of bitumen are of low concentration and are not of interest for full-scale production. And 99% of the promising and currently used bitumen deposits are located in Canada and Venezuela. It should be noted that this product is not a solid, but an amorphous substance, partially exhibiting the properties of liquids.
Natural deposits arise when oil deposits are disturbed, which can occur due to chemical or biochemical oxidation. But sometimes a tectonic process is also a "breaker". Basically, bitumen is extracted from the bowels of the earth using an open-pit or mine method. Artificial or technical bitumen is a residue from the processing of oil, coal or oil shale. There is no difference in chemical composition between it and natural products.


Specifications
Black or dark brown color is typical for bitumen. It is a thermoplastic substance that will be solid at different temperatures or acquire a resinous consistency. If you heat it up too much, it melts. But the fluidity even of a molten substance is negligible. When it cools down, the original viscosity will return, there is no unambiguous melting point.
Bitumen sometimes, in violation of safety regulations, boils in the tank. This happens if you do not drain the remaining water from there, and then serve excessively hot (about 120 degrees) product. In such a case, small "resin lakes" are spilled. Acids and alkalis usually do not dissolve bitumen, as well as salt solutions.
Pore formation is not typical for it, and even a thin layer will be completely impervious to water.


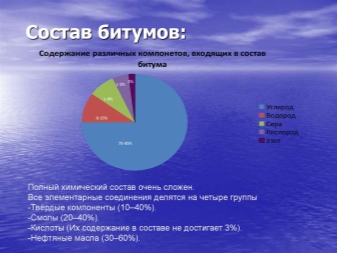
How much bitumen and substances based on it dries is determined by a number of factors. The thickness of the layer, the degree of humidity of the air, and the temperature play a role. The volumetric specific gravity is 1500 kg, therefore, 1 m3 contains exactly 1.5 tons of the substance. Typical bitumen contains:
- 70 to 85% carbon;
- 8 to 15% hydrogen;
- from 1 to 8% sulfur;
- from 1 to 5% oxygen;
- no more than 2% nitrogen.
It is very difficult to accurately characterize the chemical composition. However, elementary compounds in the composition of bitumen were divided into 4 main categories.The solid component is represented by high molecular weight hydrocarbons. Resins are amorphous substances containing sulfur. And also there are acids (less than 3%) and petroleum oils (their amount varies from 30 to 60%).

Views
Artificial
Such a product is obtained as a by-product in the oil industry in the manufacture of fuels and lubricants. Initially, however, tar is obtained, and only when blowing with hot air or heating, the actual bitumen is produced. Distillation in high vacuum makes it possible to obtain such a product based on highly resinous oil. Most often these are solid, moderately viscous substances. Oxidized bitumen is also found.
This is the same product that is created by blowing with oxygen of tar and other oil residues. Such residual substances are characterized by increased viscosity. Cracked bitumen is produced by decomposing crude oil and oils at elevated temperatures.


There are also compounded products that are produced by mixing the residues after processing natural oil.
Compounding technology usually involves the introduction of:
- coal oils;
- polymers;
- tar;
- light petroleum fractions.

Natural
Reservoir bitumen is a rock impregnated with liquid mineral resins. Often these rocks are sandstone or limestone. Surface composition occurs when liquids come to the surface. Vein bitumen is one that has a small proportion of mineral inclusions. Natural products are obtained by boiling them in hot water or extracting with organic solvents from various rocks.
Construction bitumen is used to obtain mastics, waterproofing and other materials. The roofing product is used in the production of soft roofing products. The mixture that is used for asphalt concrete is allocated to a special group. For convenience, the finished product is delivered in briquettes or in lump form. In some cases, a corrugated sheet of organic fibers is impregnated with a resinous combination, and such a product can eliminate impact deformations.


Stamps
Reduction of BND means "oil road bitumen" and eloquently characterizes the use of this substance. The numbers in the brand designation show within what limits the penetration can change normally at a temperature of +25 degrees. There are brands such as:
- BND 200/300;
- BND 130/200;
- BND 90/130;
- BND 60/90;
- BND 40/60.


Depending on the specific brand, the following may vary:
- penetration depth of the metal needle at 0 and +25 degrees;
- minimum softening temperature in the ring and in the ball;
- extensibility level;
- brittleness and flash points;
- penetration index.
BN 50/50 - bitumen with good adhesion. It is an easily overflowing composition. On flat surfaces, it will gradually float. BN 70/30 softens at 70-72 degrees. This compound has excellent adhesion and breaks down into large pieces without small debris. Such a product is ideal for waterproofing.

BN 90/10 softens at temperatures of about 90 degrees. This bitumen has excellent adhesion. It is almost insensitive to high temperatures. Such a product can be broken with a hammer. On impact, fragments are formed that have a shiny surface.
Petroleum roofing bitumens are divided into 3 groups:
- BNK 40/180;
- BNK 45/190;
- BNK 90/130.


Areas of use
It has long been known that bitumen is widely used in road construction. For this purpose, both natural and artificial products are used. Road bitumen mixtures have a very high penetration coefficient. The higher the number, the better the suitability for the northern regions. The pumping of the composition is provided by a bitumen pump.
It is impossible to use a household or even an industrial water pump in this capacity. A specialized version is required, designed for high loads and difficult operating conditions. But bituminous materials are also suitable for soundproofing cars.


Special vibration-absorbing structures are sometimes created on the basis of mastic. Some of them can be additionally covered with aluminum foil. Maximum noise protection always means mechanical sealing of materials. As a roof covering, paper impregnated with bitumen is used. But this material can also be used for packaging various products. It is delivered in roll format.
The typical roll width is 100 cm. Its standard length is 119 m. Bituminous tiles are widely used for facades. Such shingles are actively produced by a variety of suppliers. It can be attached not only to houses, but also to outbuildings.
In some cases, bitumen is bought to insulate the foundation. Moreover, this can be done both by filling with a liquid composition, and by attaching a special panel for the basement.


Another option is the use of mastic, in addition to the main component, which includes rubber powder. And also bitumen is used in the format of a decking roof. It is often represented by tiles similar to those used for wall decoration. But there are also options such as:
- roofing material;
- uniflex;
- glassine;
- bipole.
In the domestic sphere, bitumen is often used to fill the roof of the garage and other buildings. Of course, this already requires hot work, but these are the inevitable costs of the process. A more modern option is a membrane that includes polymer components. Natural or artificial resin diluted with a thinner (mainly gasoline) is used as an impregnation for wood.


Consumption
This indicator can vary widely. But it is calculated separately for each application. In any case, the cost per 1 m2 is determined according to the type of material and the option for its use. Typically, the consumption figure is given on the packaging (corrected for layer thickness). So, when applying waterproofing to the foundation with a layer of 2 mm, it will be possible to spend 3-3.9 kg of reagent for each "square" (in dry weight).
When covering the roof, the usual cost starts from 0.8 kg. It can reach (in one layer) 1.8 kg. Much depends on:
- brands;
- air temperature;
- surface preparation.


How to melt?
Solid types of bitumen must be melted. To improve the melting efficiency, it is necessary to split the bitumen into small pieces. These pieces are treated with diesel fuel or used oil (with full coverage, but without a thick layer on top). A simple household bitumen heater is usually a fire. Melting takes place in a steel barrel or bucket over a low monotonous fire. Otherwise, it will be uneven.
The molten material is left to warm up until the foam stops. A filler is added - fluffed asbestos, chalk, cement or gypsum. Then the solvent is added (in no case can oil products be used).
Liquefied bitumen does not need to be heated. It was originally prepared with an optimal consistency in mind.


What can you dilute with?
Thinning will require thinners. In this capacity, low-octane gasoline or safer white spirit is used. Mastics are diluted with aviation kerosene, white spirit or turpentine, sometimes solvent and acetone are used. The choice of dilution option is determined by the application method. It determines whether to achieve a liquid or thick consistency. Bituminous rubber mastics are very elastic. Therefore, they are actively used to protect pipes and other underground communications. The oil components are suitable for a wide variety of applications, with the exception of roofing.
They increase the stickiness and decrease the hardness of the substance. Cracking is prevented. Integrity is guaranteed for a long time.Mastics with the entry of oils are resistant to cold temperatures down to -50 degrees and to heating up to +80 degrees. The introduction of crumb rubber is a good choice for forming durable coatings even on metal roofs. The diluted compound is often used only as a primer.


How to remove from clothes?
You can remove bitumen or tar from the surface of the fabric at home with a knife or other sharp tool. Care must be taken to keep the fabric intact. But it is also necessary to use a special cleaning agent. Acetone and other solvents must not be used. They, of course, wash away the pollution, however, you will have to say goodbye to clothes. To combat tar and bituminous spots, special preparations are used. For example, Russian "Eltrans" or English Superb Degreaser. You must work strictly according to the instructions. In any case, the use of personal protective equipment and precautions is required. After cleaning, the problem area must be soaked and washed.
Small lumps and splashes can be washed off with diesel fuel or car shampoo. Some people make their own cleaning solution. For its preparation use:
- turpentine;
- clay;
- starch;
- ammonia.


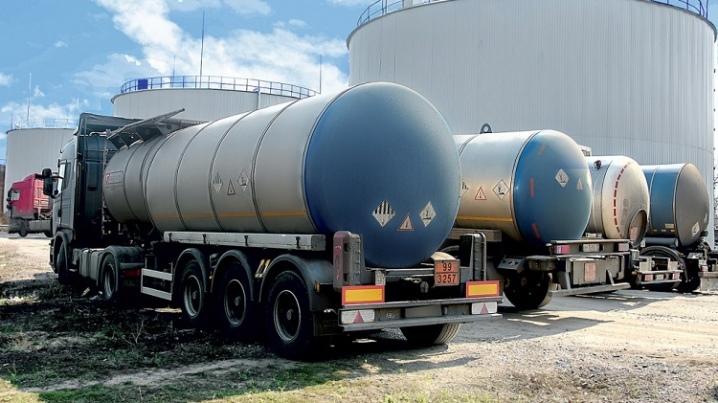
Transportation features
Correct transportation of bitumen is quite difficult. By rail, it must be transported in capacious bunker containers (collected in groups of 4). One container holds up to 10 tons of substance. Steam coils keep the product warm. Bitumen carriers (specially designed semi-trailers-tanks of the "thermos" type with double walls) usually drive along the highway.
Loading goes at 180 degrees. Bitumen enters and drains off by gravity. No auxiliary pumps are needed. If the insulation is intact, it is possible to transport bitumen without heating for up to 48 hours.
The product is heated before unloading.














The comment was sent successfully.