Melting temperature of bitumen

Knowing the melting point of bitumen is essential for everyone who is going to use it. Boiling points and flash points during heating and filling are very important in practice. Knowing at what temperature the construction bitumen resin ignites, many unpleasant situations can be excluded.
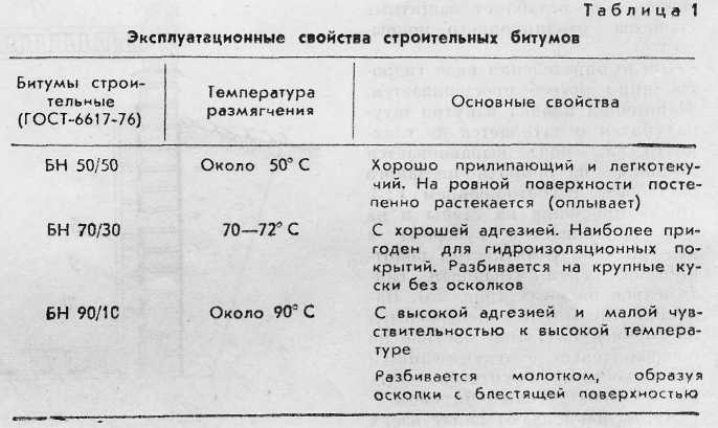
Softening point for different types of bitumen
Bitumen differ in their properties quite strongly. The quality of this product is largely determined by the degree of heating at which it loses its hardness and becomes more and more plastic. The key indicator used for measurement is the so-called penetration or penetration of the needle into the material. The fact that, instead of a specific melting point, bitumen first reaches softening, is due to the fact that they combine a variety of substances. The characteristics of a particular brand also affect.
It was found that bitumen melts when heated from 160 to 200 degrees. This temperature is easy to achieve even in normal home conditions. It is necessary to melt this substance in open areas in a metal container. Work should be done away from anything that can melt or additionally catch fire. We must not forget that 160-200 degrees is already a serious temperature for a person, so you need to be careful.
It is worth remembering that according to some sources, melting begins already at 110 degrees. True, it is not possible to find out what these judgments are based on. When preparing to work in construction or to mount various types of roofing roofing felt, tar is usually melted.

It melts already at 12-55 degrees, which makes it possible to prepare a liquid mixture even over a fire. It makes no sense to name the melting point of bituminous resin separately from other components of the substance - all the same, it is encountered only in the laboratory; when bottling in production, you need to focus, of course, on the same temperature values that have already been announced.
Flash point
Sooner or later, any solid substance passes into a liquid, and then into a gaseous phase. During melting, not only liquid parts begin to appear, but also vapors; the further the substance melts (if its heating is not stopped), the more these vapors are released. They are quite remarkable in that they can catch fire. And the state is critical from the point of view of fire safety when they start to burn, even if they are not able to maintain the process after the heat source has been removed. The bottom line is this:
-
vapors of the substance ignite when the necessary heat is introduced;
-
the combustion process is visible visually;
-
however, as soon as the heat supply is stopped, the flame disappears.

The exact temperature at which a flash is possible can be established both by calculations and by special experiments. Usually, when calculating, they are based on the so-called saturated vapor pressure.
Since it is very difficult to directly measure at what temperature a vapor or gas ignites, this value is usually understood as the temperature of the vessel wall in which the reaction takes place. This indicator strongly depends on the conditions in which the substance is located; but the boiling point of bitumen (at normal atmospheric pressure and ambient room temperature) is set exactly - 145 degrees.

Brittleness temperature
Under this term, it is customary to understand the degree of heating, upon reaching which any substance begins to collapse from a short-term application of a load. This indicator is used to judge how the substance will behave in the road surface or otherwise. In oxidized bitumen, brittleness occurs at a lower temperature than in other types. The load behavior test is carried out for 11 seconds, the exposure intensity is 1100 kg per 1 cm2. Depending on the specific composition of bitumen, the brittleness temperature ranges from –2 to –30 degrees.














The comment was sent successfully.