Bituminous emulsion: characteristics and areas of use

Bituminous emulsion is the next step in the development of the production of bitumen-building coatings. After simple bitumen and roofing material, the bitumen-emulsion composition can reduce the consumption of tar obtained from oil by the same type and amount of work.


What it is?
Before purchasing a bitumen emulsion, any distributor will offer to get acquainted with the features and rules of using this building material. The bitumen-emulsion composition is a mixture of bitumen, water and a reagent that stimulates the formation of a droplet structure when shaken before use. This reagent is responsible for the stability of the droplet-liquid structure, without which no emulsion as such can do.
Bitumen is both the main medium and its phase state. Simply put, a liquid takes the form of "oil in water" or "water in oil". The more (or less) an emulsifier is present, the more obvious the manifestation of different liquid states is.


Bitumen emulsion is unchanged in volume - when the storage temperature changes, for example, at 0 and +25 degrees. By applying the emulsion mixture to the surface prepared for work, workers are faced with the sensitivity of this building material to the state of the working area. After coating, the emulsion stratifies into water and bitumen. The water gradually evaporates, but the bitumen remains and hardens. This makes it possible to evenly cover, for example, the foundation around the perimeter, where it is planned to erect walls, in order to isolate the foam / gas blocks of each wall from the moisture of the slabs or the strip structure of reinforced concrete, without using roofing material and without heating ordinary bitumen.
The second name for BE is an emulsion primer.


Specifications
Bituminous emulsion composition is used in road construction industries. It belongs to direct mixing emulsions (the so-called oil in water). In this emulsion, bitumen in an amount of 30 to 70% is evenly suspended throughout the entire water column, bitumen particles are microscopic in size. Reverse emulsions - the so-called water-in-oil - contain water particles suspended in bitumen. The percentage of bitumen is 70-80%. The complete composition of the emulsion provides for the presence of water, an emulsifier, a stabilizing additive and an acid.

For the manufacture of bitumen emulsion, bitumen grades BND 90/130, BND 130/200 and similar compositions are used. As follows from the wording, bitumen is a road bitumen. Instead of simple road bitumen, a polymer-bitumen binder additive can be used. The adhesion of this additive is better than that of a simple resin. The water is purified with high quality - the bitumen emulsion should not contain any foreign impurities. The task of the emulsifier is to prevent the disintegration of the emulsion structure, without which the fraction will not give one hundred percent return.
Cationic and anionic surfactants are used as additives. Accordingly, the emulsion will be anionic or cationic bitumen. Instead of surfactants, mineral additives are also used, for example clay, metal oxides, salts in the form of carbonates and sulfates, as well as soot or cement. Used as a stabilizing additive calcium chloride aqueous solution or other readily soluble salts that fully manifest themselves only in cationic emulsions. Used as an acid hydrochloric, acetic or orthophosphoric - acidic environment prolongs the stable state of the emulsion without re-mixing the composition.
To make this building material more liquid, it is advisable to add an organic solvent and liquid plastic to it.


Production technology
Modern technology for the production of bitumen emulsion provides for the presence of modifying additives that improve its properties, because the "emulsion" consists not only of bitumen fraction and water. Typical additives include latex, polyethylene, epoxy filler, synthetic rubber / resin, etc. Changing the composition of the bitumen emulsion in production is carried out in two ways:
- an additive that changes the properties of the composition is introduced into the aqueous phase of the emulsion itself or at the stage of its preparation;
- the emulsifier is introduced into the already changed bitumen.
The technological process for the release of bitumen with emulsifiers is as follows. The emulsion plant has an intermittent or continuous operating principle. In intermittent work, the entire process is controlled from the remote, which is controlled by the master. The continuous principle provides for a semi / fully automatic process without significant intervention by the operating personnel. The main actuator here is a colloidal crusher. It carries out the addition of bituminous particles to pre-treated water. Then the bitumen is mixed with water until the composition becomes homogeneous.
In the process of mixing, the bitumen heats up to 160 degrees. The water phase heats up to 70. It is at this temperature difference that the emulsion takes on its original consistency. This composition is not stored for more than 2 months. The air temperature in the warehouse is at least 5 degrees Celsius. The train is transported by means of metal tanks, barrels, automatic mixing installations mounted in the tank.
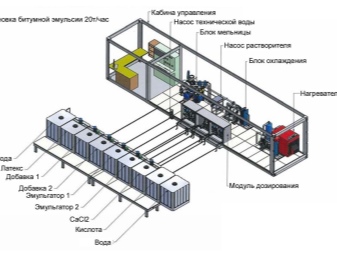
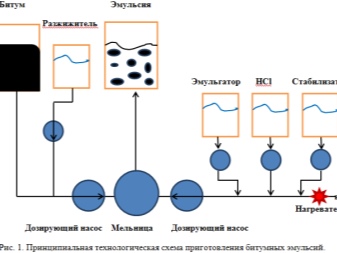
Classification
These compositions are classified on the basis of the rate of disintegration of the mixture. The emulsion composition cannot be stored forever (for years and decades) - it undergoes stratification, caking, like stale oil paint. Emulsifiers included in the bitumen-water fraction as the main additives have different quality, properties, characteristics, volume. Indoor humidity and air temperature are not the last factors driving the decay process. The decay of the emulsion is evaluated by the decay index.
According to it, this composition is characterized as follows:
- rapidly disintegrating - the separation of water immediately upon covering the surface prepared for painting and impregnation with a building material;
- medium decaying - the composition is divided into two separate media after mixing with a stone structure;
- slowly disintegrating - bitumen caking is carried out only after touching (and absorbing) a large area of stone into the structure.
It is the most highly stable emulsion.


According to the composition of the emulsifying additive, bitumen emulsions are subdivided into cationic, anionic and nonionic. In pasty "emulsions" minerals are used, in polymer-containing ones - latex and other high-molecular hydrocarbons. In polymeric ones, for example, latex can be used. The difference in the charge of surfactant particles: "emulsion" can be positive (cationic) and negative (anionic).
Repulsion (according to the laws of electrostatics) of charged particles of the same sign accelerates the sedimentation of bitumen and the separation of water. Cationic emulsion formulations work well with most additives and additives. Getting on a mineral surface (stone, brick, concrete, etc.), the composition separates water - bitumen adheres to the painted surface. This phenomenon is called emulsion breakdown. In cationic emulsions, bitumen is released due to reaction with the material of the surface to be coated, in anionic emulsions due to the immediate evaporation of water.

According to the rate of decomposition of the composition and ionic action, this building material is marked as follows.
EBA-1
Anionic composition with fast decay. They are used to care for recently laid cement concrete and cement primer. The second application is priming, as well as fixing the surfaces of soil slopes, some types of surface treatment.


EBA-2
This composition, being moderately decomposing, has found application for the preparation of black (clogged) crushed stone, for the treatment of highly porous mixtures made on the basis of carbonates. The road base under the canvas is impregnated with this composition.


EBA-3
The composition EBA-3, which decomposes into water and bitumen at a slow rate, is used for the preparation of especially dense emulsion-mineral building materials. The composition is mixed with up to 2% lime or up to 3% cement. Well suited for fixing moving sand, removing cement dust from surfaces, as well as fixing the top layer of soil on the soil of the cultivated area.

Popular brands
The leading BE brand for today is TechnoNicol. It is used as a road and building component. In addition to the formulations with the nomenclature markings listed above, Russian firms supply BEs under their own brands.
So, BE No. 1 from the same brand is a highly environmentally friendly composition.


The representative of environmentally friendly bitumen materials on a water-latex basis is a bitumen emulsion "TechnoNikol No. 31", the characteristics of which will be discussed below. Waterproofing coatings, for the creation of which a BE from this company was used, are distinguished by heat and wear resistance (they do not lose their original properties for many years).
The consumption of BE of this brand per 1 m2 is no more than 5.7 kg for the roof, and no more than 3.5 kg for covering the inner waterproofing layers. It serves as a kind of "concrete contact" and corresponds to a pressure according to GOST not less than 4.5 atm. The bitumen in this composition is at least 60%, and the liter capacity is 5% heavier than the same can of water. The composition is used in the temperature range of 5 ... 30 degrees Celsius during coating. Firm "TechnoNikol" managed to achieve a guaranteed storage period in the warehouse for at least six months.


Among other firms - BitumenTEK, Amdor, B2M and several similar ones that produce a wide range of bituminous building materials. Specific gravity of a liter (density 1 dm3) - 1.05 kg.


How is it different from bitumen?
Bitumen is simply an astringent and impregnating material. It is applied mainly hot, in a molten form. Disadvantage - if applied slowly for more than one minute, it can peel off, even when the surface is matte and grainy. Bituminous emulsion is deprived of this ability: it is brought into a usable state with the help of water and mineral-organic additives, and in the process of coating the surface prepared for work, special haste is not required.
Pure bitumen for its intended use must be heated to 100 degrees or more. It is used in a molten state for laying a road under a new asphalt pavement, waterproofing walls from a foundation (as part of a roofing material). Dissolving bitumen in gasoline, kerosene, naphtha converts it into a liquid state. Emulsification in water using emulsifiers can also turn it into a liquid material suitable for covering the inside of the roof and other structures that need protection from moisture. At 30 degrees, the bitumen dissolved in this way will retain a liquid state.


The energy consumption for the preparation and consumption of the emulsified bitumen composition is up to 50% less - it does not require heating and melting.
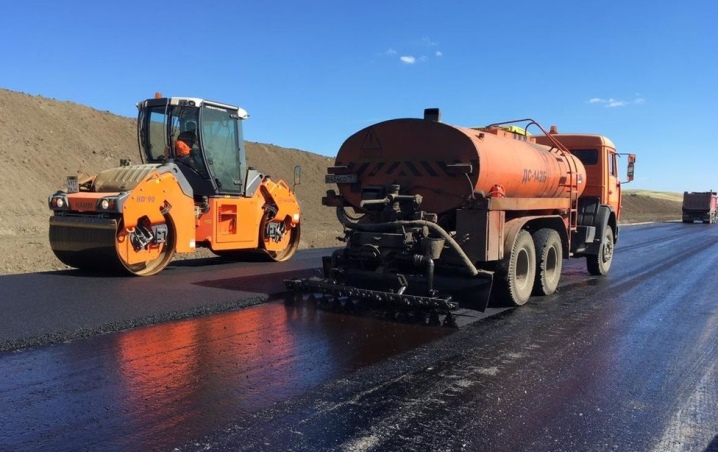
It, in contrast to a simple bituminous composition, is applied to the surfaces intended for this, even in wet, damp weather. Evaporation of "emulsion" is at least several times less than from a pure bitumen composition melt. The strength gain of cold asphalt - a mixture of sand, pebbles and bitumen emulsion (or an organic solution based on it) - is carried out not when the newly laid pavement cools, but due to the volatilization of light oil fractions. What is left is reliably compressed under the shoes of passers-by and the wheels of cars.



Application area
BE is used in such areas.
- For binding asphalt chips, crushed stone, sand and other additives to the road surface. This is one of the true cold paving technologies.
- When covering walls, foundations, blind areas, steel supporting structures (supports). After evaporation of water, the composition protects all these surfaces from moisture for many years.
- As a waterproofing layer for hydraulic engineering and underground.
- For tightening and holding soil and sand. Dust removal of roads and sites is also carried out. Before laying the asphalt, bitumen-containing mixtures are applied to the crushed stone bed.
- For partial repair of walkways and access roads for various purposes, parking areas. An example is the shedding of cracks in the roads.



All of these areas of use cover the construction and repair of roads and buildings.
Order of use
It is recommended to apply BE according to the following scheme.
- Dirt and remnants of obsolete, flaky coating are removed from the serviced surface.
- Cracked and chipped places with gaps of 3 mm or more are leveled by priming.
- Sharp corners are smoothed, rounded, then degreased with an organic solvent.
- Cover the prepared surface with a primer (pre-applied composition). Drying time is 1-2 hours.
- The first layer of BE is applied, then the second. Normally - not earlier than after 5 hours, it is during this time that the coating dries (loses water). To speed up the work, use a special spray.



All do-it-yourself waterproofing work will take no more than half a day. Finishing can be completed immediately after this time.













The comment was sent successfully.