All about road bitumen

In construction, in addition to cement, sand and crushed stone, bitumen is also widely used. It has good values for water resistance and penetration into bulk building materials, including seepage into building mixtures. Its application is road and private construction.

What it is?
By bitumen is meant a dense and viscous substance that resembles resin in its consistency. It is transported in the form of pieces of different sizes - before use, these fragments are melted until it turns into a liquid state. This material, in addition to asphalt and asphalt concrete mixture, has found application as a waterproofing layer, for example, between the concrete floor (foundation) and the first row of brick walls.
Despite the homogeneity and apparent simplicity, bituminous building material has a complex composition. Normally, these are hydrocarbon compounds in which nitrogen, metal additives and oxygen can be dissolved. But the composition of the substance does not end there: it contains a heteroorganic. The composition of bitumen is diverse enough not to immediately name all the inclusions present in it.


What are they made of?
Artificial bitumen is produced on the basis of tar - residual material after cracking (splitting) of oil. Tar, which is an oil residue after the release of gases, liquids of varying density, which are such at room temperature, is subjected to one of three procedures.
- Sedimentation of heavy fractions of oil residues using reduced pressure (vacuum). The resulting composition has sufficient fusibility and softness. The raw material for the production of "vacuum" bitumen is oil with a high sulfur and tar content.
- The tar is oxidized by heating it to a temperature of about 200 degrees and blowing it with air. When the heated tar is blown with pure oxygen, a relatively thermostable building material is released.
- The use of distillates with a mixed composition of tar. The latter can contain oxidized and residual tar in different proportions.
The resulting bitumen is classified according to certain criteria. It is supplied in the form of briquettes that can be stacked at low storage temperatures.

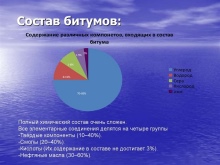

Characteristics of varieties
When specifying the type or variety of bitumen, the following characteristics are taken into account.
- The density, or specific gravity of bitumen, is 950-1500 kg / m3. The bitumen cube should not weigh more than the maximum mark - otherwise, it is worth suspecting the presence of stones and other debris in it. Not every bitumen is lighter than water. Volumetric weight - the mass of one cubic meter - is determined by the specific brand of the given building material.
- The melting point of bitumen depends on the brand. This parameter allows you to estimate at what temperature the bitumen becomes so liquid that it flows like syrup. But, by cooling the molten bitumen of any brand to a temperature below 80 degrees, you are guaranteed to get an environment with the density of village sour cream, which is no longer possible to pour out.
Each type and grade of bitumen determines its specific area of application. For example, bitumen used for the manufacture of roofing felt (roofing material) is difficult to use for road construction - asphalt can quickly crack in the cold, and in the heat it can soften and shift, bending the road surface, knocking down waves on its surface.
Such a road is in urgent need of repair.

Natural
Natural bituminous composition - combustible minerals. Specifically - natural reagents included in them. Natural bitumen is a product of oil refining by the forces of nature.It is formed when a deposit has undergone specific changes, for example, during oxidation when it reacts with the surrounding minerals, or extremophile bacteria that can change the composition of oil fractions have entered the natural reservoir where oil was located.
To access natural bitumen, mines or quarries are built.
Natural bitumen - asphalt of natural origin, ozokerite, malt - derivatives, the source of which is combustible minerals.


Asphalt Powder
It is formed among rocks, similar to limestone. When processing asphalt powder, the required reagents are extracted at a temperature other than room temperature.

Artificial
Petroleum, or artificial bitumen, is formed only during the distillation of oil. The processes of cracking, sedimentation (sedimentation) and oxidation of heavy oil fractions are used, in fact, forming fuel oil (tar).


Tarred
Bitumen fractions - by percentage - are calculated by chemical analysis of fuel oil remaining after the evaporation of gases and liquids that make up the oil. The tarry bitumen composition is an important component of warm and hot asphalt, without which it is impossible to build (or repair) roads. Other types of bituminous building materials are obtained from tar bitumen.


Other
For example, a cold compound containing additional polymer inclusions contains crumb rubber, plastics that improve its properties, and carbon-organic solvents. A melted, softened piece of bitumen used for asphalt or roofing is diluted with white spirit. A bituminous paint is formed, which creates a better effect of waterproofing walls than, for example, oil paint. But additives in cold bitumen are not limited to white spirit alone.
Bitumen, which has served its time, crumbles, and it is processed, receiving volatile hydrocarbon compounds from it, or loaded with firewood into a pyrolysis oven.
In the latter case, it is possible to get a lot of heat, which finds its application, for example, in thermal power plants and boiler houses.

Stamps
BND 40/60
One of the most fusible. Softens at 40 degrees. Its use is limited by the fact that in the southern regions of Russia, even in cloudy but hot weather, it is close to softening. It is used mainly in northern latitudes, where summers are almost never hot.
It is frost-resistant, can retain its properties in winter, is almost not subject to breaking into pieces and fragments.


BND 50/50
A composition that softens only at a temperature of 50 degrees. This is not an overestimation of the GOST requirements. In fact, it is able to heat up - in the composition of asphalt - in the summer heat. It adheres perfectly - this property is in favor of patching roads, for the complete re-laying of which funds from the local or federal budget have not yet been allocated in full.
When a piece is installed on a flat surface, this substance spreads into an even puddle. This makes it possible to obtain an even layer without unwanted changes.


BND 70/100
To soften, this grade of bitumen must be heated to 72 degrees. Differs in high adhesion. It is used for the release of roofing material. It is possible to use the composition as a lower or upper layer of asphalt - they, for example, water old asphalt before laying a new one, if the road needs to be raised by 10 or more centimeters. Breaking the asphalt produces fragments that do not raise dust from the road when they are removed.
Due to the increased softening temperature, this brand has a predisposition to the formation of cracks in the asphalt, and in the cold such a hard coating cracks faster.


BND-90/130
Heats up to 90 degrees, which refers to it as a reagent for hot asphalt. Breaking asphalt with such bitumen is complicated, but under the action of a sledgehammer or a bump stop, the road surface crumbles into fragments.
In its pure form, the broken composition of this brand has shiny, glossy chips.


Applications
Plasticity, good adhesion, insensitivity to freezing - here bitumen is indispensable for waterproofing roads (and in road construction in general), buildings, structures and structures. Bituminous building materials are difficult to damage.
BND - oil road bitumen - the cheapest material. Bituminous roofing and waterproofing walls and foundations are a great way to protect a building from dampness (wet soil and precipitation). The aforementioned roofing paper, as well as hydrostekloizol are examples of this. Mastics containing bitumen are produced on the basis of a bitumen-rubber mixture, latex, urethane, acrylic - they are used as a waterproofing roofing layer. With them, leakage in the roof and ceilings is completely excluded.
If we turn to historical monuments and structures found during excavations, then already in ancient times, bitumen was used in the construction of buildings and structures for various purposes.


Terms of use
Working with bitumen requires adherence to a certain stage of work - heating, adding additives and thorough mixing. After exhaustive preparation, the resulting composition is applied to the surface in need of such a coating.
Heating is carried out in bitumen smelters. The simplest option is to melt the bitumen in barrels over a fire. It is recommended to start stirring the bitumen after softening so that it does not burn out and does not decompose. The hissing and foaming of the composition when it is heated is a natural manifestation of the properties of bitumen. Fully molten bitumen has a smooth and shiny surface that mirrors the incident light.


The appearance of acrid smoke of air is a sign of the beginning of the decomposition of the bitumen composition, while the smoke becomes caustic, with a yellow-green palette. It is unacceptable to overheat bitumen for waterproofing layers - after cooling, due to the onset of decomposition, it will crack. When heating, it is necessary to keep a sheet of plywood within walking distance - if the bitumen catches fire, covering the neck of the tank will block the access of oxygen, and the flame will immediately go out.
When adding thinner, choose gasoline or white spirit. If the bitumen is overheated to a temperature above 160 degrees, kerosene can be used. The heavier and thicker the fraction, the more superheated bitumen you can add it without fear that it will evaporate ahead of time, without having time to liquefy the composition.
There must be more bitumen than the solvent: 30 or 50 percent of the solvent additive. The bitumen is heated with a solvent separately - this will exclude spontaneous ignition.
With a large volume of bitumen mixture, the solvent is poured into the bitumen. Small things are different.
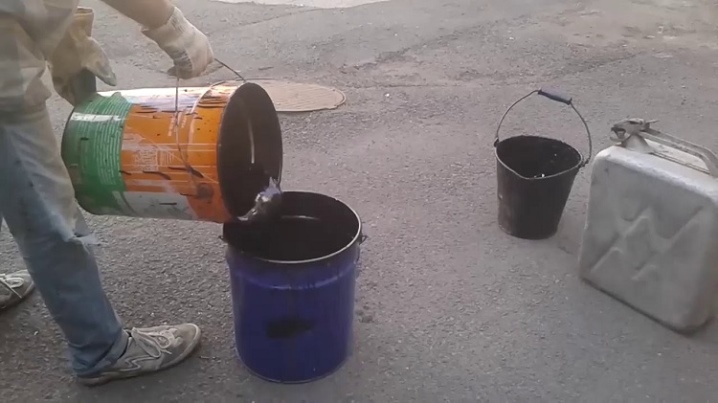

The process of filling binders - bitumen-containing mixtures - takes into account the speed of hardening of the building material. When transferring bitumen to the surface to be coated, the master will be faced with the fact that its layer thickens and dries after 2 minutes, and further leveling of the wall or floor will become impossible. The surface is pre-treated with a bituminous primer. The latter hardens significantly longer than the main bituminous composition, which means that it is permissible to use a brush or roller. When applying a thick layer of bitumen, for example, a mop, tightly wrapped in a cloth, is used.
The bitumen consumption rate varies based on the nature of the work. For waterproofing - maximum 2 kg per 1m2. Coating thickness - no more than 2 mm. A thin layer allows water to pass through, a thick layer cracks faster. For roads and sidewalks - up to 3 kg / m2. If poured, the bitumen hardens longer, and in the heat it becomes viscous. A smaller layer will not give good strength. Impregnation of asphalt (or asphalt concrete) may require up to 1 kg per 1 m2.

You can see how the asphalt is laid in the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.