Fluffy birch: features and cultivation
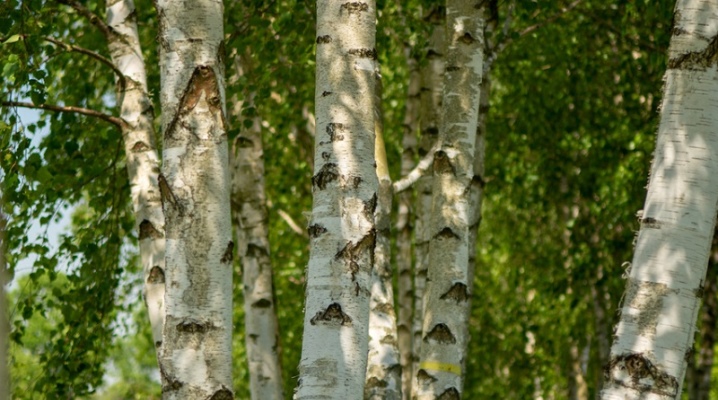

Common birch is one of the most beloved plants among the people, sung by famous Russian artists, songwriters and poets, a kind of symbol of Russia. One of the most common varieties of this plant is downy birch, it grows everywhere in the wild and is found in garden plots. It is noteworthy that in the old days it was called "white", but later they began to call it the dangling birch - to avoid confusion, they moved away from this name.
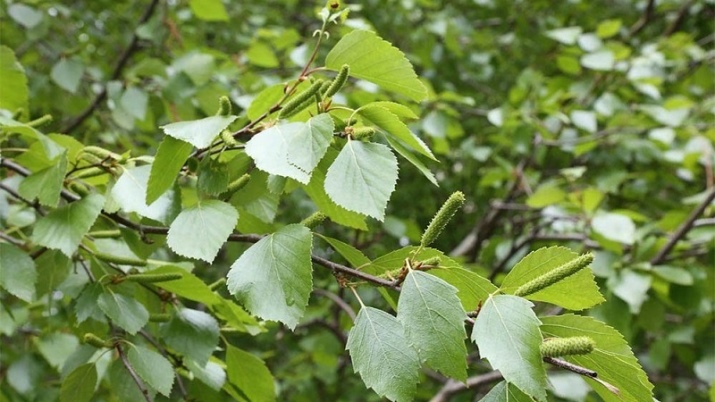






Botanical description
Fluffy birch (Betula pubescens in Latin) is a tall tree native to Europe. Its distinctive feature is smooth bark, cracks on the trunk are found only in old trees, and even then closer to the roots. Such areas are often accompanied by bast - this is a well-known phenomenon that manifests itself in the stratification of the crust into several thin layers. The trunk of a birch is erect, smooth, grows up to 15-20 m in height and up to 80 cm in diameter. Up to 5 years old, it is brown, then the volume of betulin produced gradually increases, and by the age of 10 the plant acquires a uniform whitish color. First years have dense, but lowered shoots to the ground.
Starting from the second year, the branches begin to stretch high upward; in adult trees, the crown becomes spreading. The leaves of young birch are slightly pubescent; in adults, the pile is preserved only on the lower leaf plates. The root system is powerful, well-developed, but it is located close to the surface, therefore, during strong winds such trees often fall. Spring bloom occurs in April-May. The fruits are formed in catkins, each seed has a pair of translucent wings, due to which they are carried by the wind over long distances. Ripening occurs in late summer - early autumn.
Fruiting does not occur earlier than in the 15th year of the plant's life.



Fluffy birch belongs to frost-resistant varieties. The average life span is 120 years, but under favorable climatic conditions it can be even longer. Downy birch is considered a medicinal plant. It has a number of healing properties: its kidneys contain healing oils, infusions and decoctions from them have a pronounced diuretic and antimicrobial effect. The wood of this tree is used to prepare activated charcoal, and birch sap contains many vitamins and micronutrients.
This type of birch has found its application in industry. Wood of this species is used as a plywood raw material, as well as for the production of skis. The branches are collected in brooms for a bath. The tree serves as the basis for the manufacture of tar, turpentine, methyl alcohol and acetic acid. Fluffy birch is no less popular among landscape designers. It is planted both as single plantings and in groups. This ornamental plant with a snow-white trunk and a lush crown becomes a real decoration of any personal plot. The beauty of this primordially Russian plant is unique, so there will always be a place for it in parks, squares and garden plots.



Planting and leaving
Fluffy birch should be planted in late August - early September, preferably in an unheated greenhouse. Planting is carried out by sowing seeds on prepared, loosened soil. The grown seedlings are placed in small containers and left in the greenhouse for several months, and after the snow melts, they are transplanted into open ground on a permanent site. A distance of at least 4 m should be maintained between young seedlings.
When planting, it is important to ensure that the root collar remains on the ground. It is advisable to add a complex mineral and organic fertilizer to the planting hole. This will help the root system to harden faster and provide the plant with the nutrients necessary for its full growth and development. A young birch needs about a year for the sprout to fully take root and take root in its place. During this period, it grows by about 1 m.



Seat selection
Downy birch grows best in temperate cold or temperate climates. The growth habitat is swampy areas, lakes and water bodies, as well as mountainous areas. The culture is unpretentious to the soil - it develops equally well on neutral, acidic, clayey, loamy and sandy soil. Downy birch loves moisture, its natural habitat is watersheds, low-lying swamps, forest edges.
Persistent birch forests form on plains and river banks. For all its unpretentiousness, birch has a demanding attitude to light - it prefers sunny, well-lit areas.



Watering
Young birch in the first time after planting requires intensive and abundant watering. When a tree grows up, it has enough moisture obtained from snow, melt water and rain; it does not need additional irrigation. At the initial stage, downy birch also needs top dressing, solutions of urea and mullein are considered the most effective. An adult plant is fertilized at will.


Form formation
Like any other tree, birch requires sanitary pruning - the removal of broken, dried out and diseased branches. When grown in gardens and parks, formative pruning is carried out to give the plant a more decorative appearance. It is not recommended to do the shaping of fluffy birch in the spring. The fact is that even before the buds appear in the trunk and branches, intensive sap flow begins, and if any part of the tree is cut off during this period, there is always a risk that it will run out of juice and die. In summer, the crown is formed if other trees grow in close proximity. In conditions of a lack of lighting, the branches begin to reach for the sun, become too long and thin - with a fragile trunk, this can cause the plant to break. In this case, pruning will solve the problem of competition for light and water. Crop trimming performs several tasks at once:
- thinns out skeletal branches, thus improving the illumination of the trunk circle;
- stimulates the growth of young side shoots;
- gives the plant a neat decorative look.


Topiary pruning of birches has become widespread in recent years. It allows you to form a rounded symmetrical crown on a trunk devoid of branches. However, such pruning requires skill, since any mistakes in technique can lead to the death of the seedling. In the period from October to April, the birch goes into a hibernation state. At this time, the circulation of the juice stops, so you can easily carry out a rejuvenating haircut. It is advisable to perform it every two years.
Regardless of the season, pruning is required if the trunk thickness does not match the height of the plant. In such a situation, the birch develops disproportionately, and the risk of its collapse during a strong wind increases significantly. To prevent this, the top should be trimmed. In the case when you are forced to carry out work in the spring, the cut area should be tightly covered with garden pitch.
Like many other plants, downy birch sometimes suffers from fungal infections and insect pests.They can parasitize on leaves, shoots and roots.


The most common diseases of downy birch.
- Witch's broom - an infection caused by a marsupial fungus. It penetrates into damaged areas of the branch and actively reproduces there. As a result, new shoots are formed ugly. Such a disease does not pose a threat to the life of the plant, but its decorative characteristics are significantly reduced.
- Bacterial dropsy - one of the most dangerous diseases. Swellings appear on the birch bark, and a liquid with an unpleasant odor accumulates inside. At the place of their appearance, the bark begins to die off, and with a large-scale infection, this leads to the drying out of the tree. It is very difficult to fight such a disease, most often it leads to the rapid death of birch.
- Powdery mildew - the most common pathology among birches. It manifests itself in the appearance of white bloom on the leaf plates and the suspension of the growth of new shoots. It is not dangerous for neighboring plants. To prevent the appearance of such an ailment, it is necessary to spray the tree with copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid in the spring.



Reproduction
Plant propagation is carried out in two main ways: by seed or vegetatively. In the first case, the seeds can fall into the ground by self-sowing or be planted on purpose. Sowing is carried out in the fall directly into the ground or into the greenhouse. The vegetative method is usually used when cutting an old tree. As a rule, several live shoots remain on the stump. Some of them die, while others form strong healthy branches - they can be used for further planting.
The workpieces should be placed in water, wait until they take root, and then root in a nutritious substrate. However, even with the best approach, most of the cuttings do not take root. As practice shows, no more than 10% of the trees planted in this way grows.
To rejuvenate the plant and create weeping forms, birch can be grafted. It is best to do this at the end of summer by budding the lignified cuttings of the current growth.


What is the difference from drooping and warty birch?
Fluffy birch is often confused with drooping birch. Indeed, these plants have a lot in common, but there are also differences.
- In fluffy birch, the base of the leaves is round, in drooping birch it is wedge-shaped.
- The bark of a fluffy birch is white or light gray from top to bottom. In the drooping, only the upper part is white, the bark at the base is dark, rough with a lot of cracks.
- Downy birch is more adaptable to harsh weather conditions. It grows even in northern regions and on swampy soils. But hanging is more common on dry soils.
The main difference between fluffy and warty birch is the appearance of the trunk. The latter has on its surface resinous glands, similar to warts, thanks to which it acquired its name.



In the next video, you will find additional information about fluffy birch.



































































The comment was sent successfully.