Euonymus: description of the bush, planting and care

Often, the attention of gardeners is undeservedly deprived of euonymus - an ornamental shrub that can become the main decoration of the garden and delight with its beauty throughout the season. Even with the onset of autumn, when the flowering of crops stops and the garden is immersed in dull colors, this bush continues to decorate the site.


Peculiarities
The plant can be represented under the name eonymus. The culture belongs to the euonymus family, which includes more than a hundred varieties from miniature bushes to medium trees. In the wild, the plant can be seen in East Asia, Europe, Australia, North America and Madagascar, some of the forms grow in China. In Russia, it grows in the Urals, in the middle lane, in the Far East.
The shrub is capable of reaching a size of 7 m. The flowers are usually compact, their color varies depending on the variety and variety. The number of inflorescences is up to 5 pieces. The fruits are formed in dry capsules. The culture has medicinal properties, however, the berries are very toxic due to the content of alkaloids, so it is recommended to abandon planting in the presence of small children.
The plant is unpretentious to care. For example, the shrub easily tolerates strong gas pollution or a short-term drop in temperature to -20 degrees Celsius. Seeds are often sold in a "mix" format and are a mixture of several varieties of crops, the description of which will be disclosed below.




Types and varieties
There are several types of represented culture.
Winged
Differs in fiery color of sheet plates. For this specific property, the plant is sometimes even called the "burning bush". This shrub grows for a long time, its size is about two meters, brown or green straight shoots are strongly branched. During the summer months, the foliage pleases with colorful greenery, and in September it begins to become covered with a red tint and, as a result, is completely colored. In winter, seedlings of fruits complement the decorative effect of the bush with a scarlet color, but flowers are not considered by gardeners as garden decoration.
The most popular varieties of the winged species are "Compactus" with a height of up to 1 m, "Fireball", reaching 1.5 m, and "Rudi Haag" - miniature variety, the length of which does not exceed 1 m.


European
This tree has dark green foliage, variegated varieties are found. In autumn, the leaves are painted in rich red tones. Despite the pretty bright pink or scarlet fruits, this species is not popular in gardening circles. Basically, it is customary to grow the "Red Cascade" variety, which is distinguished by a raspberry tint of foliage from the beginning of autumn.


Fortune
This group belongs to the most demanded in gardening. It has an evergreen groundcover appearance and includes many forms. The shoots of the plant are creeping, and therefore the cultivation of the variety is somewhat different from the care of other varieties.
Usually summer residents choose the following Fortune varieties for maintenance: undersized Emerald'n Gold, dark green Emerald Gaiety, dwarf "Sunspot" with unusual color of leaves, variegated "Harlequin", Sunshine with rich yellow leaves, "Silverstone" with semi-straight shoots, small-leaved Minimus with a height of only 15 cm, fast growing "Silver Queen" with white and green foliage.




Japanese
More often this variety is grown at home due to its vulnerability to cold weather. It is characterized by narrow leaves up to 7 cm long. The attention of gardeners is attracted by such varieties of the Japanese group as variegated "Bravo", broad-leaved "Golden Queen", evergreen upright dense shrub Marieke, "Aureomarginata" with green leaves with a white-yellow frame.



The flat-peaked view deserves special attention. Usually it is a tree up to 3 m high with olive shoots. Sometimes a bluish bloom is visible on the trunk. It is characterized by long leaves - up to 19 cm, their width is 9 cm.One inflorescence forms up to 30 flowers, and the height of the peduncles is 15 cm. The plant is actively cultivated to decorate gardens and summer cottages.
And also the choice of gardeners often falls on Siebold's euonymus. The size of this shrub is 2-4 m, it has simple pointed, leathery, fleecy leaves 6-17 cm long and 4-9 cm wide. The flowers are usually up to 12 cm in diameter, each inflorescence has no more than 15 flowers. In nature, this species prefers to grow in forest areas, on the edges of coniferous forests, in river and stream valleys, in the lower part of mountain slopes.


How to plant?
The presented culture is a fairly simple and unpretentious plant for growing in various regions with cold winters. Even in Siberia, it is possible to keep shrubs.
Choose a suitable location before planting the plant. The tree develops best in areas that are protected from the wind and well illuminated by the sun, the plant will feel comfortable in partial shade. If variegated varieties are planted, then you need to choose the most lighted flower bed. When planted in the shade, the culture will develop poorly, the shade of the foliage will not please with brightness.
The most favorable time is spring or mid-October. If you plan to plant a specimen with a closed rhizome, then the procedure can be performed throughout the season. When planting, it is important to take into account the shape of the future shrub. There are species that grow very well, therefore, it is advisable to observe an interval of 1.5-2 m between plantings.
Suitable soil is slightly alkaline, fertile soil with medium acidity. You can pick up a site with a shallow groundwater table. The first step in planting is digging a hole. The dug soil should be combined with compost. Expanded clay or broken brick is immersed at the bottom as a drainage layer. If the ridge is not clayey and enriched with sand, then the drainage system can be omitted.
The next layer is the mixture prepared earlier, in which the seedling is planted so that the root collar is located at ground level. Now the planting site is compacted and well moistened.




Experienced summer residents advise placing a layer of mulch around the seedlings, which will keep moisture in the ground for a long time, prevent the development of weeds, prevent the roots from overheating, and prevent the formation of fungus, to which ground cover species are especially prone. Bark or wood chips can be used as mulch. Already after a few weeks, active growth should be observed.
How to care?
Spindle tree care includes standard agricultural procedures.
Watering
During rooting, it is important to water the plant as often as possible, preventing the soil from drying out, then watering procedures can be reduced. Large varieties are recommended to be watered less often, but in large quantities. Low species are less vulnerable to drought, so it is better to water them more often, but in small doses. As in caring for other crops, in the heat, the shrub needs abundant moisture, and during the rainy season it is better to completely abandon watering.

Top dressing
If in the country the plant is planted in fertile land, then it is not necessary to add additional nutrition. It is recommended to feed the crop in the period after spring pruning.As a fertilizer, mineral mixtures for garden crops in the form of granules are suitable; it is customary to scatter them 20 cm from the bush. Once every 2 years, the plant will not interfere with feeding in the form of a solution of rotted manure.
If a ground cover variety is planted, then during rooting it can be fed with compost.


Pruning
A sanitary haircut is carried out in spring and summer. This procedure results in active branching. During the process, the gardener eliminates injured, wilted shoots, smoothes thickening. For rejuvenation, branches should be shortened by half every 3-4 years.
Formative pruning can be done in early spring and fall. This manipulation is aimed at creating an unusual bush shape. So, a popular form is a plant on a trunk. If this is a ground cover species, then during the growing season it is customary for him to pinch the tops of the shoots - this procedure activates the development of lateral branches.


Transfer
Usually, the presented culture is transplanted every 3-4 years - this is important when keeping an adult dwarf specimen. At a young age, the plant needs an annual transplant. If a tall species is grown, then transplanting is sufficient only at a young age. The transplanting process is carried out together with a lump of earth - this reduces the risk of damage to the root system during the procedure.


Wintering
European and winged species withstand winters best of all; they can overwinter without additional protection. Only young seedlings up to 3 years old need insulation. When growing Japanese species and Fortune, additional cold protection measures should be taken. If the winter is snowy, then these varieties will survive the winter, but if there is no snow, then it will be quite difficult for them.
To help the plant endure frost, it needs to be watered abundantly in mid-November and a layer of compost should be applied as mulch or spruce branches should be laid out - these measures will keep moisture in the ground, which the roots will not be able to extract from the frozen ground in winter.
If snow is not observed in winter, then it is allowed to protect the shrub with agrofibre, burlap or dry foliage. When the frosts stop and the above zero temperature is established, the shelter can be removed.

Reproduction methods
Euonymus is propagated in different ways.
Seeds
Almost all varieties of this representative of the flora can be propagated by the sowing method. The seed is collected in September, after which the sowing is carried out immediately. When planted for the winter, the seeds will naturally harden. During sowing, the seedlings are eliminated, the seeds are planted in fertile soil, moisten the planting site and cover with straw or spruce branches.
If the gardener plans to sow in the spring, it is recommended to store the seed in the refrigerator for six months, and then soak it in water for a couple of days before planting.


Cuttings
Cuttings are carried out in the summer. Cuttings 10-15 cm in size are used as planting material. The lower leaves must be removed, the top must be cut off, the ends are treated with a root-forming agent and planted in a substrate made of peat and sand. Next, the planted shoots should be watered, the container should be wrapped in plastic wrap. Further care consists of airing and maintaining normal moisture content of the substrate.
It is better to put the container in a shaded place. If the variety is winter hardy, then in October the cuttings are allowed to be planted in open ground. When breeding evergreen species in winter, it is recommended to keep the container in a cool room, and transplant in April.
You can try to propagate the shrub by cuttings in water, they quickly form roots, to a greater extent this property is expressed in Japanese varieties and Fortune.


Planting material for rooting should be collected in the second half of spring.The container with water must be removed away from sunlight, the water must be renewed a couple of times a week, and when roots appear, the cuttings must be transplanted into an individual container or into the garden.
Layers
This method is common for the reproduction of ground cover and low varietal forms. Near the bush, you need to dig a groove 2-3 cm deep, bend the side shoot, put it in the groove, fix it and add soil enriched with useful components.
After a year, the roots will form at the shoot, it can be separated and planted on another site. Fortune cultivars can form superficial roots, and therefore the cuttings are simply placed in the ground for rooting.
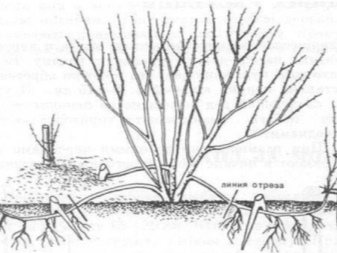

By dividing the bush
This method is used when breeding dwarf varieties, the roots of which are shallow underground. At the beginning of the growing season, the root shoots are shortened by 1/3 and cut off with a share of the rhizome, after which they are planted on a new ridge. The planting is well moistened, then a layer of mulch is applied.


Diseases and pests
Insects quite often become a problem when growing the presented plant. The most common pests are aphids and mealybugs.
- Aphid. Looks like a miniature black or green bug. Usually the culture is attacked by whole hordes of such individuals. You can spot aphids on the underside of the leaf. This pest loves to feast on juice. Insecticides and pesticides are effective control methods. You can also fight aphids by treating them with soapy water.
- Mealybug. These insects are also visible to the naked eye; they prefer to feed on the sap of young shoots and leaves. If there are not so many individuals, then you can eliminate them mechanically. Of the purchased means against insects, preparations "Aktara", "Biotlin", "Calypso", "Confidant", "Confidor", "Mospilan", "Tanrek", "Fitoverm" are good at fighting. After 1-2 weeks, it is advisable to re-process the affected specimen.


Sometimes the plant becomes a victim of various diseases. Most of them are provoked by non-compliance with the rules of agricultural technology. So, with waterlogged soil, it is possible to encounter powdery mildew. You can recognize the disease by the white bloom and drying of the crown.
If brown streaks are observed on the sheets, then it can be assumed that the culture is affected by brown spot. Both ailments are treated with fungicides. The most effective means are "Peak", "Hom", "Skor", "Abiga".
The most serious disease for a plant is called mosaic. The presence of the disease is indicated by the formation of yellow spots and deformation of the leaves. When infected, there is no point in treating the affected specimen - it remains only to dig it up and dispose of it as soon as possible.



Use in landscape design
The culture can be planted as a single plant, or participate in a collective planting. It is used to decorate lawns, it can be used for growing hedges. If you plant it in a group ensemble, then it is better to choose large, spreading species.



Tall forms make a spectacular backdrop for other crops. It is more advisable to arrange flower beds around the perimeter with dwarf varieties, as well as use them when decorating alpine slides and rockeries. In some gardens, the crop is represented as part of the lawn or as a curb that flanks the garden alley.


Sometimes plants can be used to decorate balconies, terraces, verandas. Coniferous shrubs, dwarf barberry, dogwood will become good neighbors in the development of landscape design. If Fortchun's euonymus is planted, then it is allowed to fix it on supports for landscaping various structures.


Planting and caring for euonymus in the next video.



































































The comment was sent successfully.