Tuberous begonia: description, types and subtleties of care

A perennial plant, called tuberous begonia, is considered unpretentious and one of the most beautiful flowers that can be successfully grown both in the summer cottage and at home. The key to successful breeding of tuberous begonias is proper care. The plant is not able to overwinter in the open field in the rather harsh and changeable weather conditions in Russia, therefore, the begonia tubers must be germinated anew every year. The renewed plant, in response to care, is able to please the gardener with abundant and long flowering, decorating a terrace, flower bed or balcony.

Peculiarities
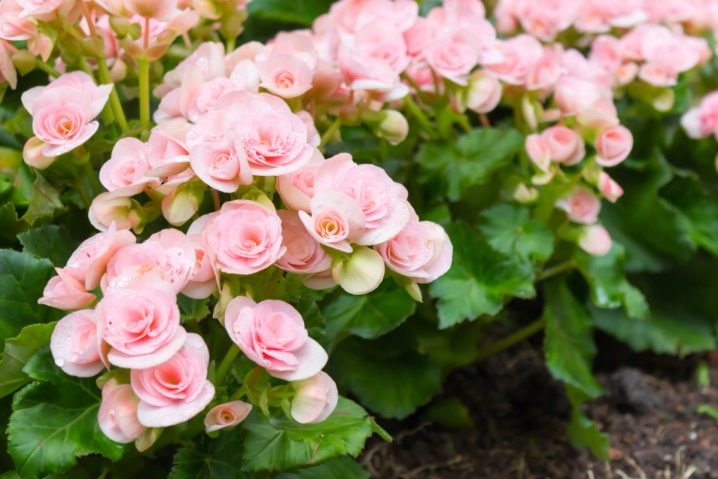
Tuberous begonia is the result of a selection in which at least 8-9 plants have been involved, previously grown in various areas around the world. Specialists began breeding work back in the 19th century, and today the results of such painstaking work are very impressive - more than 200 varieties of this perennial were born. Tuberous begonia differs from conventional cousins in that this plant can be both indoor and garden. There are ampelous, herbaceous and shrub varieties of this flower. However, the most important distinguishing feature is the presence of a developed root, which is formed in the form of a massive tuber, reaching up to 6-7 centimeters in diameter.


The aerial part of this perennial has the appearance of a green, somewhat transparent stem. This stem can sometimes grow up to 80 centimeters. In structure, this part of the plant is quite strong and well developed. In addition, leaves are fixed on the stem - their appearance and size depends on the begonia variety.
All tuberous begonias differ from their counterparts, while they are good in that they have a very abundant and long flowering. The shape of the flower is varied, it depends on the type of plant and is outwardly similar in structure to a peony, daffodil, carnation or camellia. In addition, ampelous begonias have male and female flowers - male flowers are usually larger and more attractive in appearance, unlike female ones. Flower sizes in hybrid varietal begonias vary from 3-3.5 to 18-20 centimeters. There are varieties where flowers are collected in inflorescences - such properties are most often possessed by ampelous varieties of begonias. The flowering period of hybrid begonias depends on the degree of formation of the plant - it begins in early May and lasts until the end of September - early October.


Begonia grown from a tuber does not tolerate low temperature conditions, therefore, it can be planted in open ground only at positive temperatures in late spring or even at the beginning of the summer period. It is noticed that with a group planting, plants move into growth more actively than with a single planting. If you decide to grow begonias at home, then low temperatures are not terrible for your perennials, and the green foliage that appears will actively purify the air and heal it.


In the phase of active flowering, tuberous begonias do not like permutations. - this refers to the case when you are growing a perennial at home. The flowering bush should not be rearranged or turned on its other side to the light source. In this regard, begonia is quite capricious - when changing its location, it can quickly shed its flowers.It is noteworthy that under unfavorable conditions, ampelous begonias usually shed the most beautiful male flowers, while female ones can hold out for a longer time.


Varieties
Now let's take a closer look at the varieties of tuberous begonias. The names of the varieties are very diverse and among them there are very unique and interesting specimens.
- Terry begonia "Scarlet". This variety has large red flowers and a double structure. The variety is able to adapt well both in illuminated places and in partial shade. In good light conditions, flowering will be more abundant and lasting. Due to the fact that the flowers are quite large, the plant needs to tie up its shoots to the supports. For full development, the variety needs regular fertilizing with mineral fertilizers.


- Begonia "Party Dress" - a real beauty with bright orange-yellow flowers with a red border. The flowers are large, double. The bush itself grows no more than 30 centimeters, but it blooms very abundantly. The edges of the petals are fringed and resemble ruffles. The appearance of such begonias is very spectacular - the plant will become a worthy decoration both in the garden and on the balcony.


There are so-called Scottish varieties of tuberous begonias. They are called that because they were bred in the Scottish Begonia Society. The most prominent representatives of these varieties are the following.
- Olivia variety - not only has an attractive flower appearance, but also has a sophisticated aroma. The opened flower reaches 16-18 centimeters in diameter and has a delicate apricot color. The petals of the flower are double, their size decreases towards the core of the flower. Blooming "Olivia" exudes a scent reminiscent of a rose bloom.


- Variety "Matilda" Is a pale white flower with pink edging at the tips of the petals. The older the plant, the more intensely the pink color of the edging is visible. The flower is double and large enough. When fully deployed, it can reach a diameter of 14 to 18 centimeters. The petals are wavy. "Matilda" blooms very profusely, until October. The bush of this begonia itself is quite compact, although the leaves are large.


Tuberous begonias can also be grown in hanging pots. Breeders have developed special varieties for these purposes, which are collectively referred to as ampelous begonia. There are quite a few varieties of such perennials, but the most beautiful, perhaps, can be called a few.
- Bolivian begonia - this variety means a collection of different varieties such as Copacabana, Santa Cruz Sunset, Bossa Nova and others. The shoots of such begonias initially grow upward, but when they reach about 30 cm in height, they begin to fall down in the form of a cascade. The leaves of such plants differ from their bush counterparts - they are much smaller and sharper. The flowers also have an unusual shape - they consist of several elongated petals (usually 4-5 pieces) and there are a lot of them - 3 flowers are grouped on cluster-shaped inflorescences. The color of the flowers can be red, orange, pink, white. Flowering begins in late spring and lasts until the first fall frost.


- Begonia Chanson - this variety also includes several varieties that have different colors and can be white, yellow, red or orange. The flowers of these begonias are double or semi-double. They are quite large and numerous, collected in clusters. The size of the shoots can be from 30 to 40 centimeters. The flower in the phase of full disclosure has a diameter of 4 to 6 centimeters.


Modern breeding does not stand still, and previously bred varieties are expanding due to the creation of more and more new subspecies. Breeders develop not only different color options for the color of begonias, but also pay attention to increasing its resistance to adverse factors.
Landing
There are two ways to grow tuberous begonia at home - by sowing seeds into the soil or using the tuber of an already mature plant. When growing begonias from seeds, it is important where they will grow in the future. So, for example, if you plan to grow this perennial as a houseplant, then sowing seeds should be done in December, and if you want to grow a plant in the garden, then sowing seeds for seedlings can be done in early spring.


The technique for growing begonias from seeds is as follows.
- Granular seeds of a certain variety are purchased.
- Peat tablets are used as a nutrient medium, which must first be soaked in warm water and placed in a container for seed germination.
- We put each individual seed on the surface of a peat tablet (on a small depression there) and sprinkle with warm water, while it is not necessary to bury the seeds in the soil.
- The container with peat tablets and sown seeds should be covered with glass or plastic wrap, and then placed in a warm place where there is enough light.
- Periodically, the film must be removed for the flow of fresh air and drip irrigation of future seedlings - while it is important to ensure that the peat soil does not dry out.
- From the moment of emergence of seedlings (this happens after 14-15 days), the first top dressing of mineral components is added dropwise, dissolving it in warm water at a dosage of 1: 4 of the recommended values.
- In the phase of the appearance of a third leaf in seedlings, peat tablets can be planted in small containers with soil for further formation of the root system, while the film is removed for an increasingly long time, accustoming the plant to the temperature regime of the environment.
- After waiting until the young plant is strong enough, it can be planted in a small pot or transferred to the garden, when it becomes warm, to its permanent habitat.
- When planting a young begonia in a pot, one must remember that its volume should be 1-2 centimeters larger than the previous one. If you transplant the begonia immediately into a large container, then you can not wait for flowering - the plant will put all its strength into rooting in a large space for it.


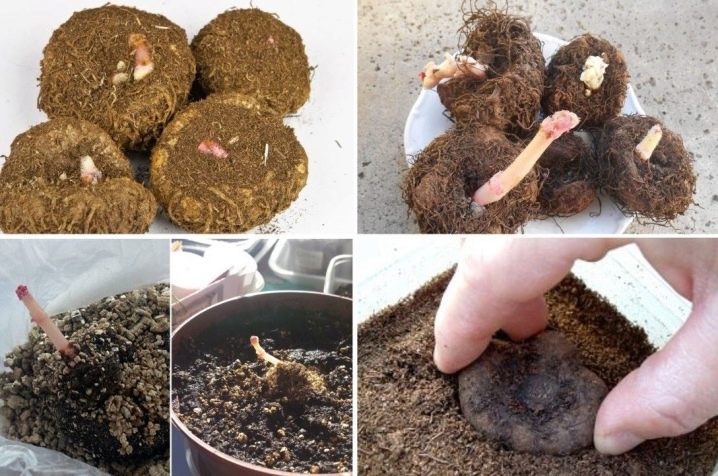
A slightly different technique is used to grow begonias from a tuber. Its essence is as follows.
- Planting material can be purchased in specialized nurseries or dug up in the fall in the garden.
- All shoots must be removed from the tuber and placed in a container with soil, which is transferred to a basement with an air temperature of 8 to 10 degrees Celsius.
- In February, the tubers need to be placed in moist soil, where they will germinate at temperatures up to 20 degrees, good soil moisture and sufficient lighting.
- As soon as buds of future shoots appear on the tuber, it is cut into pieces each having one shoot, and the cut sites are treated with coal powder and dried, thereby preventing putrefactive diseases.
- Now parts of the tuber with future shoots are planted in containers with moist soil, while deepening the tuber no more than half. If small leaves have already appeared, then it is important to ensure that they do not come into contact with the soil, otherwise rot may develop on them, leading to the death of the plant.
- For 20 days, young shoots need to be looked after - moisten the soil and provide good lighting and warmth. After this time, the plants can be transplanted to their permanent place of growth. In this case, one must not forget to add mineral fertilizing to the soil for better rooting and growth of begonias.

When growing begonias from a tuber, care must be taken to ensure that the soil is not waterlogged. In addition, it is important to choose the right pot in terms of volume - it should not be too large or too small. It is enough for the new container to be a couple of centimeters larger than the previous one.If you plan to plant begonia in open ground, you need to immediately choose a place where it will be provided with good and uniform lighting, as well as protection from drafts and strong winds.

Care
After you have finished germinating begonias and transplanted young plants to their permanent growth site, you will need to pay attention to them again. Growing begonias is a fun and interesting process. This plant is not capricious and responds well to care, so it is not difficult to grow it at home or in the garden. Any begonia loves light and warmth, but it can also tolerate a certain shade well, although the plant variety plays a significant role here. It is worth knowing that those plants with large flowers love semi-shaded habitats, and begonias with small flowers have a need for bright lighting. This principle is also true for ampelous tuberous varieties.


Another important point is that begonias' stems are fragile and brittle, so plants do not like strong winds and it is best to plant them under the protection of large shrubs or among tree trunks. In addition, do not forget that begonia loves warmth, so it may be too cool in open areas. Although there are some varieties that can bloom even at 10 degrees Celsius. But this is more the exception than the rule.
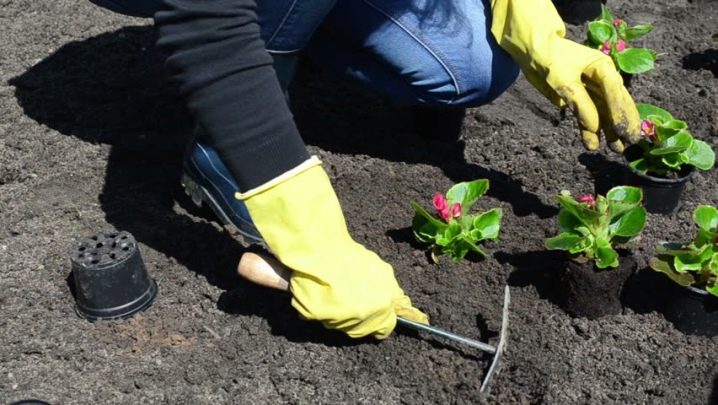

Begonias suffer greatly from heat and dryness of the soil, so it is important to ensure that the soil substrate is always moist. This rule applies to both garden plants and home begonias. When watering, you must observe the measure - excess water will lead to decay of the root system or to stop plant growth. It is especially important to observe moderation when watering newly transplanted begonias, since at this time they have an important rooting process, which consists in the growth of the root system.

Reproduction
If you did everything correctly and a beautiful begonia appeared in your garden or house, you will certainly want to propagate it. This can be done with cuttings or a sheet. This method is good because new plants will retain all the characteristics of the variety that the propagated plant possesses. Begonia is propagated by cuttings in spring or autumn. To do this, it must be separated from the mother tuber. The stalk should be taken about 10-12 centimeters long, while the slices from both it and the tuber should be sprinkled with coal powder. Next, the cutting must be dried for a couple of hours and set to root in moist soil. Cutting occurs by burying the cuttings 2-3 centimeters into the soil. On top of it you need to put an inverted glass jar, which will act as a greenhouse. In just 3-4 weeks, young begonias will take root and will be ready to be transplanted to a permanent place of growth.


Begonia can also be propagated using a leaf. To do this, you need to choose a large and healthy leaf, and then cut it off. Next, the leaf needs to be cut into triangles, but so that the lateral veins of the leaf fall into them, and the central vein must be cut out immediately - it will not be useful to us, since it does not participate in the process. Each finished piece of leaf must be laid out on top of moistened soil and secured with a toothpick. Sprinkle the edges with moistened sand. Or you can dig pieces of a leaf into the ground, deepening the lower part with a lateral vein by one centimeter. Now cover the container with the planting material with transparent glass or plastic wrap and put it in a warm and bright place. In the greenhouse you created, you need to maintain high humidity. And after 1.5-2 months you will notice young shoots. When they grow up and get stronger, the seedlings will be ready to be planted in a pot or open ground for further growth.


Winter storage
After the summer period of growth and flowering, your begonia will go into a dormant stage - the plant has to overwinter and needs to be prepared for this.Already in September, you will notice that the plant begins to prepare for a long winter nap. Begonias sleep begins in November and lasts until February. If your begonia has lived all summer outdoors, then its tubers have grown much more than those begonias that grew at home. With the arrival of the first frost, in order to save the tubers for spring planting, the ground part of the plant is cut off, and the tuber itself is dug out of the ground. After that, the tubers are given time to dry and are removed in a container with a small amount of peat for storage. Store the tubers of garden begonias in a dark and cool place. And in the spring, at the end of February, they will again be ready for awakening.

Homemade tuberous begonias are prepared for winter in a slightly different way. As fall approaches, you will see your begonia begin to wilt. Before wintering, you need to cut off the ground part of the plant, but you do not need to dig out the tuber from the pot. Watering the plant is reduced to the very minimum, but the flower pot is left to stand in the same place. With the arrival of spring, the begonia will need to be transplanted into a new container, and the tuber will need to be divided into parts based on how many buds it will have. In the event that your begonia has not wilted and did not want to shed the foliage, then you do not need to prune it. In this form, it is best to leave it until spring, reducing watering as much as possible. And in the spring, the plant will still need to be transplanted into fresh soil.


Pests and diseases
Hybrid begonia is considered a fairly strong and disease-resistant plant, but sometimes troubles happen to it. Most often, this flower suffers from powdery mildew or gray rot. Powdery mildew can appear on a plant when the soil is too waterlogged or there is too much moisture in the environment around the begonia. The disease affects the ground part and looks like a bloom of white flour on the leaves and stems. Gray rot occurs for the same reasons, but looks like a gray bloom. For the treatment of these diseases, the drug Benomil or other fungicides is used. In addition, the plant must be transferred to a drier and cooler place, eliminating sources of high humidity.


It happens that the root system of begonia is affected by black rot. Excessive moisture may again be the cause. For treatment, it is necessary to remove part of the rotten root system and treat the roots with Benomin, and then transplant the plant into a new pot with fresh soil.
Outdoor begonias can be attacked by an insect called whitefly. These pests damage the leaves of the plant, as they feed on its juices. To combat whitefly, you need to spray the leaves with a soapy solution prepared from 40 grams of liquid soap diluted in 10 liters of warm water. The most important thing is to try to prevent soapy water from getting on the roots during processing.


The roots of a perennial can be affected by a small worm called a nematode, while groin-like thickenings are formed on them, in which these pests are located. To fight worms, an aqueous solution from "Heterophos" is used, which is poured under the roots of the plant. But at the same time, the affected begonia roots will have to be removed. It happens that the entire root system is affected - in this case, it will not be possible to save the plant.


Often begonias suffer from the invasion of the red spider mite. This happens when a lot of moisture and a lot of heat is created around the flower. A diseased plant will have leaves with a marbled color, and in the future they will turn yellow and fall off. A spider mite can kill a plant in a very short time. To combat it, a drug called "Decis" is used. They need to spray the plant, paying attention to the back of the leaves - after all, this is where large clusters of mites are located.


It so happens that begonia begins to hurt and throw off leaves, not due to illness or pest infestation. This means that begonia needs more comfortable conditions.Often, she does not have enough light or it may happen that cold drafts affect the plant. By eliminating unfavorable factors, you can achieve recovery.
For information on how to properly care for tuberous begonia, see the next video.































The comment was sent successfully.