Chlorine for the pool: types, use, dosage

The owners of stationary and suburban pools are regularly faced with the problem of water purification. It is very important not only to remove foreign particles, but also to eliminate the pathogenic microflora, which is invisible to the eye, which is dangerous to human health. Chlorine is one of the most effective and low-cost products.

What is it?
Chlorine is an oxidizing substance. Interacting with organic matter, including algae and microorganisms, it prevents the development of pathogenic microflora.
For effective disinfection, the concentration of chlorine in water must be maintained at a stable and sufficient level, and if it decreases, then active reproduction of bacteria begins.
For the disinfection of swimming pools, calcium hypochlorite has been used for the last 20 years. Before its appearance, the treatment was carried out with a gaseous composition or sodium hypochlorite. Besides, disinfection is carried out using stabilized chlorine, drugs "Di-Chlor" or "Trichlor", which contain cyanuric acid, which protects chlorine molecules from destruction under the influence of solar ultraviolet rays. Therefore, such products are most often used to disinfect outdoor outdoor pools.


Advantages and disadvantages
Adding chlorine preparations to water is called chlorination. Today it is the most common disinfection method that meets the sanitary standards adopted in Russia.
Advantages of the chlorination method:
- a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms is destroyed;
- when a chemical is added, not only the water is disinfected, but also the pool bowl itself;
- the funds have a duration of active influence while in the water;
- affects the transparency of water, excludes the possibility of its blooming and the formation of an unpleasant odor;
- low cost in comparison with other analogues.

But there are also disadvantages:
- inability to suppress pathogenic forms that multiply through the formation of spores;
- with an excessive concentration of chlorine, it has a negative effect on the human body, causing burns to the skin, mucous membranes and respiratory tract;
- chlorinated water is harmful to allergy sufferers;
- over time, the pathogenic microflora develops resistance to its usual concentrations of the drug, which leads to an increase in dosages;
- some products can destroy metal parts of equipment and pool tiles over time.
As for the pools used in everyday life in the country, as a rule, they are located in the open air, and active chlorine, when disinfected under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, is gradually destroyed.
After a few days, you can even water the garden with settled water from the pool, but it is worth remembering that not all garden crops are positive about this.

Cleaning of the pool bowl and water treatment must be carried out regularly, otherwise the water will bloom, exuding an unpleasant odor, and the appearance of a man-made tank will look sloppy. It is dangerous to swim in such a pool, since water containing pathogenic microflora is swallowed during bathing.

Views
Water treatment products are available in different versions: they can be chlorine-containing tablets, granules or liquid concentrate. Pool disinfectants containing chlorine components are divided into 2 groups, in one of them stabilized chlorine is used, and in the other - unstabilized. The stabilized version contains additives that make the drug resistant to ultraviolet radiation.
Thus, the residual chlorine remains for a longer time in the concentration required for water treatment. Cyanuric acid is used as a stabilizer.
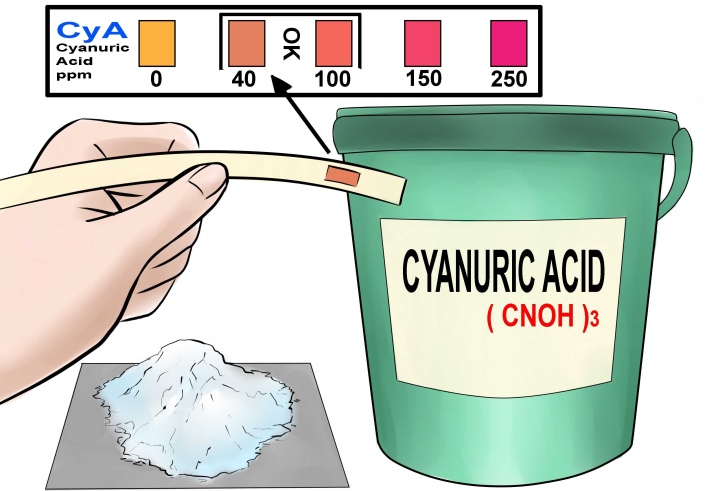
Thanks to isocyanuric acid, as well as a large dose of chlorine, equal to 84%, and the release form of tablets of 200-250 grams, the release period of chlorine in water is long, therefore such preparations are called "slow stabilized chlorine". But there is also a fast version of the drug, which differs from the slow one in that it is produced in granules or tablets of 20 grams, it contains 56% chlorine, and it dissolves much faster.
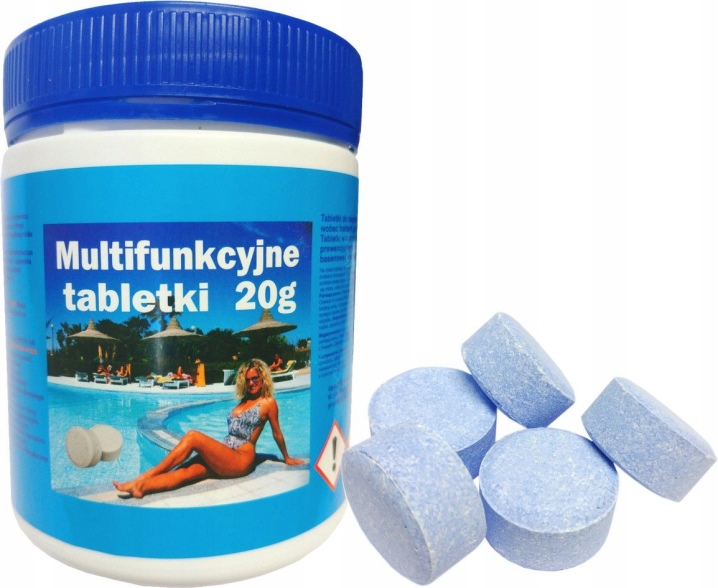

Dosage
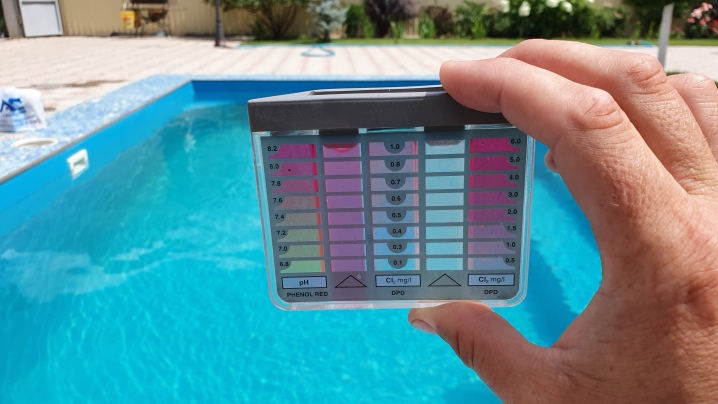
When carrying out disinfection, it is necessary to observe the dosage rates used per 1 cubic meter. m of water. According to sanitary standards, a control measurement is made before disinfection to determine the level of residual free chlorine. Its content in water should be in the range from 0.3 to 0.5 mg / l, and in case of an unfavorable epidemiological situation, an amount of 0.7 mg / l is allowed.
Total chlorine is the sum of free and combined chlorine. Free chlorine is that part of it that is not processed by the microflora of the pool, and whose concentration is the key to safe and clean water.

Bound chlorine is the part of chlorine that is combined with ammonium, which is present in the pool in the form of organic matter - sweat, tanning cream, urine, and so on.
Chlorine and ammonium form ammonium chloride, which gives off a pungent odor when chlorinated. The presence of this component indicates a low level of acid-base index of water. The disinfecting ability of ammonium chloride is almost a hundred times less than that of active chlorine, therefore, stabilized agents are used much more often for cleaning the pool, since they form a smaller amount of ammonium chloride than unstabilized counterparts.
There are certain dosages of chlorine-containing drugs.
- Slow stabilized chlorine - 200 g per 50 cubic meters of water.

- Fast stabilized chlorine - 20 g per 10 cubic meters of water is dissolved 4 hours before bathing or from 100 to 400 g in case of severe bacterial contamination of the water. Granules for every 10 cubic meters of water with low bacterial contamination are used in 35 g each, and for severe contamination - 150-200 g each.

Correct doses of chlorine dissolved in water do not dry the skin, do not irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory tract.
Instructions for use
To carry out chlorination correctly, you must first establish the amount of chlorine already present in the water, and then calculate the correct dosage for adding an additional amount of the drug. Such diagnostics allows avoiding excessive concentration of chlorine in water or its insufficient amount.
The dosage is selected depending on the type of chlorine-containing agent, the degree of water pollution, its pH level and air temperature. The higher the temperature, the sooner chlorine loses its ability to dissolve in water. The solubility of the drug is also affected by the pH level of the water - it should be in the range from 7.0 to 7.5.
Changes in temperature and pH balance results in the fact that chlorine quickly decomposes, giving off a pungent odor, and the amount of drug used increases.

Instructions for working with chlorine-containing preparations:
- tablets or granules are dissolved in a separate container and the finished solution is poured into those places where there is the strongest pressure of water;
- during chlorination, the filter must work by letting in water and removing excess chlorine;
- tablets are not placed undissolved in the pool bowl, as they render the lining unusable;
- if the pH level is higher or lower than normal, it is corrected with special preparations before chlorination;
- you can use the pool no earlier than 4 hours after applying the drug.

In case of severe bacterial contamination or in case of an unfavorable epidemiological situation, shock chlorination is carried out, when 300 ml of the drug with chlorine is taken per 1 cubic meter of water, which is a shock dose. With this treatment, you can swim only after 12 hours. In a public pool, when a large number of people pass through, shock treatment is performed once every 1-1.5 months, and regular disinfection is carried out every 7-14 days.
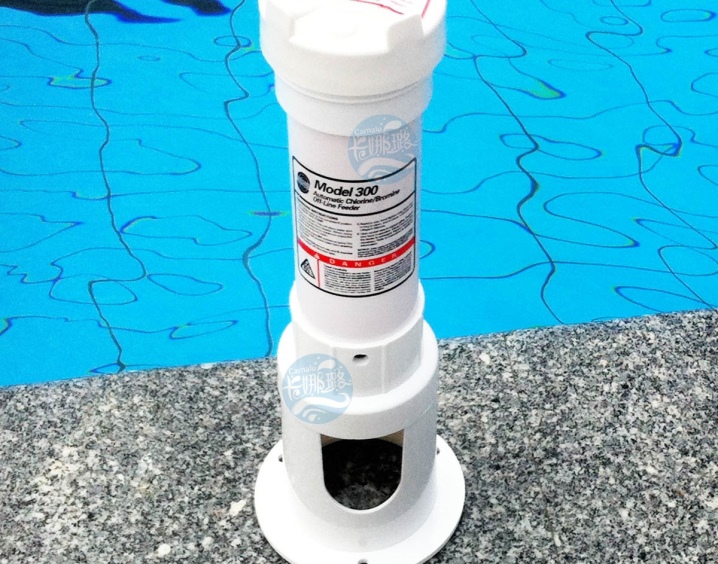
In public pools, there are automatic chlorinators that dispense a programmed amount of chlorine-containing drugs into the water, maintaining their concentration at a given level.

Security measures
Chemicals require careful handling and safety precautions.
- Do not mix chlorine with other chemicals, as this will form a poisonous substance - chloroform.
- Preparations are protected from exposure to ultraviolet radiation and moisture. It is important to protect children from contact with chlorine.
- During work, it is necessary to protect the skin of the hands, hair, eyes, respiratory organs, using personal protective equipment.
- After completion of work, hands and face are washed with running water and soap.
- In case of chlorine poisoning, you must take a large amount of water, induce vomiting and urgently seek medical help. If the solution gets into the eyes, they are washed and also immediately see a doctor.
- You can swim in the pool and open your eyes in the water only after a certain amount of time after disinfection according to the instructions for the preparation.

After cleaning the pool, a chlorine neutralizing solution is used - only after that a new portion of water is collected in the bowl. Swimming in the pool after disinfection is possible only if the chlorine sensor shows its permissible concentration. To protect the hair, they put on a bathing cap, special glasses will protect the eyes, and after bathing, so that the skin does not dry out, they take a shower.

Dechlorination
It is possible to reduce the excess of residual chlorine after disinfection of water with the help of the powder "Dechlor". 100 g of the product is used for every 100 cubic meters of water. This dosage reduces the chlorine concentration by 1 mg in each liter of water. The agent is diluted in a separate container and introduced into the filled pool in the form of a ready-made solution. Control measurements are carried out after 5-7 hours. Free residual chlorine should be between 0.3 and 0.5 mg / l, and total residual chlorine should be between 0.8 and 1.2 mg / l.
The following video will tell you whether chlorine is harmful in the pool.



































































The comment was sent successfully.