What are briquettes for a bath and how to use them?

Briquetted fuel is an updated version of the classic firewood. Fuel briquettes have a high density, at least it is not less than that of classic firewood. In fact, vegetable waste briquettes have a brick-like structure.



Pros and cons of using
A more detailed definition - briquetted wood (vegetable) fuel is compressed organic waste: sawdust and shavings, straw, grain husks, dried stems of weeds and cultivated plants, nutshells and so on. The pressure exerted during pressing allows the waste to come into contact as tightly as possible. If there is not enough of its own resinous secretions in the plant waste, an organic adhesive composition, which may turn out to be the simplest, different in bonding strength from wood glue, comes to the rescue.



However, when, for example, pine branches and bark are pressed, there are enough resin inclusions in the pine, this glue is not required. The production of briquetted fuel allows you to get much more from natural resources. In the end, all wood waste, including not even completely dried plant remains, people burned, heating their "square meters", at all times.
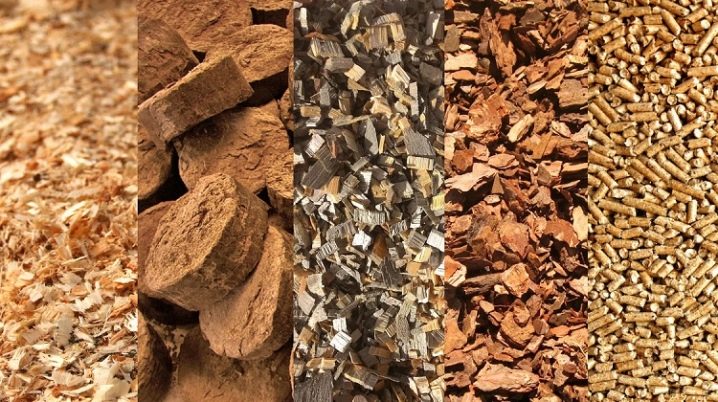

Briquettes, or Eurowood, have several advantages in themselves as a type of fuel.
- The heat output of briquettes is at least twice that of wood. It is about 5 Mcal / kg. Unlike firewood, the intensity of heating does not drop until they begin to burn out completely. The moisture content of the briquetted fuel is no more than 8%. For comparison, even well-dried firewood has a natural moisture content of 17-21%, a reduced moisture content of 13-17%.
- Due to the reduced moisture content, the briquettes will burn out, say, not in 40 minutes, but in 3 hours... This makes it possible to significantly reduce the tonnage of the fuel harvested for the winter. Due to the almost complete combustion, the exhaust gases contain only a small amount of smoke. Therefore, almost no soot forms on the walls of the chimney.
- There is relatively little ash after burning briquettes... Because of this, the process of cleaning the combustion chamber of the furnace from what is still not completely burnt out is significantly accelerated and simplified. In fact, briquettes are the same chopped firewood, they cannot burn out completely without ash.
- Fuel burns without unnecessary noise and without soot... The embers are not formed from rather small particles: they, in turn, almost do not even leave a trace. The burning of briquettes does not bring any discomfort during the pastime of people.
- Although briquettes are up to three times more expensive than simple log, the high cost is compensated by the lower consumption of briquettes by about the same number of times... Due to the greater bulk of the pieces of wood, the costs of their delivery increase.
- The briquettes do not have to be chopped - they are laid "as is", there is no need to put them in storage, after them there is no debris left.
The costs of transporting them are less due to their compactness compared to firewood, which is often shipped much more randomly.

Firewood also has advantages - these, in turn, are expressed as follows.
- Solid wood flares up faster and warms up the room.
- Firewood can be obtained from a nearby windbreakcollecting dried and broken off branches.
- If you dry them well, then a lot of heat is also given off during combustion.
- Heating up when burning, the same birch logs aromatic resins that are safe for health are released.
In some regions and districts, briquetted fuel cannot be found, which means that all that remains is to collect firewood nearby. If the owner of the property has a van, it becomes possible to deliver them on their own.



Varieties
In addition to purely vegetable briquettes, some craftsmen make combined ones - they add synthetic, easily burning materials, for example, polyethylene, there. But if foamed and film polyethylene can burn with an even blue flame with almost no residue, then other types of plastic, for example, polystyrene, burn with a smoky flame with a pungent smell of decomposed polymers, and a number of plastics - PET, PVC - do not burn on their own, only char in the presence of external flame.
It is not recommended to add rubber to briquettes: it gives a lot of waste. In general, synthetics are burned in a special furnace with an afterburner, and not in simple stoves. When the briquette contains only a small amount of polyethylene, this will not particularly harm the combustibility of the block, however, it is not recommended to form them from synthetics alone: the plastic will spread over the stove, and only prolonged burning of the combustion chamber with wood waste will clear the stove of it (it will eventually burn out completely ).


Wood bark briquettes - without wood - smolder up to 12 hours, which is why they are often used in slow-burning ovens. Peat, coal or peat-coal briquettes are up to several times more expensive, since peat is classified as a natural wealth necessary for forest growth. However, it - under certain conditions - can be made independently, by artificially recreating on your site the conditions under which it is formed.
Coal is obtained by incomplete combustion of wood, as well as from plastic, which does not burn on its own. In shape, briquettes are made both in the form of "bricks", hexagonal (hexagonal) blocks, and in the form of plates.
The form of their execution depends on the waste and the machine on which this waste was squeezed into blocks.



What is better than firewood?
As noted earlier, briquettes burn almost completely, unlike firewood, due to the reduced moisture content by half or three times. The burning time is not 40-50 minutes, like an armful of firewood, laid with significant voids, but 3-12 hours, depending on the composition of the crushed waste. It is easier to heat both the bathhouse and the living room in a country house with them - you do not need to throw up new firewood every hour.


How to use?
The correct use of briquettes depends on the structure of the oven you are using. Both the potbelly stove and the pyrolysis oven allow you to put in the firebox from several to several dozen briquettes, depending on their size. It is not necessary to use ignition fluids such as gasoline or diesel, paper, dry grass and / or finely chopped bark or wood chips are fine. Before placing the briquettes inside the oven, remove all ash from the compartment for collecting unburned residues located under the grate. Extinguished and unburned coals can be tried to burn again - this is, in fact, coal, and it will burn out along with the briquettes. The ash pan must be empty.
The more briquettes in the oven, the more heat they will give... However, compared to ordinary firewood, which burns like a box of matches and tends to burn out as quickly as possible, densely packed briquettes burn more slowly (because there is not enough oxygen for intensive combustion), but they will burn out in only a few hours. The stove should be covered with a damper so that the wood smolders, and not immediately burns out. Intense burning of wood is used only in a bath, where it is necessary to quickly get a large amount of heat.


How much is needed?
By weight, one load will need the same number of briquettes for one heating session, as in the case of firewood. They are laid in the same way, leaving only a small amount of gaps to provide oxygen from the air in order to successfully ignite. For a brick and cast-iron stove, briquettes are laid in the same way as wood. Since the materials are the same, it is possible to get the same amount of heat as from wood. The density of briquettes reaches 1.4 kg / dm3.
Finally, in terms of calorific value, the most efficient fuel briquettes are sunflower husks. This is achieved by the presence of vegetable oil in the starting material. Oil cake due to the presence of oiling causes the accumulation of a significant amount of soot in the chimney. A pyrolysis furnace will help to overcome this drawback, in which vaporous hydrocarbon fractions that have not burned out directly in the combustion chamber are re-ignited.
The use of the afterburner leads to a noticeably higher calorific value, which means that, as a result, less firewood or briquettes are needed for one session of heating the room where the oven is located.


































































































The comment was sent successfully.