All about the formation of eggplants in the greenhouse

When growing eggplants in a greenhouse, it is very important to pay attention to such a responsible procedure as formation in a timely manner. This technique allows you to significantly increase the chances of a gardener to get a rich and high-quality harvest.
The need for a procedure
The formation of eggplants grown both in open and closed ground (permanent or temporary greenhouse, polycarbonate or glass greenhouse) is carried out, first of all, in order to increase the yield of the crop. Experienced gardeners argue that without the timely removal of excess green mass (leaves, stepsons, additional lateral stems), eggplants form small and less tasty fruits than prescribed for the variety.
This statement is not unfounded, since almost all known cultivated plants, which have not undergone pruning and formation, have to spend a significant part of their energy during the entire season on the development of green barren mass. Along with this, plants consume large amounts of moisture and nutrients contained in the soil. As a result, the gardener has to water and feed more often, which requires additional time and effort, and also significantly complicates and increases the cost of the process of growing eggplants.


Another reason why greenhouse eggplants need to be formed, - the need to provide plants with sufficient light and free space. It is known that plant thickening is one of the factors leading to a decrease in plant productivity, a decrease in the quantity and quality of the resulting fruits. Also, thickening creates a favorable environment for the reproduction of insect pests and pathogens of various plant diseases in the greenhouse.
By performing the timely and competent formation of eggplants, the gardener can significantly reduce the risk of damage to his plantings by harmful insects and pathogens (pathogenic bacteria, fungi and viruses).

The ways
The formation of eggplants in the greenhouse is carried out in several ways. Their main essence is to remove unnecessary lateral shoots, ovaries and stepchildren, for the development of which plants spend a large amount of resources. Below are the main ways of forming greenhouse eggplants: in one, two, three stems or more.
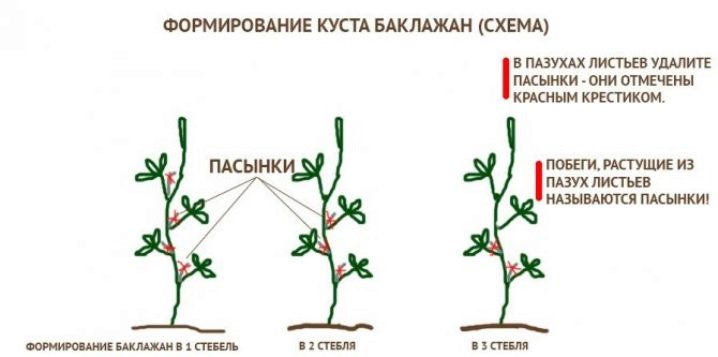
One stem
The technique of forming eggplants into one stem is considered the most radical, since it involves the removal of all lateral stems and stepchildren... After carrying out such a procedure, the plant has one main stem with a developing apical part. One should resort to this method of formation only as a last resort and under the condition that the general condition and health of the plant itself allows this to be done. It is highly undesirable to carry out radical pruning in relation to weak and emaciated bushes, as this can lead to their death.
A step-by-step instruction for the technique of forming grown eggplants in a greenhouse into one stem is as follows:
- all lateral stems and stepchildren are removed up to the fifth leaf, counting from the base of the plant (root zone);
- at the 7th leaf level, half of the formed ovaries are removed and the stepsons are completely pinched;
- completely cut off all adventitious shoots up to 10 leaves;
- at the level of 10 leaves, the adventitious shoots with ovaries on two leaves are completely removed.
As a result, no more than 3 leaves should remain at the top of the bush. Together with them, the ovaries that appear next to them are left.


It should be noted that the formation of eggplants in this way is allowed to be carried out only 2-3 weeks after planting their seedlings in a greenhouse.
In addition, before carrying out such a procedure, it is worth assessing the general condition of the plants: if they are weakened, then the formation should be postponed for 1-1.5 weeks so as not to ruin the plantings.
Two stems
As in the first case, the formation of greenhouse eggplants in two stalks is carried out no earlier than 14 days after planting. For weakened and painful specimens, this period increases to 3 weeks. The procedure is performed when the main stems of the plants have reached a height of 30-35 centimeters.
Below is a step-by-step scheme of actions on how to properly form eggplants growing in a greenhouse into two stems:
- the apical part of the main stem is pinched to stimulate the active growth of lateral shoots;
- after the appearance of lateral shoots at the top, 2 of the strongest are selected, all the rest are removed;
- the leaves located along the main stem below the two apical shoots are cut off.
2 weeks after the procedure, the apical stems are examined, the lateral shoots formed on them are stepson and part of the ovaries is removed. Thanks to these manipulations, the plant will spend its resources on the development of the remaining ovaries and, as a result, the formation of larger fruits.

Three stems or more
This method of formation is resorted to only if there is a sufficient amount of free space in the greenhouse, and the plants themselves are planted at a distance of 50-60 centimeters from each other. If the eggplants were originally planted in a greenhouse very close to each other, then their formation in this way can lead to thickening of the plantings and, accordingly, to a decrease in yield.
If the greenhouse has sufficient free space and the distance between the plants satisfies the above conditions, then it is recommended to form greenhouse eggplants according to the instructions below:
- when the plants reach a height of 30-35 centimeters, pinching the top is carried out;
- after the appearance of skeletal (lateral) shoots, all are removed except for the two strongest at the top.


After 10-14 days, the left main shoots are formed. This procedure is carried out as follows:
- on each main shoot, one strong stepson with ovaries is left, all the other stepsons are removed;
- the tops of the left stepsons are pinched after 2 sheets;
- cut off all barren shoots;
- remove the lower leaves.
Approximately a month before the predicted timing of fruit picking, all available growth points are pinched on the plants. This manipulation will contribute to an intensive increase in the mass of fruits and will bring the harvest time closer.

Follow-up care
After the formation procedure, greenhouse eggplants need competent and careful care.... The main activities that the gardener should pay special attention to are - these are regular watering of plantings and periodic feeding.
The frequency of watering eggplants in a greenhouse in a cool summer should be at least 2 times a week. In the hot dry season of planting, it is recommended to water every other day, using only warm, settled water (the approximate consumption rate is 3-5 liters of water per 1 plant). The next day after watering, the soil in the near-stem circles should be carefully loosened to provide oxygen access to the plant roots. In no case is it allowed to water greenhouse plants (any!) With ice water from a well or well.
Also, experienced gardeners strongly advise not to neglect the periodic ventilation of the greenhouse. This simple procedure will allow you to create an optimal microclimate inside the building. It is recommended to ventilate the greenhouse in the evening hours after sunset.

The first feeding of eggplants is carried out 2-3 weeks after they are planted in the greenhouse. It is not recommended to carry out top dressing earlier than this period, otherwise the applied fertilizers can burn the delicate roots that have not yet had time to adapt to the new conditions.
Before the appearance of flowers and ovaries, gardeners recommend feeding eggplants with complex fertilizers with a high nitrogen content. Such dressings will contribute to the intensive growth of green mass and the active development of the root system.
Most often, gardeners use a complex nutrient solution prepared from:
- 10 liters of settled water;
- 1 tsp ammonium nitrate;
- 1 tsp superphosphate.



The specified amount of solution is calculated for 2 square meters of plantings. Use this recipe before buds and flowers appear.
During the period of the appearance of flowers, the formation of the first ovaries and fruiting, greenhouse eggplants need fertilizing containing potassium and phosphorus. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers, as a rule, are not used at this stage in order not to provoke the growth of excess green mass. Fertilization intervals should be at least 2 weeks.
As a top dressing, gardeners most often use potassium sulfate and borofoska - a universal granular fertilizer that provides plants not only with potassium and phosphorus, but also with other useful substances: boron, magnesium and calcium.


Possible mistakes
One of the most common mistakes beginner gardeners make is refusal to form plants and pinch their stepchildren. In this case, even the most productive large-fruited varieties will not be able to please their owner with impressive results. Without formation, all their potential will be wasted on the growth and development of green mass, and not on the formation of ovaries. Given this circumstance, the formation of eggplants both in the greenhouse and in the open field is carried out regularly, in accordance with the provided scheme (with the exception of only some undersized varieties).
Another common mistake novice gardeners make is often in the mass removal of apical ovaries... Such a procedure, in their opinion, promotes the active development of the ovaries located on the lateral shoots. However, the long-term experience of experienced gardeners testifies to the opposite: the largest, fleshy and tasty eggplants are formed precisely from the apical ovaries. Thus, in order to obtain a full and high-quality harvest, the planting of greenhouse eggplants should be formed according to the proposed scheme, paying the greatest attention to lateral shoots and ovaries.


Another gross mistake that inexperienced gardeners make when forming greenhouse eggplants, - these are rough and inept actions when working with stepsons, unnecessary leaves and side stems. All excess vegetative parts of plants should not be roughly cut off, causing irreversible damage to the main and adventitious stems. Gardeners consider an ordinary garden pruner with a pre-disinfected blade to be the most convenient and acceptable tool for removing excess vegetative parts.
Useful Tips
Experienced summer residents strongly recommend that beginners who are starting the cultivation and further formation of greenhouse eggplants for the first time, first familiarize themselves with the nuances of caring for this crop. Eggplants are quite whimsical and demanding plants, so any mistake made in the process of growing them in a greenhouse can negatively affect the quantity and quality of the future harvest.
Before planting eggplant seedlings in the greenhouse, gardeners with extensive experience it is recommended to prepare a suitable soil mixture for them in advance. This culture does not take root well in poor, marginal soils, but it feels great, growing in areas with well-drained and loose soil rich in organic matter.
Therefore, before planting eggplants in the greenhouse, rotted manure (mullein), compost, dry complex fertilizers should be added to the beds in advance.


With all the desire to get as much of the harvest as possible it is highly undesirable to plant a large number of plants in the greenhouse... Eggplants are among those crops that do not tolerate crowding and thickening. Thus, by planting eggplant seedlings at an extremely small distance from each other (less than 45 centimeters), the gardener risks the quantity and quality of the future harvest.
Experienced gardeners recommend starting the formation of greenhouse eggplants then, when the plants are fully strengthened and start to grow after their transplant... Usually, for most varieties, this moment occurs when the plant reaches a height of 30-40 centimeters. At this stage, as practice shows, the formation occurs with the least amount of negative consequences (drying and dying off of lateral stems, dying off of ovaries, dropping of buds).
After the procedure of pruning and shaping, greenhouse eggplants first need protection from the effects of aggressive environmental factors... This primarily concerns the sun and high air temperatures. To protect the plants from negative consequences, they are shaded on sunny days (for this, it is enough to abundantly spray the greenhouse walls from the outside with a solution of chalk or lime), and the greenhouse itself is regularly ventilated in the evenings when the air temperature gradually decreases and no longer has a detrimental effect on planting ...










The comment was sent successfully.