Japanese azalea: description of varieties, planting and care

The Japanese azalea has an attractive appearance, blooms profusely and survives frosty winters in Russia well. However, growing and caring for it has some peculiarities.

Description
Japanese azalea is a rather valuable rhododendron. "Rosewood" becomes a decoration of any area thanks to its luxurious appearance and pleasant aroma. In nature, this plant grows in Japan on grassy and well-lit mountain slopes. It lives for about 40 years, reaches a height of a couple of meters, and is 1.2 meters in diameter. Although azalea can be grown on its own, it looks organically in various compositions.
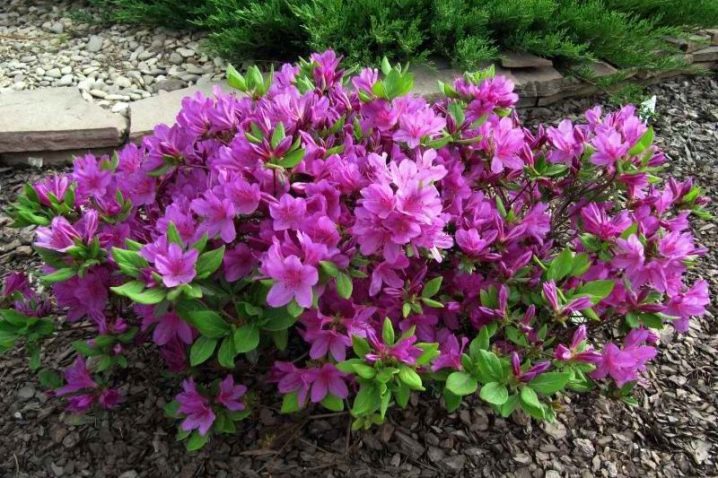

During flowering, the bush is covered with a large number of brightly colored flowers, the palette of which ranges from bright red to yellow. The buds do not appear individually, but collected in inflorescences in an amount of 6 to 12 pieces. Their size allows you to completely hide the leaf blades. The azalea sheets, by the way, are also quite large: their length ranges from 4 to 10 centimeters, and their width ranges from 2 to 4 centimeters. The skin of the thin plates is covered with bristles, and its color changes from dark green in summer to yellow-red in autumn.
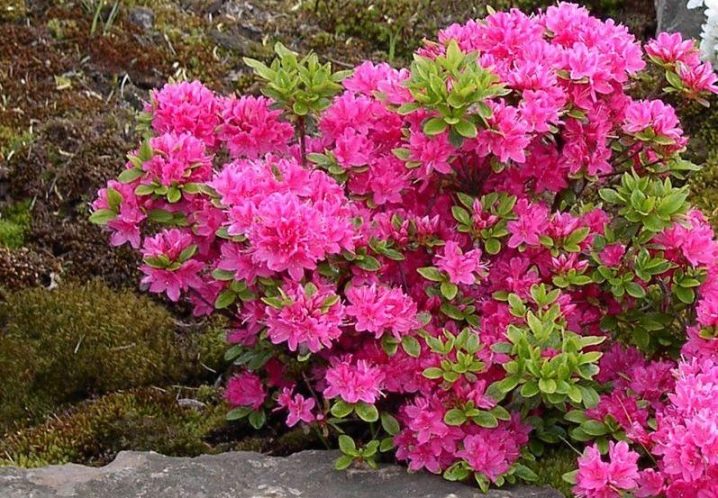

A deciduous azalea blooms for about 2 months, and during this time, it opens up from 100 to 400 flowers. This happens from May to the end of June. The shrub can be either erect or creeping. The color of the shoots changes from green to brown with age. The roots are shallow, forming a fibrous system. The wood itself has a dense resinous structure and a gray bark. Seed material is formed in the fruit capsule.
Winter hardiness of the plant is quite acceptable - if you provide him with proper conditions and high-quality care, then the rhododendron will calmly cope even with the Russian cold.

Popular varieties
Japanese garden azalea has a large number of varieties. "Petticoat" is a semi-evergreen shrub, the height of which reaches 50 centimeters, and sometimes up to 90 centimeters upon reaching the age of ten. The dense crown is 90 centimeters wide. Oval bright green leaves do not differ in large size. The flowers themselves are somewhat reminiscent of peonies in their shape. Terry petals are painted in a light pink-lilac shade.
"Petticoat" blooms in late spring. For the winter, the variety requires additional protection from winds and precipitation.
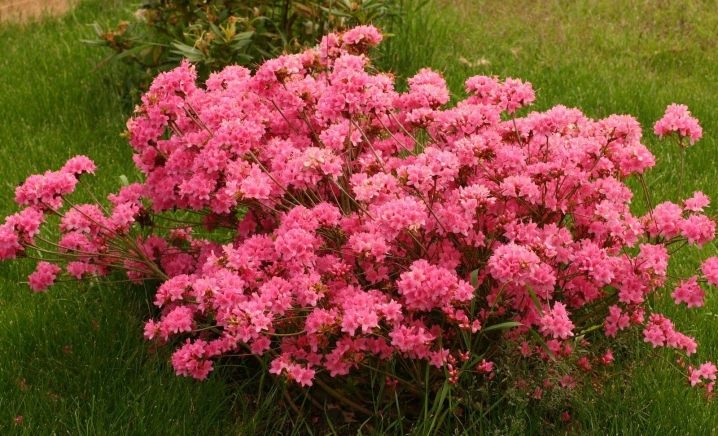

Maruschka grows up to 50 centimeters in height, and the diameter of the spreading crown ranges from 70 to 80 centimeters. Inflorescences of bright red color delight the owners throughout May. The flowers appear in such a size and in such quantity that the leaves are practically invisible. However, the plates grow small, shiny and tight. During the summer season, they are painted green, and in the fall they become burgundy.
This variety has good frost resistance, but does not react well to drought, which means that the soil must always be irrigated.

Other common varieties include Schneeperle, Purpletraum, Weeks Roseread and Geisha Pearl.




Landing
When choosing a place to land, the climatic zone should be taken into account, in which Japanese azaleas are to inhabit. For example, if the summer months are characterized by high temperatures and lack of rainfall, then it is better to place the bush in diffused shade behind the house.If the climate is temperate, then you can choose a more open area, more illuminated.

The soil for the Japanese rhododendron must be either neutral or slightly acidic... Otherwise, with insufficient acidity, the flowering of the bush will not be so abundant. A place located next to a body of water (both natural and artificial) is considered ideal. In this case, the rhododendron will always be in optimal humidity conditions.

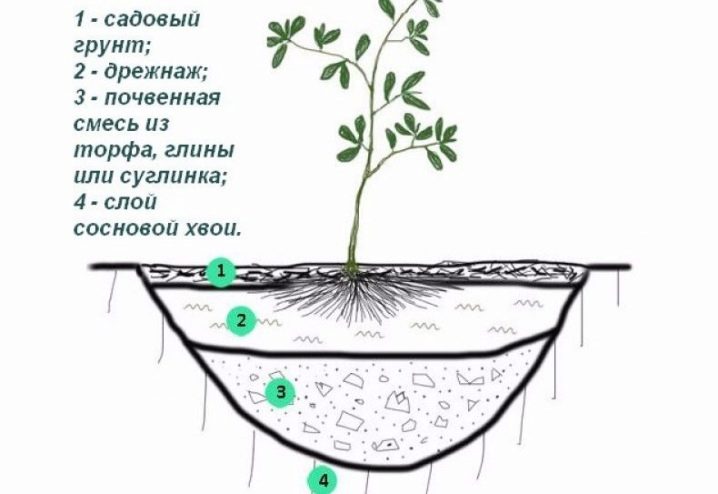
Ideally, you should combine ordinary garden soil and the top layer of peat, then pour the resulting substance half a meter thick and shovel it with the ground. In the case when groundwater flows under the site close to the surface, it is necessary to additionally form a drainage layer. The depth of the planting pit should be 50 centimeters, and the diameter should be at least 70 centimeters.
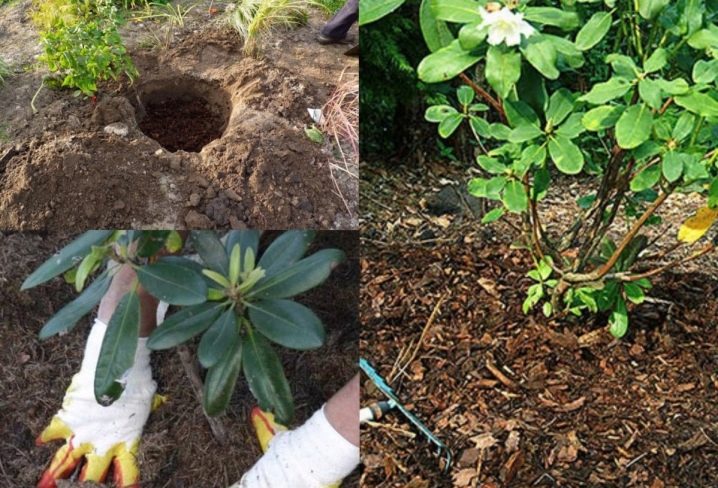

Drainage is placed on the bottom in the form of broken bricks, followed by peat, sand and leafy earth, taken in a ratio of 3: 1: 1, then you need to fill everything with water.
Lime crushed stone should not be used for drainage, as it causes deoxidation of the soil.
The seedling itself is lowered into the water along with an earthen clod until air bubbles stop coming out of the roots. This is done to moisten the soil mixture well. In this case, the root collar is not deepened. The bush plunges in the middle of the hole. The remaining space is filled with substrate, the surface is compacted, irrigated and mulched.
Care
Fertilization begins a couple of weeks after planting. It is more convenient to use complexes of mineral fertilizers sold in specialized stores. It is better to take needles from organic matter, which can be used for mulching. The height of the mulch layer is ideally 5 centimeters.
It is strongly not recommended to use ash, as it reduces the acidity of the soil.


Fertilization stops in August when the plant begins to prepare for the winter dormant period. The optimum humidity for a Japanese azalea ranges from 70 to 80%. Only automatic watering can provide such an indicator.

In the absence of the latter, spraying will have to be carried out in the morning and in the evening. Irrigation itself should be plentiful and carried out either daily or every other day. In winter, rhododendrons are able to withstand cold temperatures as low as -26 degrees. You will still have to cover the plants to create protection from snow drifts and bright winter sun. The twigs are neatly tied together without damaging the buds.
Pegs are hammered along the perimeter of each plant, it is they who fix the protective coating: burlap or polypropylene.
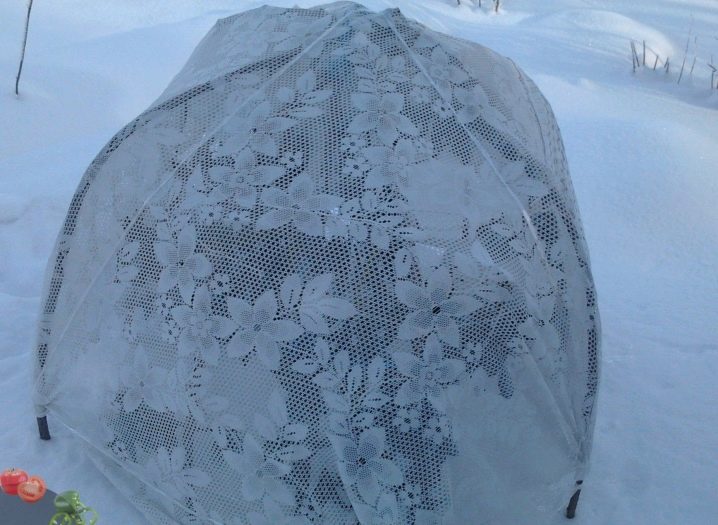

In addition to direct shelter, rhododendron in winter will also need the necessary moisture... To do this, somewhere from the beginning of autumn until frost, the bush will have to be watered every 2 days, using about 12 liters of water. Then mulching is necessarily carried out with the help of pine bark. The mulch layer should be fairly thick.
As soon as the cold weather comes, it is recommended to sprinkle the lower branches with compost, peat or, again, pine needles.

Irrigation is carried out using the settled liquid. The top layer of the soil should be wet, but not too wet, so as not to provoke rotting of the root system. If the ground dries up, the azalea will begin to shed leaves and inflorescences. Watering is also reduced in late summer. As for pruning, it is done a couple of weeks after flowering.
The main purpose of the formation is to remove wilted shoots and thin them out.

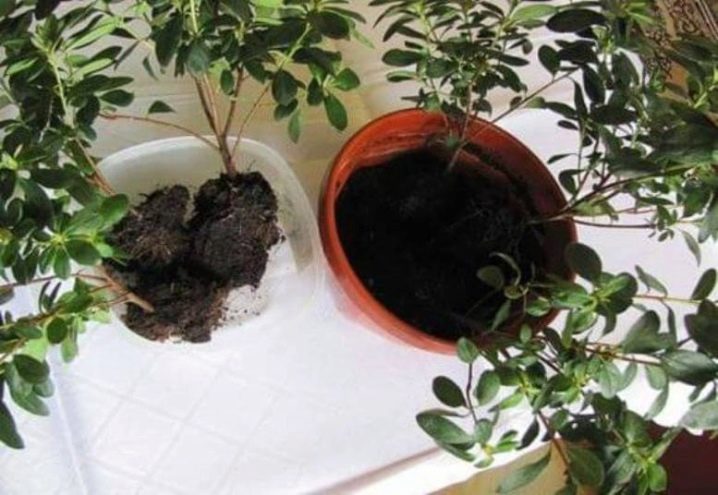
Reproduction
When breeding is carried out with the help of seedlings, it is better to take parts of plants from a bush whose age ranges from 2 to 4 years. How exactly it is carried out is described above.

Growing from seeds is no less successful. As a result, the bush grows up to 10-15 centimeters in height and takes root well in the open field. The procedure is carried out at the beginning of winter.A substrate is required, the acidity of which ranges from 4.0 to 4.5, based on peat. To disinfect the soil mixture, you will need a strong solution of potassium permanganate.


The seeds go deep into the ground by about 2 centimeters, after which the surface is irrigated and covered with either plastic wrap or a glass sheet. At least for a couple of hours a day, the greenhouse will have to be opened to provide ventilation. To successfully germinate seeds, you need to provide azaleas temperature at 25 degrees Celsius and humidity ranging from 75% to 80%. When the first shoots appear in a couple of weeks, the temperature will have to be reduced to 10-12 degrees.
In addition, you will have to organize the correct diffused lighting.

Diseases and pests
Most often, the Japanese azalea is attacked by the azalea aphid. The liquid secreted by it covers the surface of the leaves, and a red mite and a sooty mushroom appear on it. The solution to this situation is carried out with the help of fungicides and "Melatonin". The first ones stop the development of the fungus, and the second copes with aphids and other insects. Sometimes a red mite occurs when the plant is not adequately watered, causing the clod to dry out.



A white bloom on the plate appears when the rhododendron becomes infected with a spider mite. Since the pest sucks the juices out of the plant, the leaves then twist and dry out. To get rid of the pest will help drugs "Agravertin" and "Diazinon"... When black thrips settle on a plant, the leaves themselves turn black. You can destroy it with "Karbofosa".
If the petals of the flowers are covered with black dots, this indicates that the Japanese azalea is affected by the rhododendron mite.




Fungi affect the bush when the temperature drops below normal, and the humidity, on the contrary, turns out to be too high. Other common diseases include late blight, chlorosis, and fusarium wilt.
All these diseases are treated with special drugs. However, it is much better to carry out preventive treatments.



At the beginning of the growing season, the plant is treated with copper oxychloride, as a result of which a thin film appears on the leaves, preventing infections. It would be nice to spray the bush next "Fundazol", which is responsible not only for prevention, but also for the treatment of diseases in the early stages. Finally, the plant's immunity is strengthened. by applying nitrogen-containing fertilizers.


For tips on growing and caring for an azalea, see the following video.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.