Amaryllis: features and types, planting and care

Amaryllis is a plant with beautiful large flowers perched on a tall and almost leafless stem. Because of this feature, he is also called "naked lady" or "naked lady". However, a real amaryllis, despite its bright appearance and unpretentious content, can rarely be seen on the windowsills of Russian apartments. More often it is inhabited by his "twin brother" - hippeastrum. We will talk about the similarities and differences between the two colors in the article. And you will also learn how to care for amaryllis, how to plant and propagate it, what varieties of this amazing indoor flower are.



Description
Amaryllis is a perennial plant of the Amaryllis family. It was described and singled out as a separate genus by the Swedish scientist Karl Linnaeus in the 18th century - before that, amaryllis was perceived as one of the varieties of lilies.
He came to us from South Africa, where he grows in arid desert places, so the flower adores the sun, but does not tolerate frost.
Because of this, in Russia it is grown mainly as a houseplant - planting amaryllis in open ground is possible only in the southern regions, for example, in the Krasnodar Territory... Amaryllis belongs to the bulbous class: it develops from a bulb that is oval in shape and can be from 4 to 12 cm in diameter.


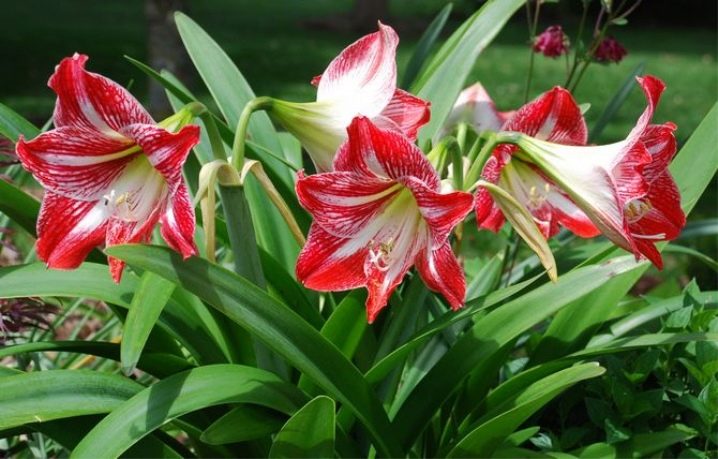
Straight narrow dark green leaves are in pairs located on the stem and reach a length of 50-60 cm, their width is 3 cm. In nature, during the flowering of amaryllis, leaves are generally absent, in room conditions they are usually there, although they are few in number. At home, amaryllis blooms most often in late spring, this phase lasts 1.5 months. In Russia, however, flowers appear in August – September and last only up to three weeks. First, a peduncle grows from the bulb. It stretches up to 40-60 cm in height and an inflorescence forms on it. Amaryllis can have 3 stems at the same time, each of which will have 4 to 12 flowers with a diameter of 10 cm.Their color can be pink, lilac, red or white.
It is important to remember that amaryllis is not only beautiful, but also dangerous, since poison is contained in the bulb and partially in the shoots.
In minimal doses, it produces a positive effect - it kills harmful microorganisms (bacteria and viruses). But if the concentration is exceeded, the consequences can be serious: from skin irritation to vomiting, dizziness, and even breathing problems. Amaryllis is especially dangerous for children and pets. Therefore, keep the plant away from them, and after contact with the flower, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
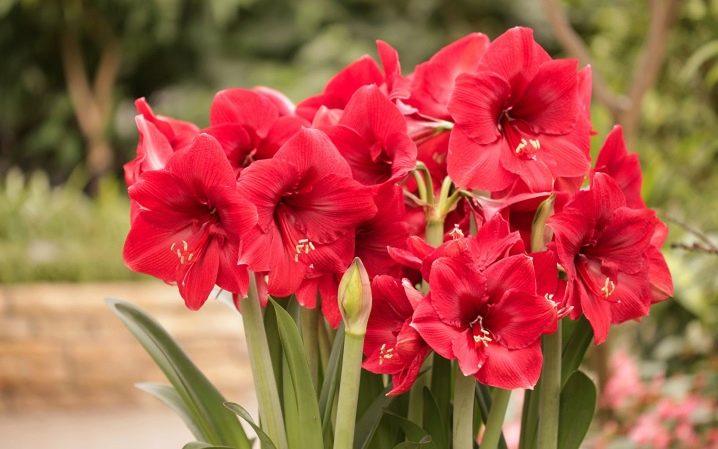

How to distinguish from hippeastrum?
Outwardly, amaryllis looks almost like a hippeastrum. Often, even amateur flower growers confuse them, and in stores, the second plant is often passed off as the first, since it is more common. However, the similarity of the two flowers is understandable, because they are the closest relatives: they belong to the same genus Amaryllis. Distinctive features of the "brothers" are also enough, they just are not always obvious. Let's take a look at them.
- The homeland of the amaryllis is South Africa, while the hippeastrum is a native of South America. Therefore, the second flower quickly gets used to the Russian climate, in contrast to the first, for which its origin in the country of "eternal summer" makes it difficult to adapt to more severe conditions. Because of this, amaryllis is somewhat more picky about care and growing conditions than its relative.


- They have different shapes and sizes of the bulb: in hippeastrum it is round, similar to a common onion, 7–9 cm in length, and amaryllis has an elongated and elongated, pear-shaped bulb, reaching a diameter of up to 12 cm and even more.


- The peduncle of the hippeastrum is empty inside, therefore, with slight compression, the edges of the rod touch. It is about 60–70 cm long and has a reddish brown tint. In amaryllis, the stem is greenish-brown in color and shorter - it grows only up to 60 cm, but it is much denser, because it does not have empty space inside.


- Amaryllis blooms only once a year - this happens in late summer or early autumn. Hippeastrum pleases with its flowers at the end of winter or early spring, and re-flowering can occur at the end of summer - it depends on the conditions of care and the variety of the plant.


- Amaryllis flowers are only of pink color: from pale pink and even white to bright red. Its relative has a richer and more varied color palette: all shades of red, including burgundy, in addition, yellow, green, orange, purple, there are even two-color and spotted variants.



- Flowers in amaryllis are funnel-shaped, and in hippeastrum they look like an orchid and, as a rule, larger ones - in some varieties they can exceed 20 cm in diameter. The number of petals in a flower is the same - 6, but the buds themselves are larger in amaryllis - their number sometimes reaches 12 pieces, although usually there are 5-7. Hippeastrum usually has 2–4 flowers per inflorescence.


- Amaryllis exudes a strong and pleasant aroma during flowering, but its relative loses here - the hippeastrum has practically no smell or it is very weak, barely perceptible.


- Amaryllis has only 2 main types. (according to some classifications - 4), the other numerous varieties are the result of selection. And in hippeastrum only in nature there are about 80-90 varieties, plus more than 2000 have been artificially bred.


These are just the main differences between the two colors. Other, smaller, distinctive features can be distinguished.
Varieties
Until recently, it was believed that the amaryllis has only one species - belladonna. This is a plant with pale pink or pale lilac flowers, similar in shape to a bell.
However, in the late 90s of the twentieth century, another representative of the Amaryllis genus was discovered in the mountains of Africa - it was named paradisikola.
It was distinguished from belladonna by wider leaves, the presence of a larger number of pink buds (21) and a more intense and rich smell.
At the moment, there are up to four species of amaryllis growing in nature. And on their basis, especially from the ancestor of belladonna, which is rarely seen on the counters of Russian flower shops and, accordingly, on the windowsills of apartments, a large number of varieties have been bred. They differ from each other in color and texture of flowers, as well as their shape, size and number of petals. The following popular hybrids are worth considering:
- "Nymph" - double white flower with thin pink veins on the petals;


- "Red Lion" - royally luxurious large bright red flower, up to four buds sit on one stem;
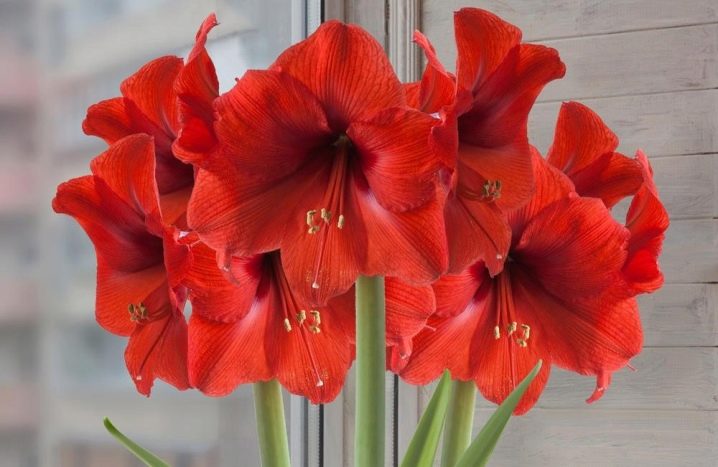

- "Faith" - delicate miniature pale pink flowers with a mother-of-pearl tint;
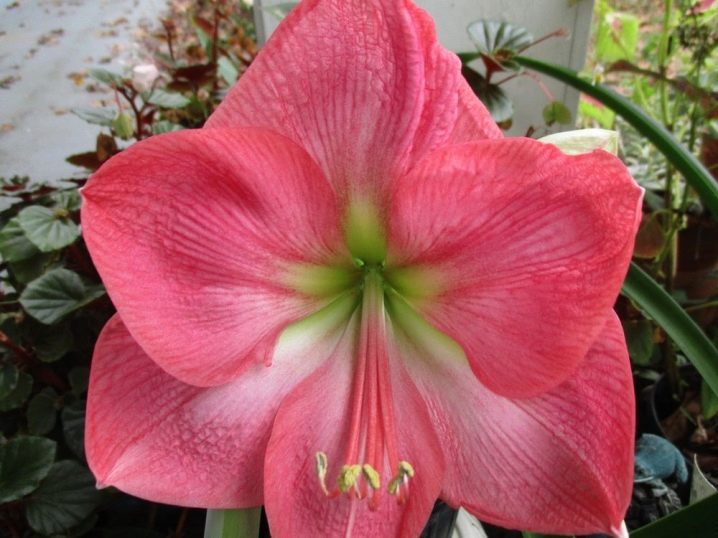

- "Macarena" - a large flower with bright red double petals and white longitudinal stripes;
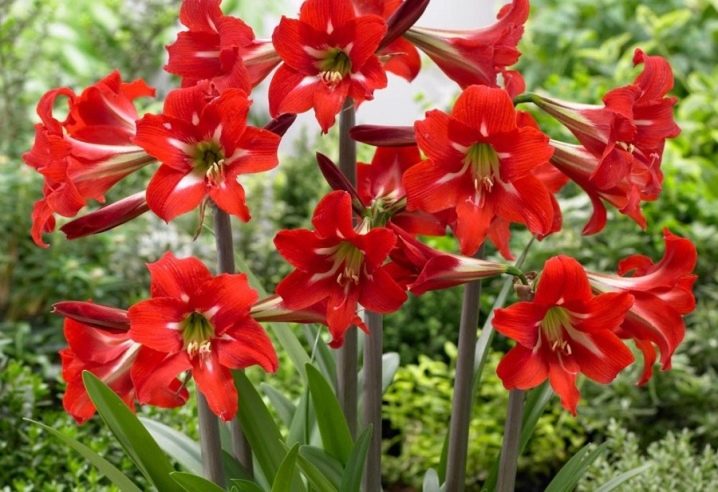

- "Durban" - Terry bright red flowers with white "rays" in the center, the petals are long and pointed with jagged edges;
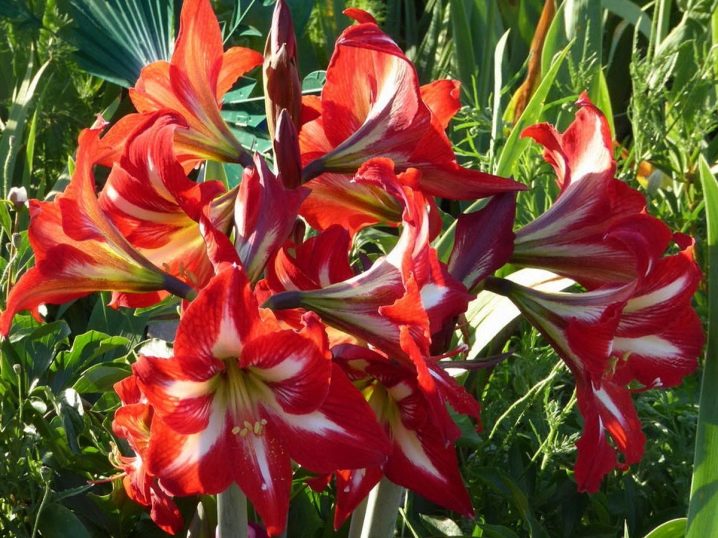

- "Parker" - bright pink flowers of large size with a yellow center;
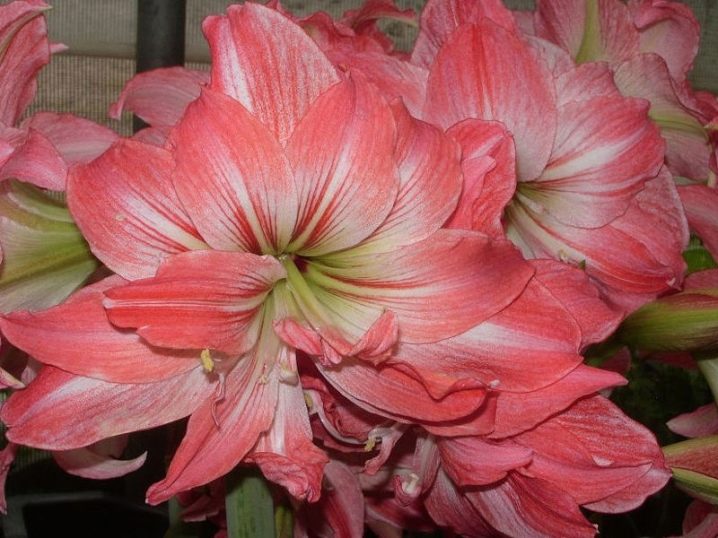

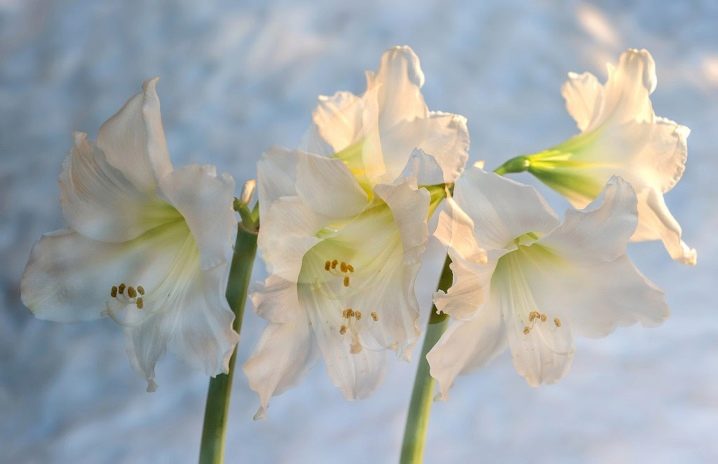
- "The Snow Queen" - large snow-white flowers with wavy edges and a shiny bloom;

- "Double Dream" - large double bright coral flowers with a white border around the edges of the petals;


- "Aphrodite" - can be of different colors, but most often there are white flowers with red or pink veins and edges;


- Gervase - on a peduncle, which can reach up to 80 cm in height, there are 25 centimeter flowers; they can be of different colors: cherry, pink, red, white and even orange;
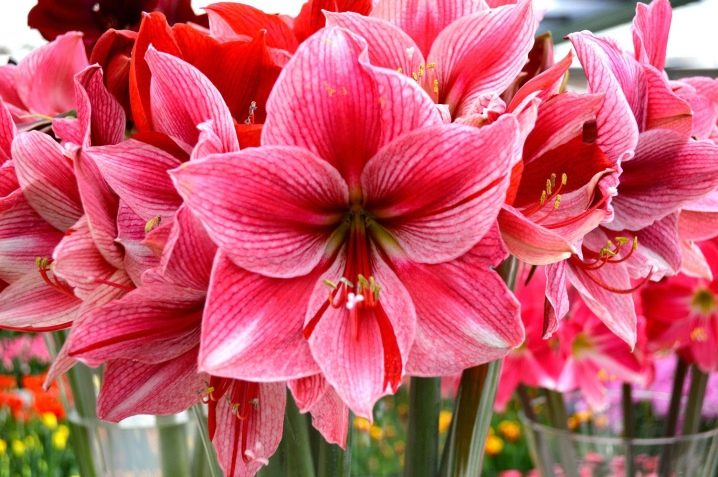

- Ferrari - velvety fiery red flowers on a high stem.

Conditions of detention
It is not so difficult to provide amaryllis with suitable conditions of detention. However, it should be remembered that it has a growing season and a resting phase. And during these periods, the requirements for the location, lighting and temperature, as well as watering and feeding will differ significantly.
Light and temperature
A plant that was born in a hot African climate is vital for bright sun, so a pot of amaryllis should be placed in the southern zone of the house. It is better that it was southwest or southeast, as too "straight" rays of the sun can burn the leaves, so try to make the lighting diffused.
Daylight hours should last at least 14 hours, while the daytime temperature should be from +20 to +25 degrees, and the nighttime temperature should be about 5 degrees below it.
It is necessary to provide the same portion of sunlight to all parts of the plant. To do this, during the day, the pot must be turned so that the flower gets an even "tan" on all sides, and the stem does not twist.


Humidity
The humidity should be proportional to the temperature - the higher the thermometer, the more moisture the flower should receive. Therefore, in the hottest periods, amaryllis must not only be watered, but also sprayed. The flower does not like drafts, but needs periodic ventilation.

Dormant period
When the plant has bloomed, and its outer part has died out, the bulb should be moved to a shady cool zone with a temperature of + 10– + 13 degrees. In such conditions, amaryllis will "rest" and gain strength for a new active phase. A perfect habitat for a plant during the "hibernation" period will be, for example, a cellar or basement.

Planting and transplanting
Pot selection
Finding the right pot for planting is very important. It is better to give preference to heavy options made of ceramic or clay - they are more stable, therefore, more suitable for a tall and thick amaryllis stem, reducing the risk of the flower tipping over with the container.
In addition, the roots of a plant sitting in a "house" made of natural materials are well supplied with oxygen and get rid of excess water.
The pot should be high and of such a width that the distance from its edge to the bulb is 2-3 cm. In a larger flowerpot, abundant baby formation may begin. Therefore, it is better to plant several bulbs in one container at a distance of 3 cm from each other.


Priming
The easiest way to buy soil for planting amaryllis is at a flower shop - a substrate for bulbous plants is suitable as such. However, you can prepare the soil yourself, adhering to the following recipes:
- sod land (2 hours) + leafy ground (2 hours) + sand (1 hour) + humus (1 hour);
- sod land (1 hour) + garden land (1 hour) + river sand (1 hour) + humus (1 hour) + peat (1 hour).
Important! Whichever soil option you choose, do not forget to sterilize it before planting by sprinkling it with boiling water - this is necessary to destroy harmful microorganisms.

Bulb selection
Planting material must be carefully selected. The bulb must be healthy in appearance, smooth and even: free from spots, mold, soft dents, rot and other damage. An unpleasant smell should not come from it either. The optimum planting bulb size is 7 cm in diameter.

Landing algorithm
The planting process includes the following steps:
- before planting, dark scales are removed from the bulb until it all becomes a uniform light green color; then it is soaked for 30 minutes in potassium permanganate or any other fungicide, after which it is sent to dry for a day;
- drainage is placed on the bottom of the pot, for which expanded clay is best suited;
- the selected substrate is poured over the drainage and the bulb is buried in it so that 2/3 of its "body" remains on the surface;
- the ground around the circumference of the bulb is crushed and then moistened.
Important! The amaryllis bulb contains poison, so all manipulations with it are performed only with gloves.
Amaryllis transplant is usually carried out once every 3 years. But if the flower has grown a lot, then it can be transplanted earlier. You just need to wait until the end of the flowering period.



How to care?
Caring for a plant at home is easy. During the rest period, you do not really need to do anything. Only when amaryllis enters the flowering phase does it require regular watering and periodic feeding in order for the buds to form and flowers to bloom.
Watering
Amaryllis, as an inhabitant of the African deserts, does not like excess water. Moisten the soil only when it has become dry.
You need to water the plant with settled water at room temperature, and it is not poured on top of the flower, but preferably into the pan so that the bulb does not become damp.
During the dormant period, watering is reduced to 1 time in 1.5–2 months. However, the decrease in their frequency is not sharp, and 3-4 days after the leaves began to fade. Full watering is resumed in the summer when the peduncle reaches a height of 10 cm.


Top dressing
It is produced only during the growing season. Fertilizers are applied once every 14-15 days to provide the plant with nutrients for effective growth and flowering. As a top dressing, a mullein diluted in water is suitable. You can also buy organic and mineral mixtures from flower shops and give them to the flower one at a time. Just make sure that there is not too much nitrogen in the composition of such fertilizers.



Bloom
At the junction of summer and autumn, large beautiful flowers grow on the amaryllis, which last up to 25 days. However, the plant can be made to bloom by a certain time if the bulb is transplanted 2 months before the desired budding date. It is worth considering in more detail what needs to be done after all the petals wither and fall off.

Cut
After the end of the growing season, it is imperative to cut off the peduncle and begin to gradually reduce the frequency of watering. When the last leaves leave the stem, the bulb in a pot or dug out of it is transferred to a cool place, where it “rests” for three months.
A good rest is one of the prerequisites for productive flowering.
But amaryllis may not bloom on the home windowsill. There can be many reasons for this, namely:
- improper care of the plant during the dormant period, insufficient rest phase;
- the pot in which the flower grows is too large for him;
- the bulb is still young, not yet three years old (and when planted with seeds - seven);
- the bulb is buried too deep in the ground;
- lack or excess of fertilizer, a large amount of nitrogen in its composition;
- the plant is infected with a fungus or harmful microorganisms live on it;
- unsuitable soil composition for amaryllis;
- lack of sunlight, which is essential for plant growth and development;
- low temperature, especially during the growing season.


Reproduction
There are three ways of reproduction of amaryllis: by seeds, by children (vegetative) and by dividing the bulb. Let's talk about each of them.
Seminal
This is the most laborious and time consuming way of obtaining new copies of amaryllis, therefore it is rarely used at home. Artificial cross-pollination is required to produce seed for sowing. To do this, you need to collect pollen from the pistil of one plant (it is better to do this with a brush) and place it on the stamen of another. It takes about a month to ripen the seeds. Then they are collected and immediately planted in a container with soil to a depth of 1 cm.
It is best to use a soil mixture for planting, consisting of turf, leafy soil and humus in proportions of 1: 2: 1.
The soil needs to be watered a little before planting.
Then the container with seeds is covered with plastic wrap to create a greenhouse effect and placed in a darkened place where the temperature will not be lower than +23 degrees.A month later, the first shoots should appear. It is possible to transplant them in separate pots only when 2 leaves grow on the sprouts. This will happen in 2.5–3 months. Keep in mind that seed-grown amaryllis will only begin to bloom after 5-8 years. Therefore, other methods are more suitable for indoor breeding.



Vegetative
Amaryllis is a very prolific "large" plant, so it is best to get new copies of it by vegetative means. Moreover, this is quite quick and easy to do. It is necessary to separate the little "kids" from their "parents" and plant them in separate pots.
It is advisable to take containers for planting slightly larger in size than those in which the "adult" individuals sit - in the "babies" in the first year of life, the root system will actively develop.
For successful growth, they need to be placed in a warm, sunny place, watered regularly and periodically fed. Subject to all of the above conditions, already in the second or third year of their life, they will delight you with beautiful flowers.


By dividing the bulb
This method is applied after the end of the flowering period, when the plant has entered a dormant phase. An adult healthy bulb is dug up, its top is cut off along with the leaves and a little cut from the bottom. Then divide the onion into 4-12 vertical parts. Each of them is first put in a disinfection solution, for example, fungicidal, for half an hour, and then planted in the soil. However, experts recommend placing it in wet river sand for 1 month before planting in the ground, and after the appearance of the first pair of leaves, transplant it into the soil.

Diseases and pests
Amaryllis can be affected by pests and various diseases, especially fungal. It is worth considering the most dangerous diseases for the African flower.
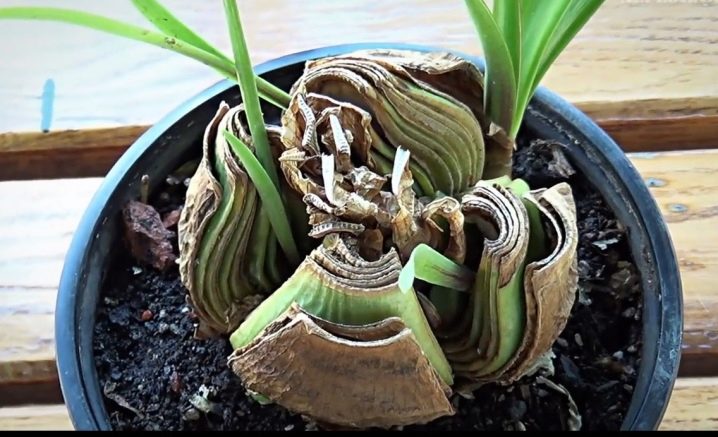
Stagonosporosis (red burn)
Signs: red spots on the bulb and shoots. Reasons: overmoistening, hypothermia, or a sharp change in temperature. Treatment: the disease is serious, the flower may die from it, so treatment should consist of the following stages:
- it is necessary to plant the plant from other indoor inhabitants, since this fungus is contagious;
- then all damaged areas should be removed, but before that, the plant can be placed in a solution of potassium permanganate for 1 hour;
- further, we take out the amaryllis to fresh air and dry it for 1 week;
- we treat the flower with a disinfection preparation, for example, "Fundazol";
- watering is minimized.

Anthracnose
Signs: Leaves develop dark brown spots surrounded by a purple border and then begin to dry out. If the plant is left untreated, it will die. Treatment includes the following:
- cut off parts of the plant damaged by the fungus;
- treat the flower with "Fungicide" or another antifungal drug;
- reduce the frequency of watering.


Gray rot
Signs: gray-brown spots on the leaves and bulb, rotting of the plant, accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Reason: too abundant watering or hypothermia of the soil. Treatment is as follows:
- dig up the onion;
- remove damaged areas;
- spray the plant with "Fundazol" or treat with brilliant green;
- put to dry for 2 days;
- transplant it into another pot on new soil.


Fusarium (root rot)
Signs: Root damage causes the plant to dry out and wither. Reasons: a sharp change in temperature or a lack of nutrients in the soil. Treatment consists in performing the following actions:
- isolate from other plants so that they do not get infected;
- dig up the onion and treat it with "Fundazol" or other insecticidal preparations;
- it is advisable to transplant the plant into new soil.


It is worth considering the pests most often attacking amaryllis.
- Thrips - these are small brown bugs that settle on the leaves and look like black dots.From their vital activity, areas of a silvery-white color appear on the leaf, and then it begins to turn yellow and dry. The plant "inhabited" with thrips should be washed with warm water, then transplanted into new soil and treated with "Fitoverm" or another insecticidal agent.


- Mealybug settles on leaves and roots, covering them with white cotton balls and mucus. It is not difficult to deal with it: you need to wipe the amaryllis with a sponge dipped in warm water. If this method does not help, then you need to treat the plant with any insecticidal preparation.


- Spider mite - its presence can be determined by its characteristic feature: a white spider web on the leaves, which provokes a gradual wilting of the plant. To get rid of a spider mite, you need to spray the shoots with any insecticide, for example, "Kleschevit", "Neoron" or "Oberon".


- Onion mite very badly damages parts of the plant, especially the bulb, because of which it begins to rot and crumble, the leaves turn yellow and fall off, and the growth of the plant stops. For this pest, insecticides that contain phosphorus are harmful.


- Amaryllis bug affects the bulb of the plant, due to which the leaf formation process completely stops. You can cure the plant by cutting off all damaged areas and treating it with any insecticide. It is advisable not to be limited to the performed single procedure, but to carry out insecticidal spraying within a month.

- Aphid - a small insect that sucks nutritious juices from the plant, from this its leaves begin to turn yellow and curl. You can destroy aphids by wiping the leafy part with a sponge dipped in soapy water.


- False shield. Its appearance is indicated by white or brown spots on the leaves, covered with scales, inside which there are insects. They feed on plant sap, causing the foliage and then the entire plant to turn yellow and dry. False shields are easily destroyed - washed off with soapy water.


- Legtail (collembola) - a white insect that lives in the upper layer of the soil and feeds on both the remains of rotten plants and parts of living plant organisms. To get rid of springtails, insecticidal treatment is carried out and the topsoil is renewed.



Tips for caring for amyryllis at home in the video below.

























The comment was sent successfully.