Speaker enclosures: features and manufacturing

The sound quality of acoustic systems in most cases depends not so much on the parameters set by the manufacturer, but on the case in which they are placed. This is due to the materials from which it is made.
A bit of history
Until the beginning of the twentieth century, the sound of the device was reproduced through a loudspeaker horn.
In the 20s of the last century, in connection with the invention of speakers with paper cones, there was a need for volumetric enclosures, in which it was possible to hide all the electronics, protecting it from the external environment and giving the product an aesthetic look.


Up to the 50s, models of cases were produced, the back wall of which was absent. This made it possible to cool the lamp equipment of that time. At the same time, it was noticed that the case performed not only protective and design functions - it also influenced the sound of the device. Different parts of the speaker had unequal radiation phases, so the presence of the duct walls affected the strength of the interference.
It was noted that the sound was influenced by the material from which the body was made.
The search and research began for the acoustic properties of raw materials suitable for creating boxes that can accommodate speakers and convey good sound to the public. Often, in the pursuit of perfect sound, boxes were produced at a cost exceeding the equipment they contained.
Today, the production of cases in factories takes place with an accurate calculation of the density, thickness and shape of the material, taking into account its ability to influence vibration and sound.



Types and characteristics of materials for the body
Enclosures for acoustic systems are made from different materials: chipboard, MDF, plastic, metal. The most extravagant items are made of glass, the most mysterious ones are made of stone. Choosing a simpler material for home making, which is easy to process, for example, chipboard. Let's tell you more about what else you can make them from.
Chipboard
Chipboards are made up of shavings and large chips, pressed together and bonded with an adhesive base. Often, such a composition emits toxic fumes when heated. Plates are afraid of moisture and can crumble. But at the same time, chipboard refers to budget materials, it is easy to process.
These enclosures do an excellent job of handling vibrations, although sound passes through them freely.
Small options are made from chipboard with a thickness of 16 mm, large products will need a material with a thickness of 19 mm. To give an aesthetic appearance, chipboard is laminated, covered with veneer or plastic.

Plywood
This material is made from thin (1 mm) compressed veneer. It can have different categories depending on the derived wood. A product of 10-14 layers is suitable for boxes. Over time, plywood structures, especially when the air is humid, can deform. But this material perfectly dampens vibrations and keeps sound inside the system, so it is used to create cases.

Joinery
A blockboard is made from double-sided veneer or plywood. A filler made of bars, laths and other material is placed inside between the two surfaces. The plate weighs a little, lends itself well to processing. Thanks to these qualities, it is used for the manufacture of boxes.

OSB
Oriented strand board is a multi-layer material consisting of recycled wood waste. It is a durable, resilient product that can be easily processed. The texture of the OSB is very beautiful, but uneven. For the manufacture of cases, it is polished and varnished. The stove absorbs sound well and is resistant to vibrations. Disadvantages include evaporation of formaldehyde and a pungent odor.


MDF
Fiberboard consists of small particle fractions, its composition is harmless. The product looks stronger, more reliable and more expensive than chipboard. The material resonates well, and it is this material that is most often used for the manufacture of factory cases. Depending on the size of the speaker system, MDF is chosen with a thickness of 10, 16 and 19 mm.

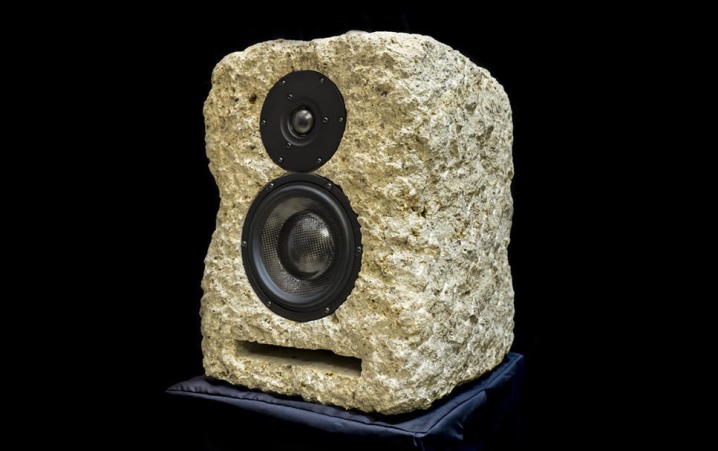
Stone
This material absorbs vibrations well. It is not easy to make a case out of it - you need special tools and professional skill. Slate, marble, granite and other types of ornamental stone are used for products. The bodies are surprisingly beautiful, but heavy, due to the increased load, it is better for them to be on the floor. The sound quality in this case is practically perfect, but the cost of such a product is too high.

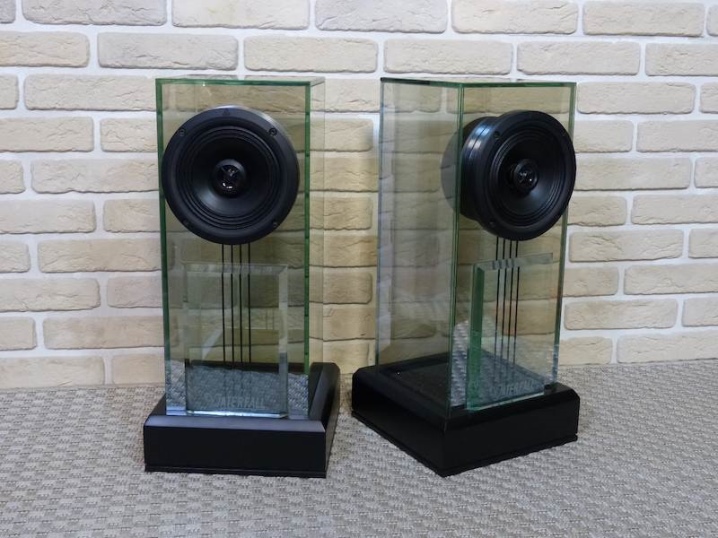
Glass
Plexiglas is used to create the cases. In terms of design, the products have an incredibly beautiful appearance, but for acoustic capabilities this is not the best material. Despite the fact that glass resonates with sound, prices for such products are quite high.

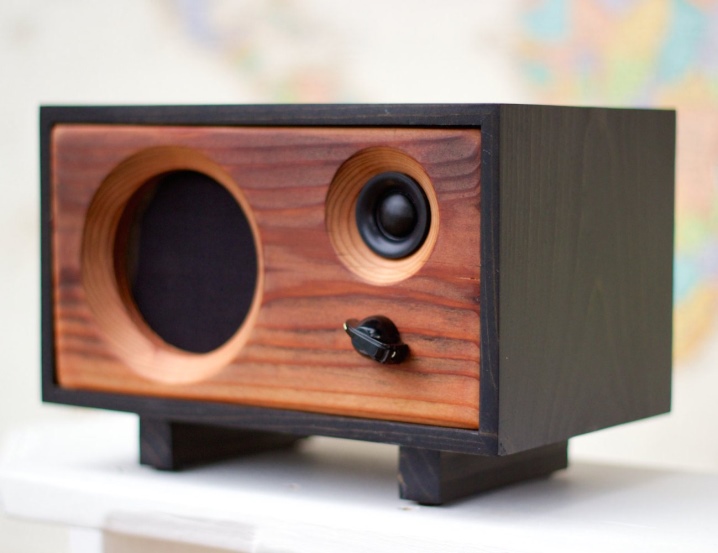
Wood
Wood is considered a valuable material for loudspeaker enclosures because of its good absorption characteristics. But wood tends to dry out over time. If this happens to the case, it will become unusable.

Metal
For the manufacture of boxes, lightweight but hard aluminum alloys are used. The body made of such metal contributes to good transmission of high-frequency sounds and dampens resonance. To reduce the effects of vibrations and increase the absorption of sound, the speaker boxes are made of a material consisting of two aluminum plates with a layer of viscoelastic sandwiched between them. If you still cannot achieve good sound absorption, the sound quality of the entire speaker will be affected.


Types of structures
Before embarking on the active phase of making a case with your own hands for a home speaker system, let's consider what types of structures there are.
Open systems
Speakers are mounted on a large-sized shield. The edges of the flap are bent back at a right angle, and the rear wall of the structure is completely absent. In this case, the speaker system has a very conventional box. Such a model is suitable for large rooms and is not well suited for reproducing music with low frequencies.

Closed systems
Familiar box-like designs with built-in speakers. Have a wide range of sound.
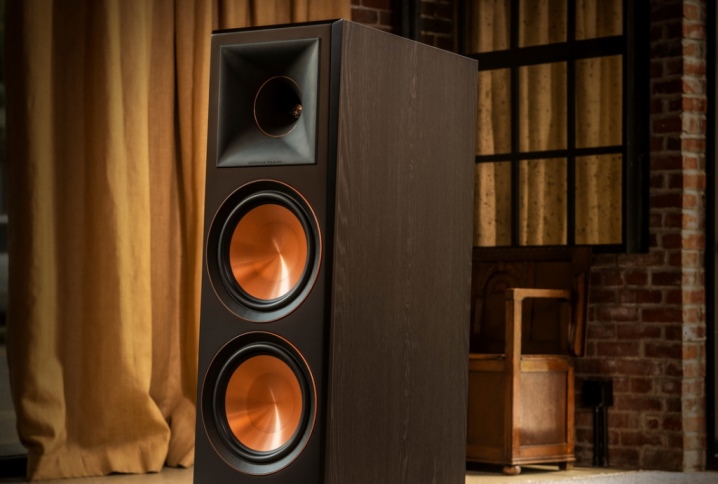

With bass reflex
Such cases, in addition to the speakers, are endowed with additional holes for sound passage (bass reflex). This enables the deepest bass to be reproduced. But the design loses to closed boxes in the clarity of articulation.
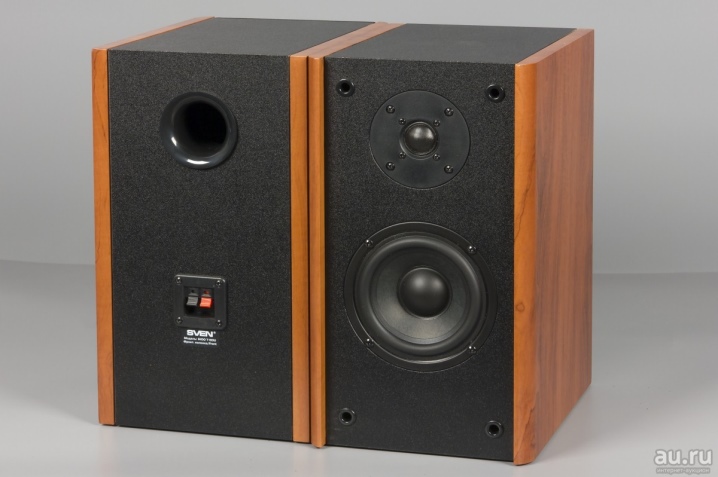

With passive emitter
In this model, the hollow tube was replaced with a membrane, that is, an additional driver for low frequencies was installed, without a magnet and coil. This design takes up less space inside the case, which means that the size of the box can be reduced. Passive radiators help achieve sensitive bass depth.

Acoustic labyrinth
The interior of the body looks like a maze. Twisted bends are waveguides. The system has a very complex setup and costs a lot of money. But with the right fabrication, perfect sound delivery and high bass fidelity occur.


How to make it yourself?
To properly fabricate and assemble a homemade enclosure for your audio playback system, you should first prepare everything you need:
- the material from which the box is to be made;
- tools for performing work;
- wires;
- speakers.
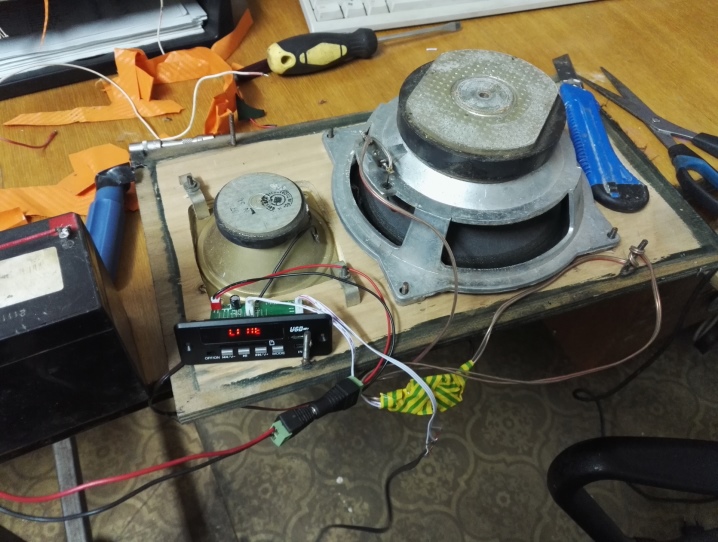

The process itself consists of a specific sequence of steps.
- Initially, the type of speakers for which the boxes are made is determined: tabletop, floor standing and others.
- Then drawings and diagrams are drawn up, the shape of the box is selected, the size is calculated.
- On a plywood sheet, markings are made of 4 squares with dimensions of 35x35 cm.
- Inside two blanks, smaller squares are marked - 21x21 cm.
- The inner part is cut and removed. A column is tried on into the resulting opening. If the cutout is not large enough to fit, it will have to be widened.
- Next, the side walls are prepared.
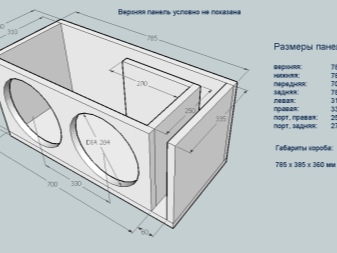
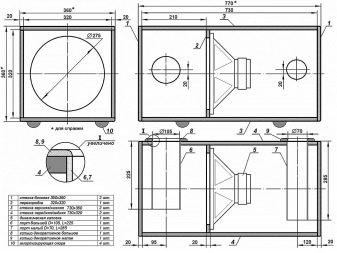
Their parameters are as follows:
- the depth of the model is 7 cm;
- length of one set of walls (4 pieces) - 35x35 cm;
- the length of the second set (4 pieces) is 32x32 cm.
7. All workpieces are carefully cleaned and brought to identical dimensions.
8. The joints of the joints are planted on liquid nails and fixed with self-tapping screws.
9. In the process of manufacturing the structure, the inner part is pasted over with padding polyester or other vibration-absorbing material. This is necessary for subwoofers.


How do I put the content inside?
One speaker is built into the manufactured boxes. If there is a need to accommodate two speakers, in order to avoid deformation of the structure from vibration loads, spacers are installed inside the case between the front and rear walls.
The embedding process itself is straightforward if the speaker hole is made to measure.
The wires should be placed without kinks, make sure that small elements of the system do not move during vibration. After installing the inner contents, the last panel is mounted to close the box.
If the enclosures are made for ceiling or wall mounting, a soundproofing underlay will be required. A special stand is required to place the product on a floor or table.
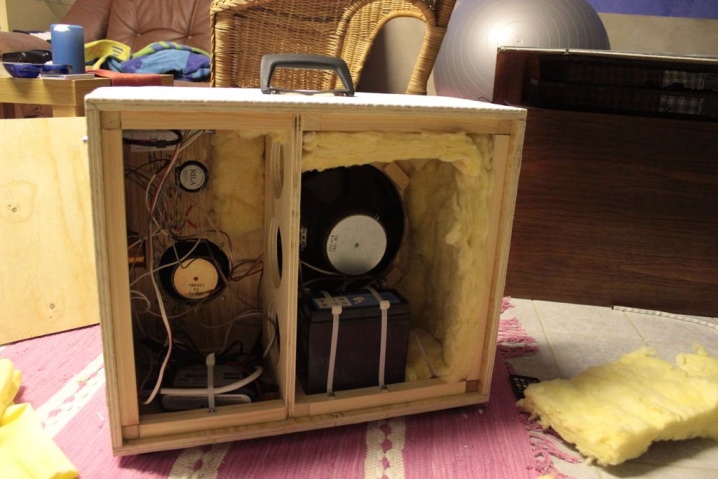

In conclusion, I would like to add that the acoustic sound depends not only on the technical content and the body of the product, but also on the whole with the room in which the speaker is located. The purity and power of sound are 70% dependent on the capabilities of the hall and its acoustics. And one more thing: compact boxes take up little space, it's nice. But the overall design, created for the speaker system, always wins in sound delivery.
What to make a case for acoustics, see the video.













The comment was sent successfully.