All about actinidia

Knowing everything about actinidia - not just the description of the plant as a whole and the characteristics of its fruits - gardeners can get the most out of this crop. Competent planting and complete outdoor care allow you to count on good results. The cultivation of shrubs in Siberia and the Leningrad region has its own characteristics, and in other regions they are also quite found.
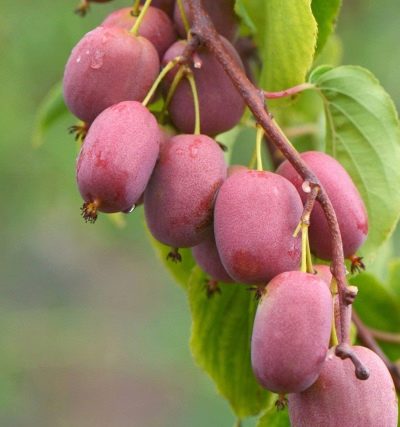

general description
A plant like actinidia is quite familiar to domestic gardeners. But that is why it is necessary to study it very carefully. From a botanical point of view, this is a genus of lianas, which is part of the Actinidia family; curiously, the most famous species in the genus is the kiwi. The actinidia family includes 2 more genus little known to the general public; it is included in the order of heathers, and within the framework of its "relatives" actinidia can be considered:
-
cage;
-
hard to get;
-
persimmon;
-
ebony;
-
lingonberries;
-
rhododendron;
-
heather;
-
cranberries;
-
primrose;
-
loosestrife.


The genus includes 75 different species. It grows mainly in Southeast Asia and the Himalayan mountains. In Russia, in natural conditions, 4 varieties of actinidia have mastered: kolomikta (aka northern kiwi), acute, polygamous and Giraldi. Chinese actinidia is also culturally significant on the Black Sea coast. Structurally, it is a typical liana-like shrub, whose leaves fall off with the approach of winter.
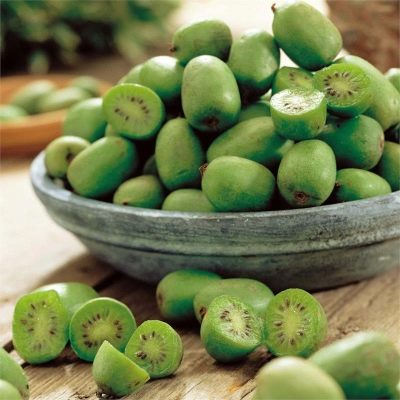

The kidneys are largely, and sometimes completely hidden in leaf scars. The foliage is arranged according to the next scheme. The individual leaves themselves have a solid structure.
Their edges are serrated or serrated; stipules are not formed. During flowering, in the first half of summer, flowers appear 10-30 mm in size.
They are grouped in leaf axils by 3 pieces, but sometimes they develop singly. The corolla looks like a calyx and is white by default. Odors are not found in most actinidia species. However, some of them still exude quite pleasant aromas. The fruits of such lianas are oblong berries with a yellow-green or light orange color.
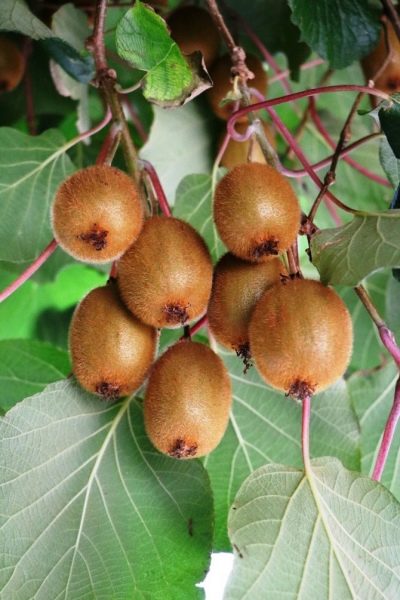

Some species of actinidia give a completely edible crop. The plant ripens approximately in September. But sometimes it is possible to harvest the fruits already at the beginning of August. Since ripe berries quickly crumble, harvesting lasts from 2 to 3 weeks. Actinidia Giralda ripens closer to September, even later they will be ready to collect the "development results" of polygamous and purple forms; unlike the harvest of kolomikta, they do not crumble, however, if there is a danger of frost, it is better to pluck them in advance.
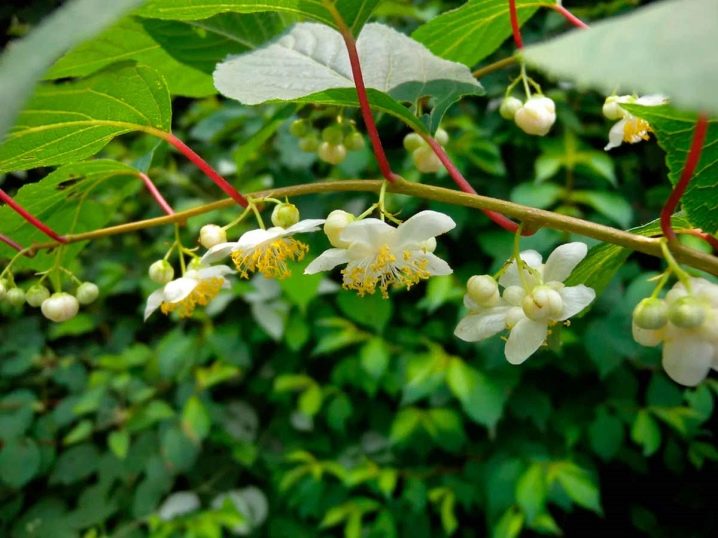

The foliage of actinidia is both thin and leathery in structure. They are the main source of the external grace of the plant. Their variegated color is not so common in our country. Both the stems and the shoots of actinidia will have to be supported. The fruit has a sweet and sour pulp that gives a strawberry-pineapple flavor.
Types and varieties
Actinidia kolomikta is the most winter-hardy species in the genus, and it is excellent for the Moscow region. Growth height above sea level - up to 1.3-1.4 km. However, on the northern borders of the range, it does not exceed 0.5 km. In nature, this species is found in:
-
cedar-broadleaf;
-
fir-broadleaf;
-
broadleaf-spruce;
-
fir and spruce forests.
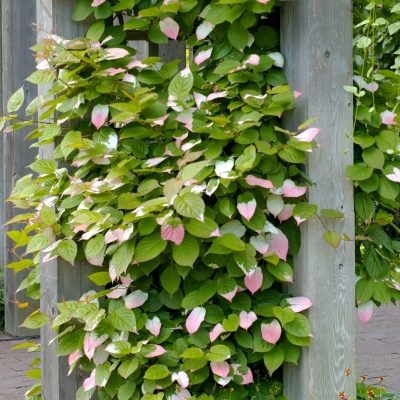

The best conditions for plant development are created where fir and spruce grow in approximately equal amounts, and they are mixed with inclusions of cedar and broad-leaved trees. Out-of-tier liana in natural conditions grows to a height of 10-12, sometimes 15 m. On supports with a thickness of not more than 0.1 m, the plant can spiral spirally. The foliage of the kolomikta has a variable color.

Other features:
-
actinomorphic flowers that appear from the age of 5;
-
flowering in the second half of June for about 20 days;
-
a large number of small seeds (up to 90 pieces per berry);
-
growing season - approximately 150 days;
-
active development in the first 3 years after disembarkation;
-
the edible nature of the fruit.
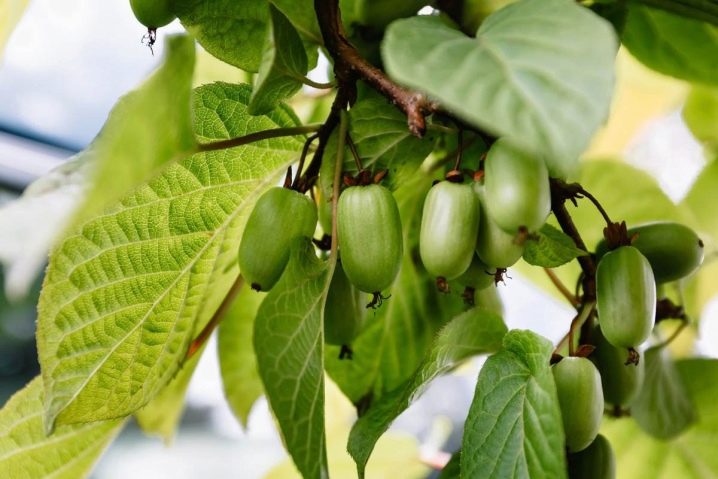

Arguta is a typical dioecious plant. The stem is 12 centimeters thick and reaches 25 m in length. When grown in garden, this species requires very strong supports. Stems are light gray in color. The shiny foliage on top has a dark green tint; it is necessary to wait for the beginning of flowering at the junction of June and July.
Actinidia Giraldi is distinguished by its comparative thermophilicity. The length of the stems reaches 30 m. The weight of the fruits is 0.07-0.08 kg, but they are not too fragrant. The collection of fruits from 1 tree is up to 20-25 kg per year. The name of the species was given in honor of a major Italian botanist of the 19th century.


Actinidia is polygamous, it is also nosed, it is distinguished by increased decorativeness. The length of the lianas is up to 5-6 m. The orange fruits are pointed. They have an original peppery-fig flavor. The species does not differ in particular endurance.
The large-fruited variety is very good. He was taken out to the Pavlovsk station of the VNIIR. It is a self-fertile plant with a high level of winter hardiness. Fruit weight reaches 4.3 grams. For 1 bush per season, there can be up to 1.4 kg of berries.
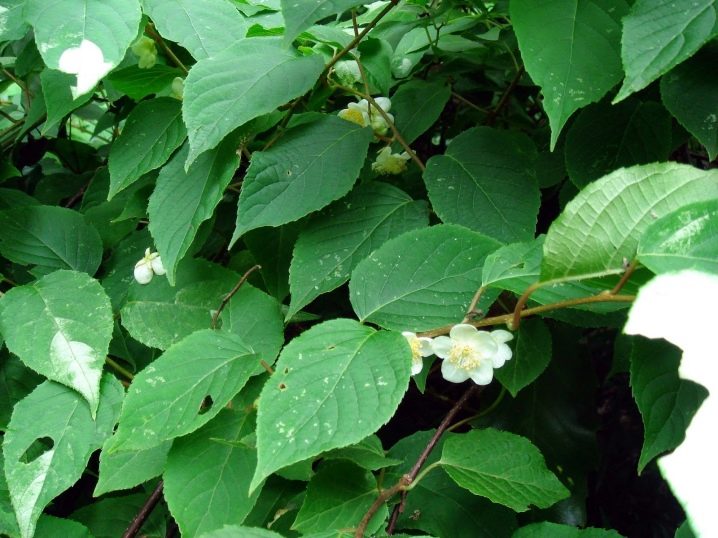

Actinidia purpurea garden is characterized by low cold resistance, even in the middle lane it hibernates with difficulty. The length of the vine reaches 7-8 m. Resistance to pests and diseases is noted. Productivity is at a high level. The foliage is shaped like an elongated ellipse.
The Primorskaya variety ripens by September. The fruits are oval in shape, their cross-section is about 24 mm, and the weight is slightly more than 8.3 grams. A green or yellowish green surface looks good. Productivity at a decent level. The sweet and sour taste and apple flavor are noted.


Variety of Native produces fruit similar to barrels. Their length is about 2 cm. The late ripening period is characteristic. An apple-pineapple flavor is noted. The culture needs cross-pollination.
Actinidia Geneva grows up to 7 m. It bears fruit abundantly, and the ovaries are well preserved even in severely unfavorable conditions. The fruits, again, look like barrels. In winter, the plant experiences cold temperatures up to -30 degrees.


It is also supported by the honey flavor and expressive aroma.
Landing
The time to plant actinidium plants comes with the onset of spring or autumn. The optimum age of finished nursery seedlings is 2 to 4 years. It is critical to choose the right site for planting. If you avoid mistakes, the plant can develop in one place for up to 30 years. Although the liana is shade-loving, normal development is ensured only with stable illumination.
Actinidia cannot grow next to an apple tree. But currants are a good companion for her. The culture will not grow on clay soil.

Moist and loose soil is required, characterized by full drainage. Optimal slopes and elevated places.
Care
Watering
Irrigation of actinidia in the open field must be carried out very actively. This moment is especially important during a period of drought. The soil near the root collar must be continuously moist. Taking care of the shrub means also spraying it during dry periods. The procedure is carried out in the morning and evening hours.
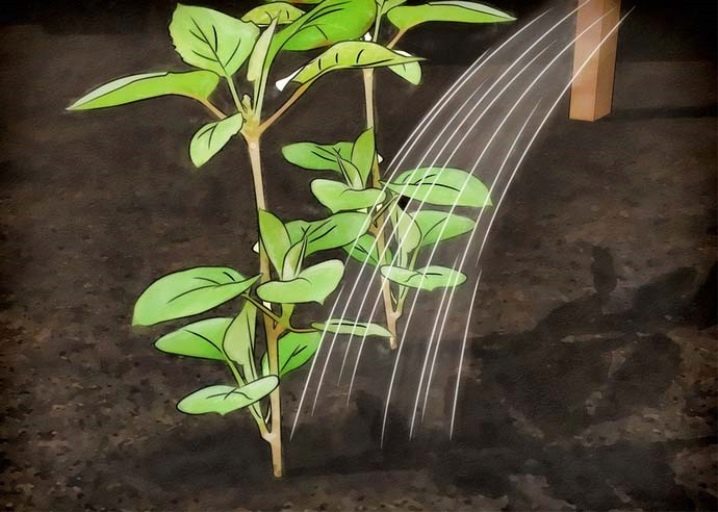

Top dressing
It is advisable to feed any variety of this shrub in the summer (in the first half of the season).During this period, a liquid solution of cow dung is introduced 1-2 times. It is diluted 10 times. Instead of mullein, you can use weeds fermented in a barrel or chlorine-free solutions of mineral fertilizers. To grow actinidia, it needs to be fed once in winter with a mixture of humus with superphosphate and potassium chloride.

Pruning
Lianas are characterized by rapid growth. If you do not form the crown, it will be overly dense. Symmetrically placed vines are more winter-hardy and productive. Actinidia should be cut off in the 3rd year of development. In the first 2 years, they are limited to pinching the shoots.
The shrub is formed by:
-
bush method;
-
according to the fan technique;
-
by the horizontal cordon method.
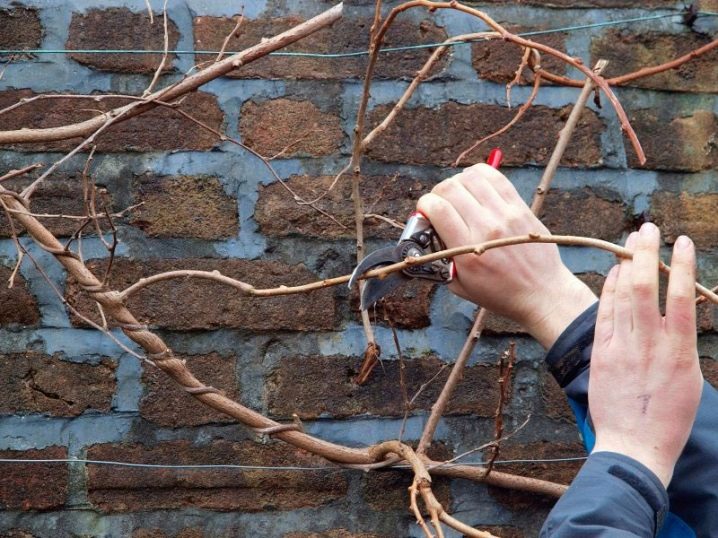

To properly prune actinidia, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of a particular species and variety. The general rule is to keep the productive or decorative parts and remove the non-essential parts.
Too many vines removed leads to a decline in productivity. What ceases to bear fruit is cut off annually. Additionally, dry and too weak shoots are eliminated.
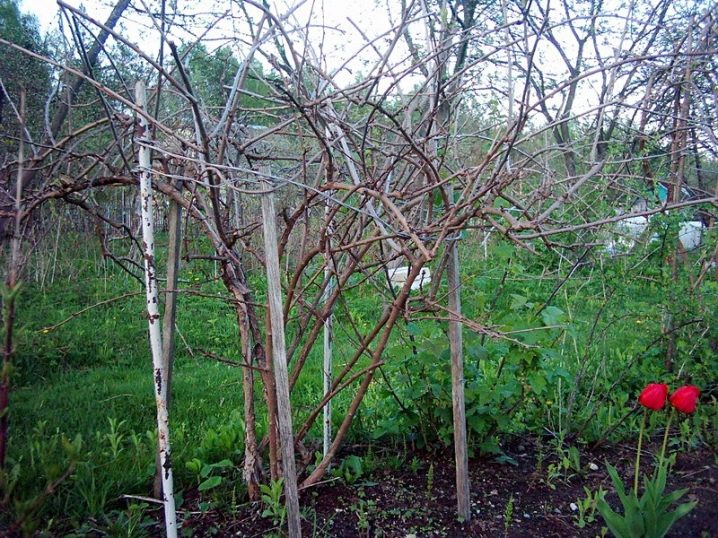

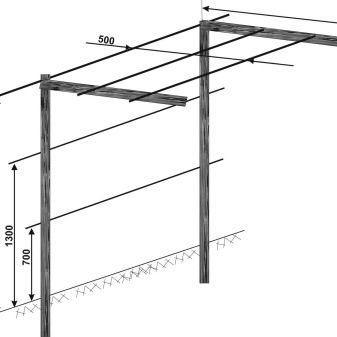
Installing the trellis
You can tie actinidia in the country to oak pillars, concrete or metal pipes. Galvanized wire is drawn in between at different levels. The initial level is exactly 50 cm. In cold regions, collapsible trellises are used. They are inserted into metal pipes buried in the soil.
Vines can also be placed on trellis shields. It is recommended to tie plants to supports using twine, which does not harm them as much as coarse wire. In the southern regions, for tall bushes, letter-shaped trellises are used:
-
G;
-
NS;
-
T (they are more voluminous).

The nuances of growing in different regions
It is extremely difficult to find good actinidium seedlings in Siberia. The main breeding centers for this crop are too remote, which reduces the availability of planting material. For the winter, the plant and trellis will have to be laid on the ground, so enough space must be left for them. In the first year of life, planting should be watered more often than the general rate. In the Urals, it is advised to plant no earlier than the beginning of May in order to insure against recurrent cold weather.

Hybrid varieties with frost-resistant qualities are most preferred in cold regions. They are also distinguished by an increased level of immunity. In the Leningrad region and places comparable with it in terms of climate, there are no special requirements for the cultivation of actinidia. As a support, not only trellises are useful, but also walls and other suitable structures, including mesh and stakes specially nailed into the ground. Leaving is quite common, the main thing is to choose varieties that are stably rooting in a particular region.

Reproduction
Actinidia, like other dioecious plants, can reproduce itself only if male and female varieties grow nearby. The easiest way to organize a special breeding is to organize it by layering the roots. In the spring, they choose the moment when the juices begin to move, and the flowers bloom profusely.
The shoot should be a growth one that is well developed. Pressing against the soil is provided by pins or wire flyers.
Cuttings are used to get fast shoots of valuable varieties. Green cuttings are carried out in June. The stems are cut in the morning. It is necessary to root the planting material in a greenhouse or greenhouse. The soil is saturated with a complex mineral fertilizer that does not contain chlorine.

Diseases and pests
The leaves and fruits of this plant are often affected by fungal infections. Phylostictosis is visually expressed in the appearance of sharply outlined spots on the leaves. They are irregular in shape. Fungal lesions are avoided by minimizing moisture. Treatment of leaf spot involves spraying with Bordeaux liquid or suspension colloidal sulfur.
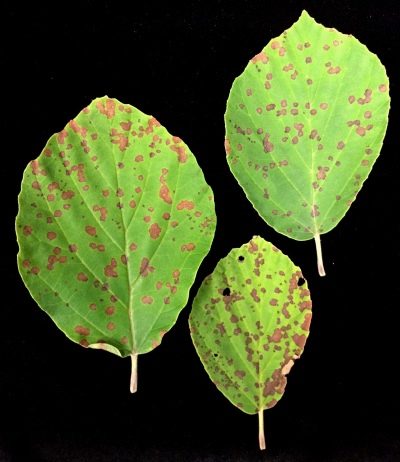

Powdered sulfur helps to suppress powdery mildew, which is used to pollinate plants. Rot and mold lesions require urgent removal of problematic parts of the crops. Deformed and drying out shoots are removed in advance. Actinidia does not bear fruit, not only from disease, but also when attacked by leaf beetles. This insect eats up the leaves completely, as a result of which the crop is lost or is extremely small and tasteless.

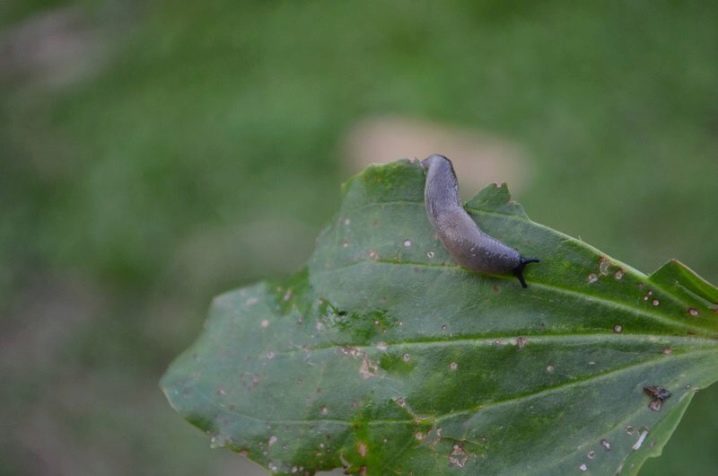
The danger is also posed by:
-
caterpillars of the kishmish moth;
-
moth caterpillars;
-
slugs;
-
locust filly;
-
lacewing;
-
bear;
-
cats.

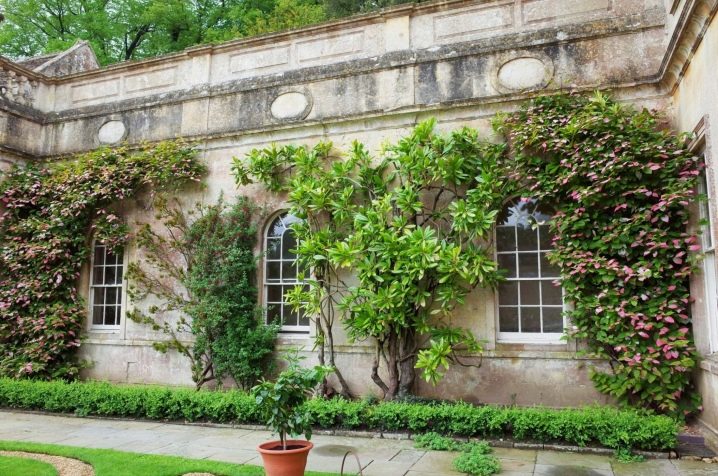
Application in landscape design
Actinidia is widely used in the garden. This culture is a good choice both as a background for other plants and as an independent dominant filling of the territory. Actinidia are mainly used for vertical landscaping. Trees and stairs, terraces, gazebos and other fences are well wrapped in this view. A wall made of it will reliably protect the area from excess sun, wind and dust.

Actinidium plantings are also widely used to cover bad looking areas:
-
electrical panels;
-
garage walls;
-
wooden sheds.













The comment was sent successfully.