All about planting an apricot

A few decades ago, apricot was an exceptionally thermophilic crop, unable to withstand severe frosts. However, breeders have done a great job, and today gardeners from regions with cold climates can grow such fruit trees. But in order for the plant to take root in a new place, it is necessary to study in advance all the subtleties of its correct planting.

Timing for different regions
The time of planting a fruit crop is always determined by the climatic conditions of the regions. So, in the southern regions it is easiest for summer residents, since they can choose to plant both in spring and autumn. Spring planting in open ground can be done already in the last days of March, when the temperature outside will not drop below +5 degrees. It is important that the buds have not yet had time to swell on the trees. If planting is carried out in the fall, you need to do everything so that a month remains before the arrival of cold weather. In most southern regions, this is October.

The daytime temperature should be +10 degrees, and the nighttime +5.
When it comes to the northern regions, it is not customary to plant apricots here in the fall. Frosts can come suddenly, and sometimes even forecasters cannot guess when exactly this will happen. Therefore, it is recommended to plant a fruit tree in the spring. So, in Siberia and the Urals, seedlings are placed in the ground at the very end of April or in early May. At the same time, very winter-hardy varieties are chosen. The same recommendations apply to the Leningrad Region. In central Russia, disembarkation begins in mid-April. They choose early winter-hardy varieties that bloom late. As for Belarus, here gardeners also prefer spring planting, focusing on the time of arrival of heat in their region.

Selection of seedlings
In order for the tree to quickly grow in a new place and delight gardeners with tasty fruits for many years, it is necessary to choose the right seedling. Consider a few gardeners' recommendations in this regard.
-
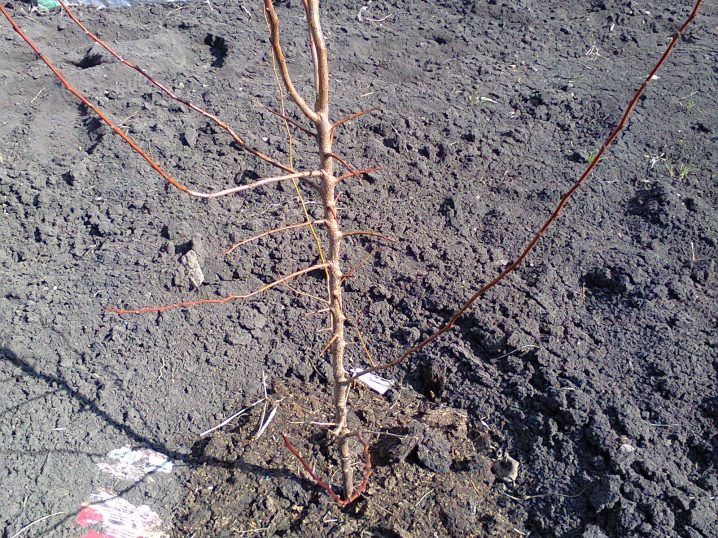
The seedling should be about 2 years old. Determining your age is easy. The seedling you need will have 1-3 lateral processes without branching, roots 0.3-0.4 meters long and a total height of a meter or one and a half. In this case, the trunk diameter will be several centimeters.
-
Planting material must be vaccinated. On good seedlings, the grafting site is very clearly visible.
-
When buying, you should always look at what the plant looks like. There should be no cracks or wounds on it. The seedling cannot be bent, deformed, or have dry roots.
-
In order for the tree to take root, it is best to look for proven nurseries in your area. This will prevent you from placing the seedling in unfamiliar conditions. It is worth noting that the roots can be either open or with an earthen lump (in a container).


Distinguishing an apricot sapling from a plum sapling can be difficult for a beginner. It is important to look at the appearance of the material. A two-year-old plum has a minimum of 4 lateral processes, while an apricot, as already mentioned, is from 1 to 3. The roots of a plum are lighter, moreover, they reach a maximum of 30 cm, and apricot roots can grow up to 40. However, the most obvious difference is lies in the foliage. Plum leaves are light green and narrow, while apricots have darker and wider plates.


How to preserve seedlings before planting?
If you bought a seedling in the spring and plan to plant it immediately, then the measures for the safety of the material will be the simplest. You just need to properly transport the tree home. To do this, its roots (open) are wrapped with a damp cloth so that they do not dry out. However, most gardeners prefer to shop in the fall in order to plant the plant on the site in the spring.
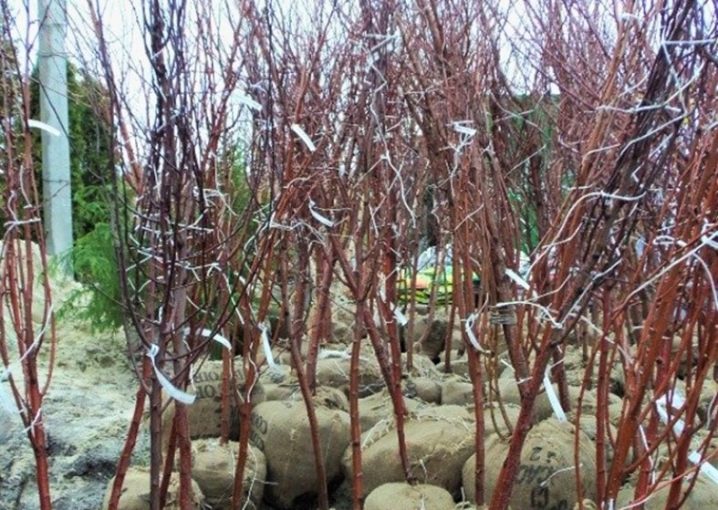

In this case, you need to know a few rules for winter storage of culture.
-
Storage in the cellar. If you live in a private house, and there is a cellar, then it is recommended to store the seedling there. The room temperature should be between 0 and +10 degrees. The roots should be placed in wet sand or peat. This mixture must not be allowed to dry out.
-
Under the snow. This technique is suitable for areas where there is a lot of snow in winter. It is necessary to dig a small hole in the ground, the place should not be sunny and windy. The bottom of this hole is lined with straw. The seedlings are removed from the foliage and soaked in water for five hours. Then they put snow on the straw, the layer thickness should be 0.2 m. The roots of the seedlings are wrapped with agrofibre and the material is placed in a hole. On top of them they put more snow, about 15 cm, as well as sawdust, also 15 cm.
-
Digging in. This method is suitable for storing several trees. You need to dig a furrow in the ground. The direction of the trench is from west to east. The south side should be flat. As in the previous case, it is necessary to remove the leaves from the seedlings. The plants are then dipped in clay. Then they put them in the trenches so that the future crowns look south. The trees should not touch each other. After that, the plants are covered with a 20-centimeter layer of soil, the soil is tamped. Having finished with work, dry soil is mixed with sawdust and seedlings are additionally sprinkled with this composition, forming hills.



It should be understood that exceeding the storage temperature of seedlings, if they lie, for example, in the basement, is unacceptable. Due to the heat, such specimens may begin to wake up, the kidneys will swell early on them. If this happened soon after storage, then the tree is better planted, there is a chance that it will take root.
The earth in the near-trunk circle must be mulched. You can also try to dig in such seedlings in the yard, overlaid with peat. If the seedling has dry roots after winter, then it can be reanimated with water or a solution of a growth stimulator. It is better to remove the frozen roots.


Preparation
Before planting a tree, you need to prepare a place, soil and organize a planting pit.
A place
Apricot fruits gain the necessary sweetness only when there is enough sun. At their summer cottage, they will need the most illuminated landing zone. Trees can be placed both on a flat area and on a light hill. It should be borne in mind that young apricot seedlings are very susceptible to the north wind, so the planting area should not be deserted.

It is recommended to provide protection in the form of a fence or some kind of structure, house. However, such protection should not give a shadow.
The soil
Apricot is very fond of loose soil. The substrate should be crumbly; the culture will not grow in dense soils. It is necessary to choose a slightly acidic soil, it can be black soil, sandy loam, loam. If the soil on the site is highly acidic, it is lime in advance. Wood ash can also reduce acid. Too clay soils are diluted with sand from the river, and if the proportion of the sand itself in the soil is too high, it is mixed with clay.


Care must be taken to ensure that the soil is well aerated. Moisture and air must flow freely to the roots. But excessive soil moisture is inappropriate here. The abundance of moisture leads to rot of the root system, the spread of the fungus over the site. Therefore, apricots are never planted in lowlands, in swampy soils, in soils with high groundwater.

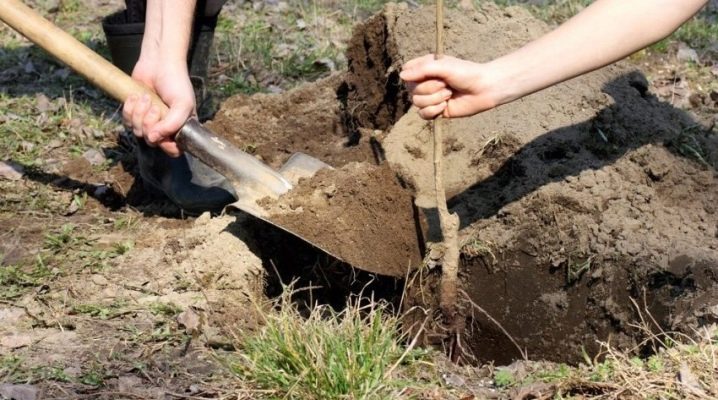
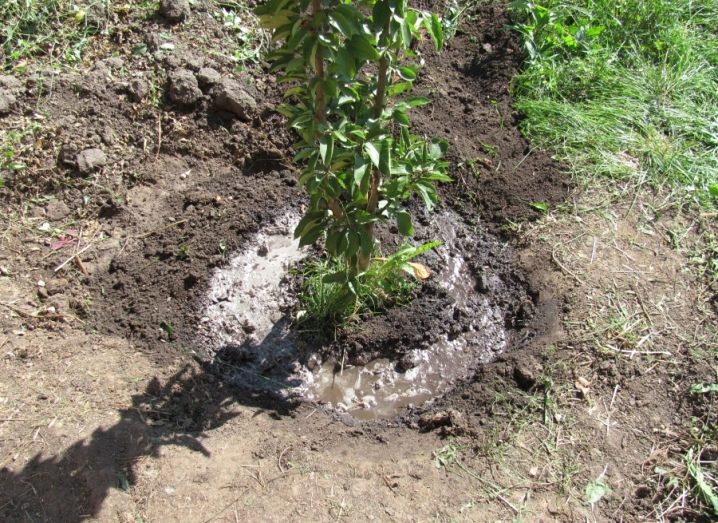
Landing pit
Planting holes must be prepared in advance so that the earth in them has time to settle at least a little. If a spring planting is planned, the site is prepared in the fall, and if the autumn planting, from the summer.If it is impossible to prepare in advance, the pits are dug at least 30 days before planting. Let's see how to do it right.
-
First you need to tackle the site itself. To do this, the planting area is cleared of debris, old foliage, roots and other plant debris. The earth is carefully dug up.
-
Next, pits are formed. The depth should be 0.8 meters and the width should be 0.7. The top layer of soil from the hole is laid separately.
-
A drainage layer is placed at the bottom of the well. You can take broken brick, crushed stone, expanded clay. The drainage layer is from 10 to 15 centimeters.
-
Next time they approach the pit 21 days before the planned planting of seedlings. At this moment, it is customary to apply fertilizers to it. The pit is filled with earth, which was set aside, with humus and nitroammophos. The dosages are as follows - 2 buckets, 1 bucket and 0.4 kg, respectively. And also a little superphosphate can be added to the hole - up to 50 grams. It is not necessary to fill the hole completely, but by ¾. After that, it is sprinkled a little with a clean substrate, watered.

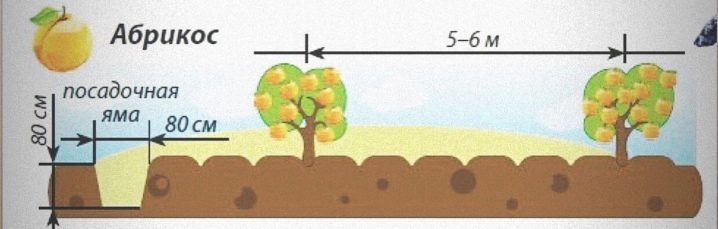
Layout scheme
As long as the seedling is small, it will not need much space. However, it is worth remembering that apricots are tall trees, and after a few years they will acquire a huge crown. This must be taken into account when disembarking. Usually seedlings are arranged in rows. Moreover, each tree should have 5 meters of free space around it on all sides. The same distance is maintained in the aisles.
If the trees are of a very high variety, then the distance will need to be increased.
Another point concerns the nutrition of the tree. Not everyone knows that the root system of an apricot is twice the size of the crown. This is a colossal scale. Therefore, if the plot is small, it is not recommended to plant more than one or a couple of apricots, since the roots will pull out all the nutrients from the soil, and other plants will not get anything. It is recommended to plant trees in small areas in one row.
And it will also be appropriate to mention the neighborhood. Apricot loves being alone. He does not tolerate the close location of other fruit trees, raspberries and currants, gooseberries. All these crops should be placed at a distance from the tree. No vegetable crops are planted under the huge crown, since they will simply die from the shade. However, there are many groundcover plants and flowers that love shading. For additional decorativeness, they can be used to decorate the area under the tree.



Step-by-step landing instructions
Consider the rules for planting apricots in the garden in more detail. Let's start with the spring procedure.
-
A couple of hours before planting, the root system of the seedling is placed in warm water so that the plant receives a large supply of moisture. Then the roots will need to be dipped in a clay mash and wait for them to dry.
-
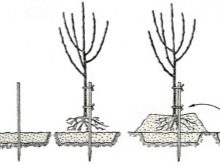
A peg-shaped support is placed in the center of the hole. It should rise 100 centimeters above the soil level.
-
The roots of the seedling are carefully untangled, and then they are placed in the center of the pit, gradually covering the roots with earth. It will be more convenient if two people are engaged in boarding at once.
-
The earth, as it is poured, must be carefully tamped. After the end of the procedure, the root collar should remain on the surface, even with parts of the roots together. It is categorically impossible to bury it in the ground.
-
The last steps are tying the tree to the stake, high-quality watering and laying peat mulch.


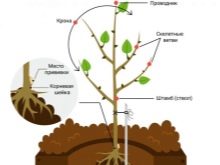


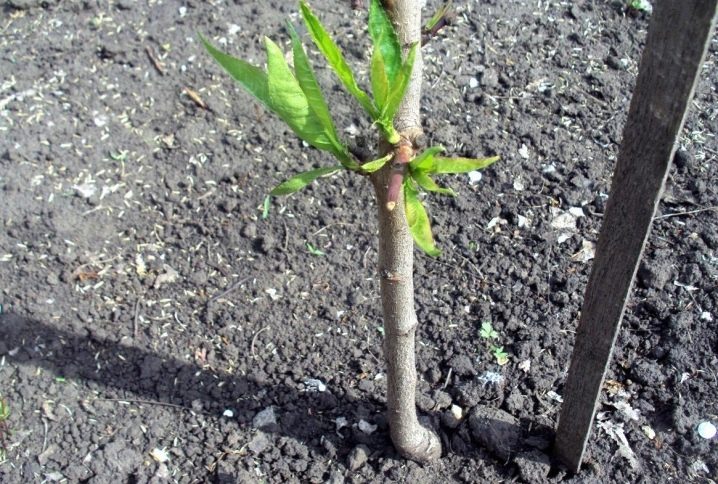
If you buy a tree from a nursery, then it already has a graft. But it also happens that gardeners grow seedlings on their own or take them from friends and neighbors. Then the vaccination will have to be carried out without fail. In the south, this is done in March, in the northern regions - in May. Grafting is carried out on skeletal branches if it is a two-year-old seedling.
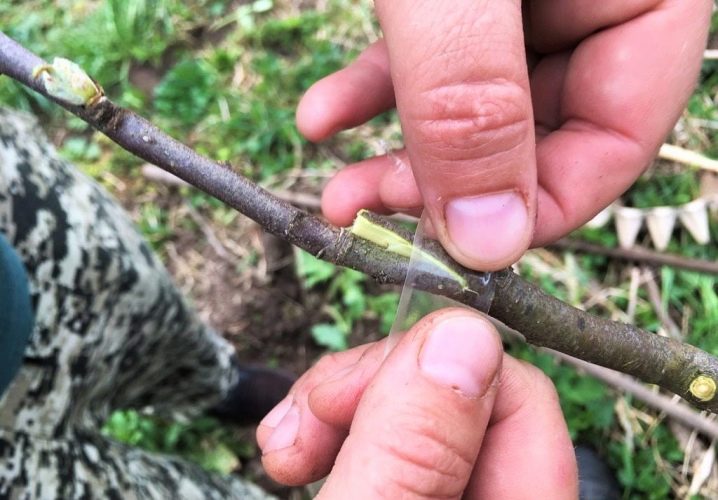

The procedure is carried out in the morning on the north side of the seedling. This will protect the vulnerable spot from direct sunlight.
As for the autumn planting, the technique is generally the same, but a few nuances must still be taken into account. When planting, foliage is removed from seedlings, and their roots are placed in a special liquid. It consists of water, mullein and Bordeaux mixture. The latter should be 1%. After disembarking, the trunk must be whitewashed.
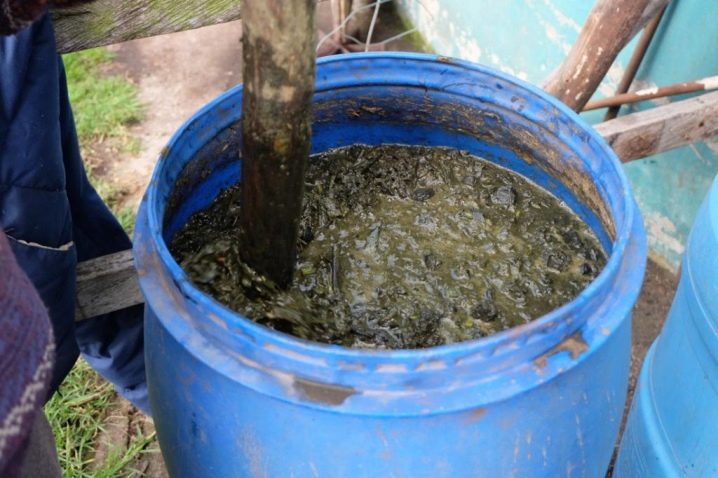

There are a few more important rules:
-
after finishing planting, the lateral branches of the seedlings are cut off (you only need to leave 2, cutting by half), and the central conductor is shortened so that it rises 25 centimeters above the lateral processes;
-
in the middle lane, trees are planted on a hill or on a slope, but the latter should not be south;
-
in the Moscow region, they use not shallow drainage, but solid slate sheets, thanks to which the roots will not grow very deep;
-
in the same region, the trunk circle is always mulched with grass, which can be sown near the tree itself;
-
in the Urals, plants are most often grown from seeds, and not purchased as seedlings, the same applies to Siberia;
-
in Belarus, they also prefer the stone fruit method of growing, and also often use vaccinations.








The comment was sent successfully.